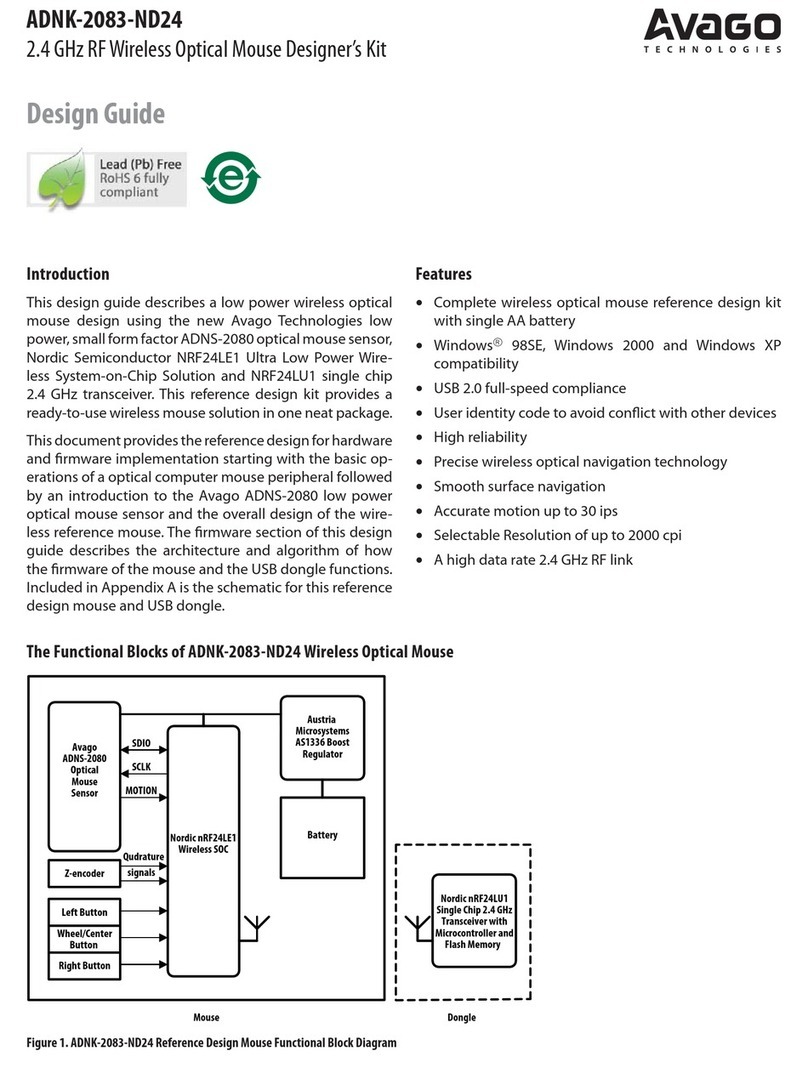
ADNK-5023-HTP2
Optical Mouse Designer’s Kit
Design Guide
Introduction
The IBM Personal System/2 (PS/2) is an industry standard
serial interface between a computer and peripher-
als such as a mouse, joystick, keyboard, etc. This design
guide describes how a cost-eective PS/2 optical mouse
can be built using Avago Technologies small form factor
ADNS-5020EN optical mouse sensor and Holtek Semi-
conductor HT82M35A-1002 masked microcontroller. The
document starts with the basic operations of a computer
mouse peripheral followed by an introduction to the
Avago Technologies ADNS-5020EN Optical Navigation
Sensor and the HT82M35A-1002 masked microcontroller.
A schematic of the HT82M35A-1002 masked microcon-
troller to the ADNS-5020EN optical mouse sensor and
buttons of a standard mouse can be found in Appendix A.
The ADNS-5020EN data sheet is available from the Avago
web site at http://www.avagotech.com/. The HT82M35A-
1002 data sheet is available from the Holtek web site at
www.holtek.com.
Optical Mouse Basics
The optical mouse measures changes in position by
optically acquiring sequential surface images (frames),
and mathematically determining the direction and
magnitude of movement. The Z-wheel movement is
done in the traditional method by decoding the quadra-
ture signal generated by optical sensors. In this reference
design, PS/2 protocol is used to provide a standard way
of reporting mouse movement and button presses to the
PC.
Introduction to ADNS-5020EN Optical Mouse Sensor
Avago’s ADNS-5020EN optical sensor is used in this
reference design as the primary navigation engine. This
Optical Navigation Technology contains an Image Ac-
quisition System, a Digital Signal Processor, and a three-
wire serial port. The HT82M35A-1002 periodically reads
the ADNS-5020EN’s Delta_X and Delta_Y registers to
obtain any horizontal and vertical motion information
happening as a result of the mouse being moved. The
three-wire synchronous serial port is used to set and read
parameters in the ADNS-5020EN, and to read out the
motion, (delta) X and (delta) Y information.
This motion information will be reported to the PC to
update the position of the cursor. The advantages of
using ADNS-5020EN optical sensor are: good tracking
accuracy, small form factor, sensor programming ex-
ibility via SPI port, and the automatic frame rate feature.
Furthermore, ADNS-5020EN sensor has built-in oscilla-
tor and on-chip LED driver to minimize external compo-
nents. Additionally, Burst mode is another special serial
port operation mode which may be used to reduce the
serial transaction time for motion read operation
Motion Read is activated by reading the Motion_Burst
register. The ADNS-5020EN will respond with the
contents of the Delta_X, Delta_Y, SQUAL, Shutter_Upper,
Shutter_Lower, Maximum_Pixel and Pixel_Sum registers
in that order.