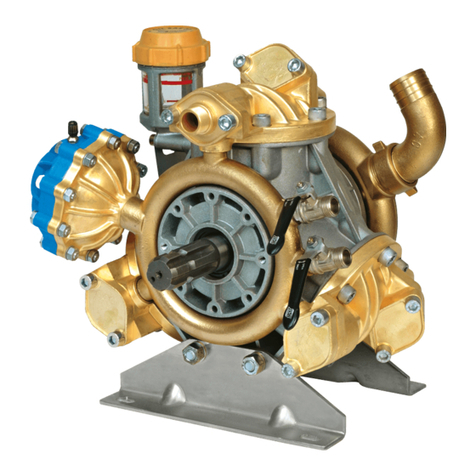
Bertolini CHX Series Operating instructions

1
PISTON PUMPS
CHX Series
Via F.lli Cervi 35/1 42124 REGGIO EMILIA - ITALY
Operation,
maintenance and
repair manual
CHX Series
Pumps
EN
Reggio Emilia - Italy

2
MANUFACTURER IDENTIFICATION DATA:
Manufacturer: IDROMECCANICA BERTOLINI S.p.A.
Address: Via F.lli Cervi 35/1
42124 REGGIO EMILIA - ITALY
Tel. +39 0522 306641 Fax +39 0522 306648
E-mail: email@bertolinipumps.com
Internet: www.bertolinipumps.com
Release: July 2018
Revised on: 1 June 2019
“BERTOLINI” thanks you for your preference. The product you have purchased is the
result of the most modern technology and has been manufactured with materials able to
ensure the best quality, durability and functionality.
Thank you for your confidence in us.
Please read this manual carefully and always keep it within easy reach. You will find it
useful in resolving any problem you may have concerning the characteristics and
functionality of the product.
Thank you for having chosen “Bertolini”
We at Idromeccanica Bertolini S.p.A.recommend that you read this
operation and maintenance manual before installing and using the pump.
Keep it within easy reach for further reference when required. This manual is
an integral part of the pump itself.
The pump user and plant engineer are obliged to know and comply with the pertinent laws
in force in the country where the pump is used. They are also required to follow the
instructions in this manual with care.

3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1-GENERAL SAFETY REGULATIONS..................................................................................................5
2-DESCRIPTION OF THE PRODUCT ....................................................................................................6
3-TECHNICAL FEATURES .....................................................................................................................7
3.1 Identification of components.................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Instructions for use.................................................................................................................................... 9
4-INSTALLATION...................................................................................................................................10
4.1 Pump connection to the frame ............................................................................................................... 10
4.3 Pump-motor coupling ............................................................................................................................. 10
4.3 V-belt transmission ................................................................................................................................. 11
4.4 Hydraulic connections ............................................................................................................................. 11
4.5 Filtering and feeding circuit .................................................................................................................... 12
4.6 High pressure circuit................................................................................................................................ 13
4.7 General installation layouts .................................................................................................................... 14
5- SAFETY AND FAULT PREVENTION DEVICES .............................................................................16
5.2 Fault prevention ...................................................................................................................................... 16
5.2 A) Protection against overpressure.................................................................................................... 16
5.2 B) Protection against abrasive particles ............................................................................................. 16
5.2 D) Protection against overheating...................................................................................................... 19
5.2 E) Protection against insufficient or no water supply........................................................................ 19
5.2 F) Energy saving / correct use of the pump........................................................................................ 19
6- FAQ .....................................................................................................................................................21
7- PUTTING INTO SERVICE .................................................................................................................22
7.1 Start-up .................................................................................................................................................... 23
7.2 Use ........................................................................................................................................................... 23
7.3 Leaking water from the gaskets.............................................................................................................. 23
7.4 How to stop the pump ............................................................................................................................ 23
8- TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................................................................................24
9- WARRANTY .......................................................................................................................................25
10- ROUTINE MAINTENANCE..............................................................................................................26
10.1 Maintenance of drive mechanism and lubrication .............................................................................. 26
10.2 Hydraulic circuit maintenance……………………………………………………………………………………………………………27
10.3 Disassembly of head and sleeves ......................................................................................................... 27
10.4 Replacement of the suction and delivery valves.................................................................................. 28
10.4 A) Suction valves ............................................................................................................................... 28
10.4 B) Delivery valves .............................................................................................................................. 29

4
10.5 Replacement of high-pressure gaskets................................................................................................. 30
10.6 Complete re-assembly of the suction-delivery valves ......................................................................... 31
10.7 Replacement of low-pressure gaskets.................................................................................................. 32
10.8 Replacement of pistons......................................................................................................................... 33
10.9 Re-assembly of head and sleeves ......................................................................................................... 34
10.10 Replacement of shaft oil retainers ..................................................................................................... 36
10.11 List of tools required for repairs ......................................................................................................... 37
MANUFACTURER’S DECLARATION..................................................................................................38
a) This manual conforms to the state-of-the-art applicable at the time the product was
marketed and cannot be considered inadequate solely because it was updated on the
basis of new experience. IDROMECCANICA BERTOLINI S.p.A. is entitled to update
the products and relative manuals without being obliged to update previous products and
manuals, except in cases where this is required for exclusively safety reasons.
b) The “Bertolini Technical Service” is at your disposal for any requirement as may arise
when the product is used or serviced, or when relative accessories must be chosen.
c) No part of this manual may be reproduced without the written permission of
IDROMECCANICA BERTOLINI S.p.A.

5
The high energy produced by the high-pressure jet is a source of serious danger.
The pump must only be used by specifically trained personnel.
The high-pressure pipes must be type-approved for the permissible maximum
pressure of the installation and equipped with unions mechanically crimped by the
manufacturer. The maximum temperature and overpressure must be stamped on
them as well as the name of the manufacturer and date of manufacture.
Always check the conditions of the installation before beginning work.
More specifically, check the conditions of the high-pressure pipes and unions. Make
sure that the trigger of the gun functions smoothly, without jerking, and that it
immediately returns to its original position when released.
Never use a defective high-pressure pipe and do not attempt to repair it. Replace it
immediately with an original spare.
Keep children and animals well away from the system when it is operating.
The system must be installed on a stable, sound, secure base.
Wear protective goggles when using the system.
Always hold the spray gun with both hands when it is operating.
Do not point the jet towards people, animals or fragile objects in general.
Do not spray onto electrical equipment, electric power sockets or in their immediate
vicinity.
Keep all parts of the body well away from the pressurized jet.
Only use a fan spray to clean delicate surfaces and keep the nozzle at least 75 mm
away.
If the system is operated by an internal combustion engine, make sure that the
installation area is adequately ventilated. EXHAUST GAS FUMES CAN BE LETHAL!!!
All moving parts, especially the transmission components, must be adequately
protected against accidental contact.
Do not use the machine for cleaning surfaces containing asbestos.
Strictly comply with the laws in force governing the disposal of substances that detach
from the surfaces through the action of pressurized jets.
Idromeccanica Bertolini declines all civil or criminal liability for damage or accidents to persons or
things deriving from failure to comply with even only one of the aforementioned safety regulations.
1-GENERAL SAFETY REGULATIONS

6
Bertolini high-pressure piston pumps are suitable for use with clean water at a maximum
temperature of 60°C.
Contact the “Bertolini Technical Service”if particularly corrosive additives and higher
temperatures are used.
The pump must be used in compliance with the specifications given on the data plate (fig.
1). Removal of the data plate will void all forms of warranty.
As soon as the pump arrives, make sure that the data plate is similar to the one depicted
below.
The data plate gives the following information:
1. Pump model
2. Serial number
3. Maximum permissible pressure in bars
4. Maximum permissible pressure in P.S.I.
5. Flow rate in l/min
6. Flow rate in US GPM
7. Rotational speed
8. Power consumption of pump in kW
Never exceed the maximum pressure and rpm rate indicated on the
data plate.
If the data plate becomes worn or illegible during use of the pump, contact the
dealer or an authorized assistance center and have it replaced.
1
5
3
4
8
6
2
7
2-DESCRIPTION OF THE PRODUCT

7
PUMP CHARACTERISTICS CHX SERIES
PUMP
MAX motor
rpm
FLOW RATE
at max
pressure
MAX
PRESSURE
POWER trans. to shaft at
Shaft
PISTONS
MODEL CODE
MAX pressure and flow rate
rpm
l/min
GPM
bars
PSI
kW
HP
No.
Ø mm
CHX 13-1000 74.1035.97.3
750 17 4.4 1000 14500 32.9 44.1
1“3/8 DIN
9611
3 14
CHX 24-1000 74.1036.97.3
750 18.8 5 1000 14500 36.9 49.5 3 15
CHX 21-1000 74.1030.97.3
1000 21.2 5.6 1000 14500 41.7 55.9
Ø 40
3 14
CHX 25-1000 74.1037.97.3
1000 24.4 6.4 1000 14500 47.9 64.2 3 15
3-TECHNICAL FEATURES

8
3.1 Identification of components
1. Crankcase
2. Oil fill plug with level dipstick
3. Eyebolt for lifting
4. Head or pump body
5. Delivery duct
6. Suction duct
7. Bearing supports
8. Pump shaft
9. Identification plate
10. Oil level plug
11. Oil drain plug
12. Drain pipe union

9
3.2 Instructions for use
•The pump is exclusively designed for:
–Use with clean water at temperatures between +4°C and +60°C for non-food
purposes.
–Use of detergents in a watery solution.
•The pump cannot be used with:
–Watery solutions with viscosity and density values exceeding those of water;
–Chemical solutions of which compatibility with the materials with which the pump
is made is not known;
–Sea water or water with a high concentration of salt;
–Fuels and lubricants of all kinds and types;
–Inflammable liquids or liquefied gases;
–Food-grade liquids;
–Solvents and diluents of all kinds and types;
–Paints of all kinds and types;
–Liquids at temperatures lower than 4°C or higher than 60°C;
–Liquids containing granules or solids in suspension.
•The pump must not be used for washing: persons, animals, electrical equipment,
delicate objects, the actual pump itself or the system in which it is installed.
•The pump must not be used in places where there are particular conditions, such as
corrosive or explosive atmospheres, for example.
All other use is considered improper.
The manufacturer shall not be liable for any damage deriving from improper or
incorrect use.
The pump is supplied with oil type SAE 80W - 90. Use a product with the same
characteristics if the oil must be changed or topped up.

10
Bertolini pumps comply with the safety regulations laid down by standard EN 809 and are
designed to be coupled, either directly or via a transmission, to an electric, heat or hydraulic
motor.
The machine or system of which the pump is a part must be constructed in
accordance with good engineering practice and with the safety regulations in
force in the country in which the machine itself is installed.
In Europe, this condition is testified by the CE mark and by the declaration of
conformity provided by the machine manufacturer.
Correct installation is a key factor for the smooth running and long life of the
pump. 90% of faults and failures are caused by:
•Incorrect pump-motor coupling.
•Incorrect sizing or poor construction of the feeding circuit.
•Poor quality or incorrect calibration of the maximum pressure or bypass valve.
Idromeccanica Bertolini declines all liability regarding failure to comply
with the following instructions:
4.1 Pump connection to the frame
The system must be installed on a stable, sound, safe base using the six M14 holes at the
base of the crankcase.
4.3 Pump-motor coupling
The manufacturer of the system is responsible for choosing and correctly
sizing the drive system, also in relation to the risks to people that the chosen
system could cause.
When connecting to electric motors, comply with the instructions given by standard
EN60204.1 against risks of an electrical nature.
To prevent their accidental contact with parts of the body, all moving components that
transmit motion from the motor to the pump must be adequately protected, as
specified in Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC or according to the regulations in force in
the country of use.
If the pump shaft has a double prime mover, the unused one must be suitably
protected.
If the transmission or shaft protection is damaged or breaks, stop the system
immediately and have it checked by a specialized technician.
Do not touch the shaft protection with the hands or feet during use.
4-INSTALLATION

11
The pump must operate with the axis of the pistons horizontal in order to ensure that all
its moving parts are properly lubricated.
The pump-motor assembly must be securely fastened to a sufficiently large and strong
base.
All the electrical connections must be made by specialized technicians.
If the motor is directly coupled, make sure that:
–The drive shaft is perfectly aligned with the pump shaft.
–The steady pin is of the prescribed length.
–The connection coupling is the right size.
If a reduction gear is used, the recommendations given in the previous point also apply
with reference to the coupling between drive shaft – output shaft and layshaft - pump
shaft.
4.3 V-belt transmission
The pump can be controlled by a system of V-belts or timing belts.
Minimum diameter of driven pulley (on pump shaft)): ≥ 250 mm.
The radial load on the shaft must not exceed 7500 N.
Consult technical manuals or contact the “Bertolini Technical Service” if the sizing is
different.
If pulleys are used for coupling, check that:
–There is no play between shafts and pulleys.
–The pulleys are parallel and aligned.
–The belts are pre-tensioned to the correct value. Excessively tight belts will lead to
early wear on the bearings.
4.4 Hydraulic connections
The body of CHX series pumps features two 3/4” GAS inlets and four 1/2” GAS outlets,
2 of which can be used for a pressure gauge and safety valve. There is also a union for
connecting the drainage outlet of the cooling circuit to a zero-pressure vessel or to the
suction circuit, so as to re-circulate the fluid.
COOLING CIRCUIT
DRAINAGE

12
1-Feeder tank
2-Suction line
3-Drainage line
4-Pump
IN-Suction union (there are two unions, but one can be used if preferred - on the
side that facilitates the installation work)
OUT-Delivery union (there are 4 unions available, to be used as required)
D-Drainage union (there are two unions, but one can be used if preferred - on the
side that facilitates the installation work)
NOTE: If there is no tank in the application, connect the drainage line to the pump
suction side
4.5 Filtering and feeding circuit
The feeding circuit must be sized so as to avoid the risk of cavitation. Instructions on
how to size the feeding circuit are given in the next section 5.2 D. Always check to
make sure that the pressure does not drop below -0.2 bars for 750 rpm pumps or +2
bars for 1000 rpm pumps by positioning a pressure switch/pressure gauge behind
the pump suction union (shown in point 7 of the assembly layouts).
The pump feeding pressure must never exceed 5 bars.
The feeding line must be equipped with a filter, with 200 mesh filtration grade for
non-supercharged pumps. Filters with higher filtering grades can be used for
supercharged pumps. Whatever the case, the filters installed must not lower the
suction pressure indicated above. Consult section 5.2 B for further details. The
presence of the filter leads to a concentrated pressure drop which reduces the height
from which the pump can draw fluid. A filter with an adequate nominal flow rate must
be chosen to prevent this height reduction from being excessive. It is advisable to
use a filter with a nominal flow rate equal to at least 2.5 times the nominal flow rate of
the pump.
The diameter of the filter ducts must not be less than the diameter of the pump
feeding union.
The filter must be installed as near as possible to the pump and in an easily
accessed position. It must be inspected regularly, depending on the degree of
cleanliness of the water.
If water is supplied under pressure by a centrifugal pump, make sure that the flow
rate supplied is at least 1.5 times that of the pump.
Comply with the following instructions if the supply comes from a tank
–The tank capacity must be at least four times the pump flow rate per minute.
–The pump feeding pipes must be positioned near to the bottom of the tank,

13
with a water head of at least 200 mm to prevent siphons from forming.
–The suction area must be protected against turbulence created by the tank
feeding pipe and return pipes, using closed diverters on the bottom.
–The tank must be equipped with the safety devices indicated in sections 5.2 E
and 5.2 F.
–It is advisable to install a section of pipe right beside the pump using suitable
hoses and to insulate the rest of the system from the vibrations produced by
the pump-motor assembly.
–Only use crush-resistant reinforced rigid or flexible pipes.
–The feeding lines must be as straight as possible, with curves, bends and
sharp changes in section reduced to the minimum.
–Do not use fittings of the oil-pressure type, 90° bends, multiple-way unions,
swivel-joints, etc.
–Avoid using foot valves or check valves in general.
–Do not install detergent suction devices along the pump feeding circuit.
Before it is connected to the pump, make sure that the feeding line is perfectly clean
inside.
4.6 High pressure circuit
The minimum performance values (pressure and flow rate) of all the high-pressure
circuit components must be at least 30% higher than those the pump can reach.
The high-pressure circuit must be equipped with a pressure regulating valve and a
safety valve, as indicated in section 5.2 A
The name of the manufacturer and the pressure, flow rate and maximum operating
temperature values must be stamped on the safety valve and regulating valve.
If the safety valve continues to trip, immediately stop the pump and have the system
checked by a specialized technician.
Do not connect the safety valve outlet or regulating valve outlet to the feeding line.
If the regulating valve is the automatic type, it is advisable to install an adequately
sized pressure accumulator immediately after the pump.
The accumulator must be sized to suit the performance of the pump and must comply
with the instructions supplied by the manufacturer.
The following data must be stamped on the body of the device: manufacturer's
trademark, permissible max pressure, test pressure, preload pressure, capacity and
date of manufacture. When tests are to be performed, the serial No. and test code
required in the country where the machine is installed must also be indicated.
It is advisable to make the first section of pipe using hoses able to insulate the rest of
the system from the vibrations produced by the pump-motor assembly.
The hose pipes must be stamped with the name of the manufacturer, date of
manufacture, permissible maximum temperature and pressure values, and their
unions must be mechanically crimped directly by the manufacturer.
Use glycerin-filled pressure gauges able to withstand pulsating pressure.
The high-pressure circuit must be equipped with a pressure shut-off device for pump
start-up.
As already mentioned regarding the feeding circuit, the high pressure circuit is also subject
to loss of pressure depending on its conformation. So much so, it is normal for the pressure
at the application to be lower than that measured at the pump head.

14
4.7 General installation layouts
TYPICAL CHX PUMP INSTALLATION
1) Level switch;
2) Thermostat;
3) Minimum tank capacity= pump flow rate x 4;
4) Closed diverters on bottom;
5) Feeding line clear passage Ø37
6) Filter on suction side (200 mesh 750 rpm; ≥200 mesh 1000 rpm);
7) Pressure switch / Pressure gauge to monitor supply;
8) Safety valve;
9) Safety valve bypass;
10) Regulating or pressure relief valve;
11) Regulating valve bypass;
12) Delivery;
13) Pressure gauge;
14) Bypass line;
15) Tank feed;
16) ¾” pressure shut-off cock for pump start-up;
17) Minimum passage Ø22.

15
4.8 Errors to avoid
1) Avoid, otherwise a “siphon” effect could be created;
2) Avoid 90° bends;
3) Avoid reductions in diameter;
4) Never connect the bypass line to the feeding line return.

16
5.1 Safety devices
The system in which the pump is installed must always be equipped with the safety
devices described below:
Safety valve: this is an appropriately calibrated relief valve, which relieves the
excess pressure if a fault occurs in the high-pressure circuit.
Pump shaft protection: Prevents the operator from accidentally coming into contact
with moving parts of the shaft and transmission.
Pressure regulating valve: This valve allows the operating pressure to be regulated
and excess fluid to flow back into the tank, thus preventing the pressure from rising
dangerously.
5.2 Fault prevention
5.2 A) Protection against overpressure
This is a displacement pump, so the same amount of water always comes out at each turn
of the shaft. Since the liquids are practically incompressible, if an impurity accidentally clogs
the nozzle and prevents the water from flowing out, the pistons would actually push against
a solid element. Without a protection valve, the pump would be immediately destroyed in
these conditions.
Safety valve.
A good quality safety valve of the right size overcomes these problems.
If, however, during normal use (with a spray gun and washing system for instance),
the water is frequently shut off, it is re-circulated by the relief valve at calibration
pressure, causing overheating and consequently damaging the pump.
Automatic regulating and bypass valve.
An automatic valve reduces this problem since the water is re-circulated at a very low
pressure in this type of valve and takes much longer to heat.
5.2 B) Protection against abrasive particles
No water is free from impurities and abrasive particles, even drinking water.
Not only do abrasive particles rapidly damage the seals, but they also cause the inlet and
delivery valves, the regulating valves and nozzles to wear out very quickly.
A filter, of an adequate size, installed immediately upstream of the pump guarantees
a long service life to the entire system
However, remember that the filter must always be efficient and clean and must
be inspected even daily.
5.2 C) Protection against cavitation and sizing of the suction circuit (NPSHr)
Cavitation is caused by the formation of gaseous bubbles in the feeding circuit and leads to
wear on the gaskets and erosion of the metal parts of the pump.
The most evident sign of cavitation is a continuous or intermittent hammering sound from
the pump. In addition, the performance, pressure and flow rate often reduce or become
discontinuous.
All liquids tend to form vapor, and this tendency is especially evident when the temperature
rises or when the suction head drops.
During their return stroke, the pistons generate a vacuum which draws water into the
pumping chambers. The greater the resistance the water opposes along the route from the
5- SAFETY AND FAULT PREVENTION DEVICES

17
tank to the pump, the higher will be the value of the vacuum created by the pump, a
condition which consequently increases the risk of cavitation.
This resistance is due to two crucial factors.
Concentrated pressure losses: due to the presence, along the line, of bends, curves,
unions, cocks, filters, etc., all obstructions to the regular flow of water which oppose a
certain resistance, mainly depending on their size and geometric shape.
Distributed pressure losses: due to the friction created between the moving water
and sides of the pipes. The value of these losses is proportional to the length of the
pipe. It increases as the roughness inside the pipe increases and, water flow rate
being equal, increases as the internal diameter of the pipe decreases.
Other pressure losses are due to: the temperature of the water and altitude of the place
where the pump is used with respect to sea level.
When a system is designed, one must therefore remember that the pressure of the water at
the pump inlet will always be lower than that at the beginning of the feeding line.
To prevent cavitation, the minimum difference in level Hz between the level of the
water and the pump must comply with the following relation:
Hz>(NPSHr+C)+H1 + H2 – (Hatm – H3 ) (m & °C) or (ft & °F)
Where:
NPSHr: net positive suction head required at the suction port of the pump. The value to
assign to CHX pumps is 6.5 m (21.3 ft)
Hz = minimum difference in level (positive or negative) between the pump and the water in
the tank;
C = 0.5m (1.65 ft);
H1= pressure losses in the pipes and unions (see tabs. 1and 2);
H2= pressure losses depending on the temperature of the water (see tab. 3)
Hatm = barometric pressure at sea level = 10.33m (33.9 ft)
H3= pressure losses due to height above sea level (see tab. 4)
DATA FOR THE CALCULATIONS
Table 1 Equivalent length of unions, for various dimensions, in m (ft) of steel pipe

18
Table 2 Losses per 10 m (10 ft) of steel pipe for various Table 3 Loss of suction with
dimensions and flow rates temperature of the water
Table 4 Suction loss depending on height above sea level

19
CALCULATION EXAMPLE
Example of a calculation for a CHX 21-1000 pump installed at 500 m above sea level
The calculation shows that the pump can suck from a height of 1.98 m (6.53 ft). If the Hz
value is positive, the pump should be supplied under the head of water.
5.2 D) Protection against overheating
Besides reducing the life of the gaskets, operation with very hot water can cause cavitation
and must be avoided.
Reduced rotational speed of the motor.
If the pump is connected to an electric motor controlled by a speed converter, it is
worthwhile installing a device that reduces the rotational speed of the motor and,
consequently, the pump flow rate, when the bypass valve is operating. This ensures
that the water does not heat so much.
Athermostat installed in the tank that trips when the water becomes too hot or,
when possible, stops the pump motor, is another recommended safety system.
5.2 E) Protection against insufficient or no water supply
The pump must never operate dry, since this would lead to abnormal wear on the gaskets
and cause overheating, which could break the pistons or irreparably damage the pump
itself.
Alevel switch that signals when there is insufficient water in the tank or, when possible,
that stops the pump motor, is recommended for the purpose of preventing the pump from
running dry.
A pressure switch, which trips with an alarm signal or, if possible, which stops the motor
when the supply pressure drops below the value liable to cause cavitation, should be
installed upstream of the pump suction duct.
If the level switch, thermostat or pressure switch trip and stop the motor, the switch
used must be the manual starting type to prevent the motor from restarting on its
own.
5.2 F) Energy saving / correct use of the pump
It is fairly frequent for the flow rate of the pump to be oversized with respect to the effective
requirements.
To correctly size the system, the water re-circulated through the regulating valve must not
exceed 10-15% of the pump flow rate.
Length of pipes (drawing)
1+1+2=
4.00
m
3.3+6.6+3.3=
13.20
ft
Equivalent length
2X1.31=
2.62
m
of unions (tab.2)
2X4.31=
8.62
ft
Total length
6.62
m
21.82
ft
H1 (tab.3)
0.6X6.62/10=
0.4
m
0.6X21.8/10=
1.31
ft
H2 (tab.4)
30°C
0.40
m
86°F
1.31
ft
H3 (tab.5)
500 m
0.55
m
1640 ft
1.80
ft
NPHSr
RPM 1000
6.50
m
RPM 1000
21.30
ft
Hz>(6.5+0.5)+0.4+0.4-(10.33-0.55)=
-1.98
m
Hz>(21.3+1.65)+1.31+1.31-(33.9-1.8)=
-6.53
ft
Size of pipes and unions G1” 1/2

20
Otherwise, besides causing an unnecessary waste of energy, the water in the supply tank
will overheat and contribute towards increasing the risk of cavitation. In addition, all the
components in the circuit, especially the regulating valves, will be subjected to continuous
and excessive stress.
In short, the flow rate of the pump must always be adapted to the effective requirements of
the system by reducing the rotational speed of the pump itself.
This manual suits for next models
8
Table of contents
Other Bertolini Water Pump manuals
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands

WITA
WITA HE OEM 4 40 Series Translation of original operating instructions

BD Sensors
BD Sensors KHP 4002 user manual

EINHELL
EINHELL GC-DW 1000 N Original operating instructions

Pentair
Pentair NOCCHI VSD manual

WIKA
WIKA 6 Series operating instructions

Aspen Pumps
Aspen Pumps mini aqua pump Instruction guide

Mallory
Mallory 4060FI installation instructions

GORMAN-RUPP PUMPS
GORMAN-RUPP PUMPS 12B20-B/S1 Installation, operation, and maintenance manual with parts list
DEMA
DEMA 574 installation instructions

Zoeller
Zoeller 2701 manual

Pentair
Pentair Myers SRM4 Series Installation and operation manual

Watson Marlow Pumps
Watson Marlow Pumps 501CC user manual