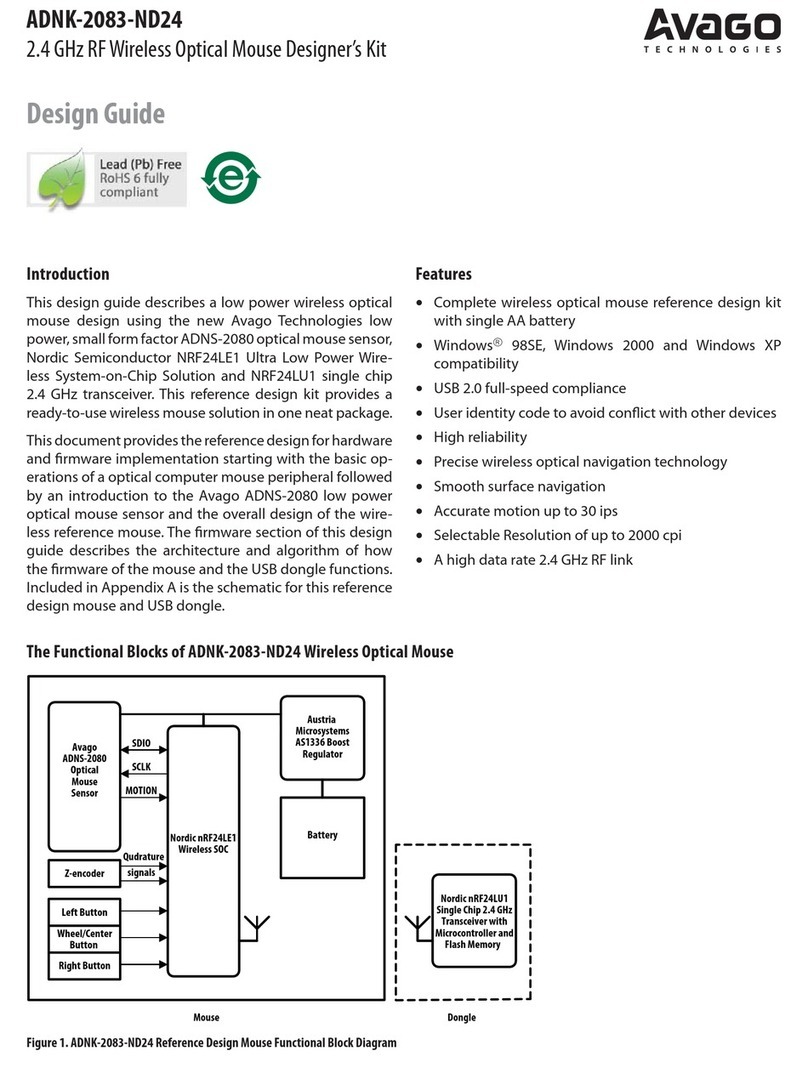
ADNK-5003
Optical Mouse Designer’s Kit
Design Guide
Introduction
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard se-
rial interface between a computer and peripherals such
as a mouse, joystick, keyboard, etc. This design guide
describes how a cost-eective USB optical mouse can be
built using the Avago Technologies ADNS-5000 optical
sensor. The document starts with the basic operations
of a computer mouse peripheral followed by an intro-
duction to the Avago Technologies ADNS-5000 Optical
Navigation Sensor. A schematic of the ADNS-5000 optical
sensor and buttons of a standard mouse can be found in
Appendix A. The ADNS-5000 data sheet is available from
the Avago Technologies web site at www.avagotech.com.
USB documentation can be found at the USB Implement-
ers Forum web site at www.usb.org.
The ADNS-5000 navigation sensor along with the ADNS-
5100 round lens or ADNS-5100-001 trim lens, ADNS-5200
clip and HLMP-ED80 LED form a complete and compact
mouse tracking system. There are no moving parts, which
means high reliability and less maintenance for the end
user. In addition, precision optical alignment is not re-
quired, facilitating high volume assembly.
Optical Mouse Basics
The optical mouse measures changes in position by opti-
cally acquiring sequential surface images (frames), and
mathematically determining the direction and magni-
tude of movement. The Z-wheel movement is done in the
traditional method by decoding the quadrature signal
generated by optical sensors. This design guide shows
how to connect to and manage a standard conguration
of mouse hardware, as well as handle the USB protocols
as a standard way of reporting mouse movement and
button presses to the PC.
Optical Navigation Sensor
Avago Technologies ADNS-5000 optical sensor is used in
this reference design as the primary navigation engine.
This Optical Navigation Technology contains an Image
Acquisition System, a Digital Signal Processor and USB
stream output.
The IAS acquires microscopic surface images via the lens
and illumination system provided by the ADNS-5100,
ADNS-5200, and HLMP-ED80-XX000. These images are
processed by the DSP to determine the direction and
distance of motion. The DSP generates the ∆x and ∆y
relative displacement values which are converted to USB
motion data.
Mouse Z-Wheel
The motion of Z-wheel is detected using the traditional
method by decoding the quadrature signal generated by
optical sensors:
For mechanical Z-wheels the following must be imple-
mented.
1. Use a rotary switch equivalent to the Panasonic part
EVQVX at http://industrial.panasonic.com/www-
data/pdf/ATC0000/ATC0000CE20.pdf (The key point
is stable “A” switch state in all detent positions).
2. Solder the rotary switch into the PCB such that the
common pin is closest to the cable end of the mouse.
(Metal plate faces to left)
3. Connect the “A” terminal of the rotary switch to “ZA”
and the “B” terminal to “ZB”. ZA MUST be connected
to“Signal A”in Figure 2 where the z-wheel detents are
mechanically stable.
As shown in Figure 2 below, traveling along the quadra-
ture signal to the right produces a unique set of state
transitions, and traveling to the left produces another set
of unique state transitions.