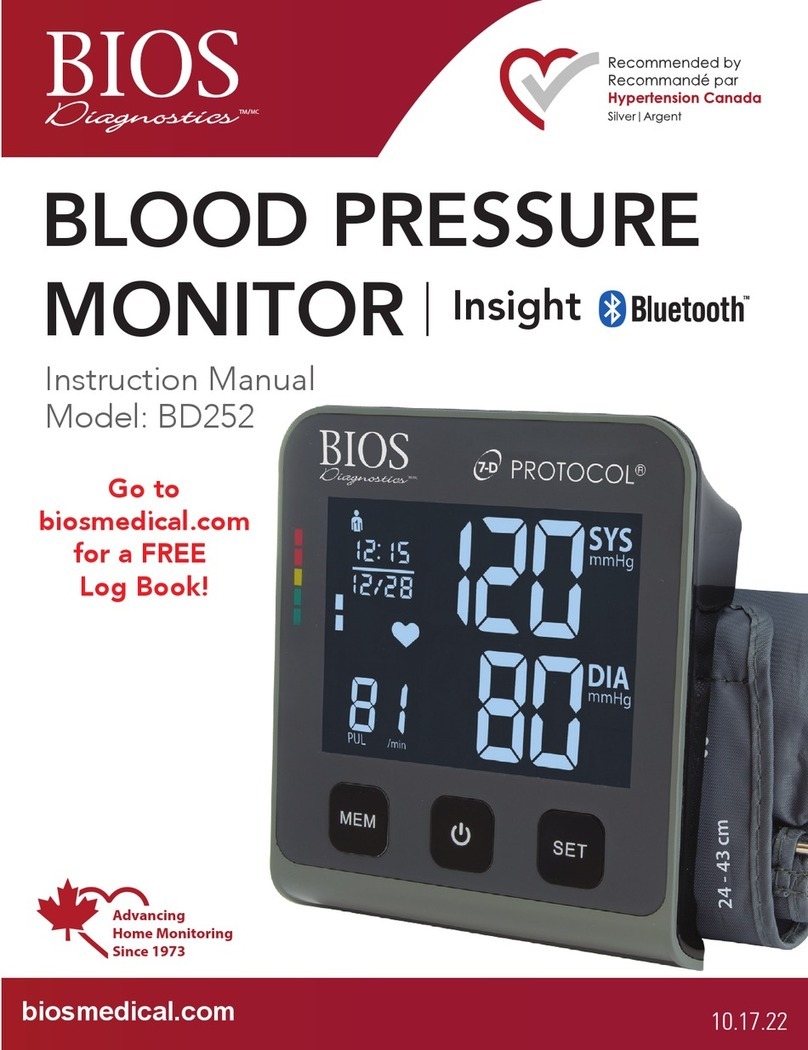
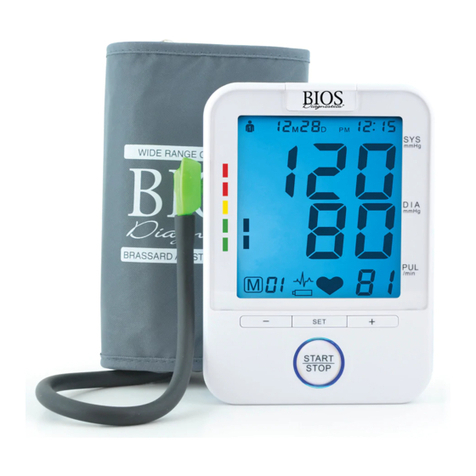
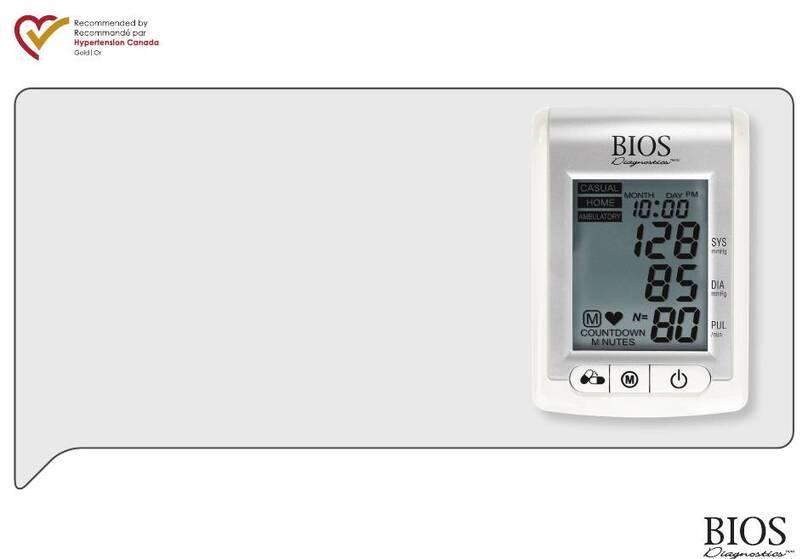
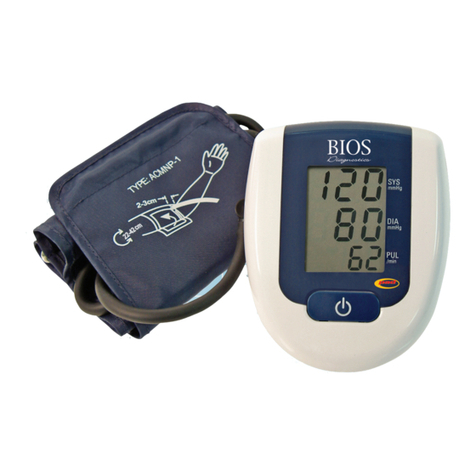
mastectomy.
The cuff should be applied as tightly as comfortable for the patient.
A too loose application may result in longer or aborted measurements, because the device has to pump even to reach
the proper tightness. Longer measurements may cause inconvenience for the patient, and aborted measurements
result in less data for evaluation. If the patient removes the cuff for a period during the monitoring session, it should
be reapplied with appropriate tightness, with help from another person, if necessary.
The cuff is the component which, by definition of the relevant standard, is protected against a defibrillator discharge.
The substitution of a cuff different from that supplied by BIOS Medical might result in measurement error and/or in
certain cases it causes damage to the monitor.
10. Batteries
The ABP-01 operates either with two 1.5V AA normal batteries or with two 1.2V AA rechargeable batteries.
A set of properly charged, high capacity batteries will enable the recorder to perform 250 blood pressure
measurements during a 24-48 hour long monitoring session. If you use alkaline batteries, choose high capacity, long-
life batteries to enable reliable operation.
In order to change batteries, take the recorder out of the holder pouch and remove the battery compartment cover on
the back-side. Place two properly charged, high capacity AA rechargeable or two new, long-life AA alkaline batteries
into the compartment then close it.
a. Use standard alkaline or NiCd/NiMH rechargeable batteries
Use only standard long-life (alkaline) batteries, or standard NiCd or NiMH rechargeable batteries of the proper size.
Do not use lithium batteries. Do not mix different battery types; do not mix new and old batteries. Never use batteries
of low or unknown quality or pre-used batteries, as they may not cover the power needs of the monitor, and they
may damage the monitor, or they may contain acidic electrolytes which may leak and corrode electronic components.
Never use batteries damaged in any way.
b. Do not start a new monitoring session with low batteries.
It is strongly recommended to use freshly charged or new batteries with each patient so that batteries do not run down
during monitoring, even in case of very high blood pressure values and/or a long monitoring session. After inserting
batteries in the ambulatory blood pressure monitor, it is advised to check their voltage before programming them. The
typical voltage for fully charged rechargeable batteries should be over 2,5V and for fresh alkaline batteries, over 3V.
Battery voltage check: Press the START button for at least 5 seconds.
c. If measurements do not start in due time keep fresh batteries in the recorder
If the monitor is not used for a long period (4-6 months), the built-in backup cell, ensuring the operation of the internal
clock, may get discharged. In this case keep freshly charged batteries in the monitor for at least one day; this will
recharge the backup cell. It is possible to use the monitor afterwards. If the backup cell is not properly charged, the
internal clock may work incorrectly, and the monitor may not start measurements in due time. If the recharging of the
cell is not successful, the backup cell must be replaced. This is an out of warranty act.
d. If the batteries run down, replace them even during a monitoring session
Should the batteries run down during a monitoring session, they can be replaced. Monitoring will continue and data
will not be lost.
e. Remove the batteries if the monitor is out of use
If you do not use the monitor, it is advisable to remove batteries since they may run down due to the constant small
power consumption of the integrated circuits of the device. Data in the recorder are not lost even if batteries run
down or are removed.