Blamsoft VK-2 User manual

1.0.0 User Manual – Rev B

2
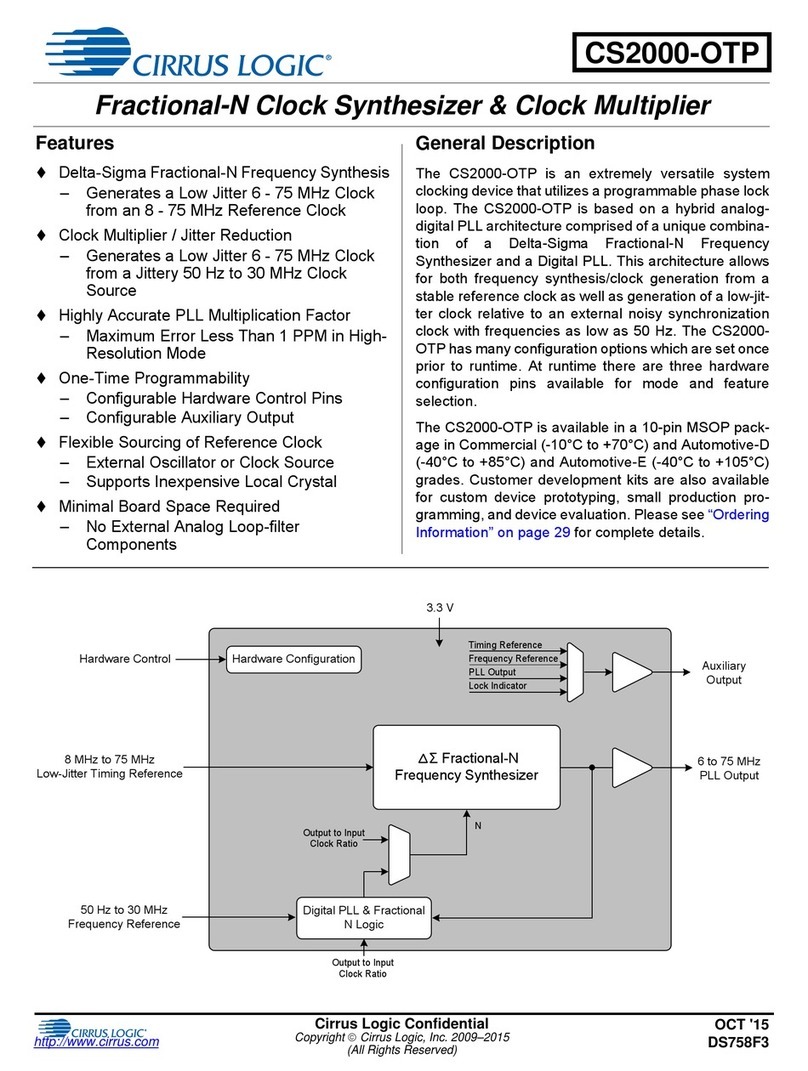
Overview
VK-2 brings you the power of a modular synthesizer without the hassle of cables. All of the
individual synthesis components can be freely routed giving you ultimate power and flexibility.
You can just as easily use VK-2 as a mean sounding hardwired analog synth in the default
configuration. At the heart of VK-2 are three analog modeled oscillators with waveforms from
famous modules. Throughout the device there are DSP enhancements that add analog realism
to the sound, from the modeled CP-3 mixer clipping to the Zero Delay Feedback filter section.
Pristine effects polish your sounds to perfection. You’ll soon be creating modular patches like a
pro without leaving the comforts of your own computer.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

3
Sections
Getting familiar with the overall layout is a very import first step to learning VK-2.
"
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.
Oscillators
Filters
Mod Busses / LFOs / Effects
Performance / Unison
Envelopes
Amp
Mixer

4
Modulation Connections
There are many LCD displays on VK-2 that allow you to connect
modulation sources to a target destination. Each display, located in the
modular sections, represents a parameter that can be modulated, for
example oscillator frequency. You can think of the parameter displays as
control jacks on a hardware module.
Shift-drag from any parameter display to a source hot-spot on the panel to make a connection.
For example, you can shift-drag from one of Oscillator 1’s frequency to an LFO. This connects
the source (from the hot-spot) to the destination (the display). Alternatively, you can select
modulation sources from the menu available with a simple click.
The modulation amount knobs allow you to adjust the amount of modulation, and invert it when
the knob is to the left of center.
Note that there are two parameters labeled “Signal”. Instead of being for modulation, these
select the input for that section’s signal path. These typically are connected to audio outputs
from another section.
There is a common list of sources available at each parameter display.
Note, Velocity, Aftertouch,
Mod Wheel, Pitch Wheel
MIDI control values
Constant
A constant maximum positive value
Random
A random value for each note played
Oscillator waveforms
Waveforms of various shapes for each oscillator
Mixer
Output of the mixer section
Filters
Output of the filters section
Amp
Output of the amplifier section
Pink noise, White noise
Two types of audio noise
LFO waveforms
Waveforms of various shapes for each LFO. Note: SH 1 is a
sample and hold, SH 2 is a smoothed sample and hold
EG1, EG2
Envelope signals
Mod Busses
Outputs from the two mod busses
CV Inputs
CV inputs are located on the back panel
Audio Inputs
Audio inputs are located on the back panel
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

5
Performance/Polyphony
This lower left section includes performance controls, pitch modulation, and polyphony.
•Pitch Wheel – Controls the pitch during performance.
•Mod Wheel – Performance control that is selectable as a modulation source.
•Pitch Bend Range – Adjusts the range of the pitch wheel effect in semitones. You can set the
pitch bend range to 0 and use the pitch wheel as a performance parameter.
•Polyphony – Adjusts how many simultaneous notes can be played by setting the number of
synth voices. In the monophonic and n-voice modes, a synth voice is active when its
envelopes are running. In the modular mode, a single voice is always on, it does not shut off
with the envelopes.
•Pitch Modulation – The source and amount of pitch modulation of all three oscillators
simultaneously can be set.
•Keyboard Mode – The keyboard mode determines how notes are played in monophonic
polyphony modes (Mono or Modular):
•Last – The last key pressed sets the pitch.
•Lowest – The lowest key pressed sets the pitch
•Highest – The highest key pressed sets the pitch
•Single – A key will set the pitch as long as it is held regardless of other key presses
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

6
Patches
You can browse the factory sound bank, or save and load your own patches in the middle right
Patches section.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

7
Oscillators
The upper left Oscillators section provides control
over the three main oscillators. These oscillators
have basic shapes, as well as a variable shape
from VK-1.
•Coarse - Normally, this controls a semitone
offset from the keyboard pitch. In Sync mode, this
controls the beat division. In Low mode, this
controls the octave.
•Fine - Normally, this controls the fine tuning of
the oscillator in cents. In Sync and Low modes, the
fine tuning is in semitones.
•Range - The range switch sets the octave of the
oscillator, or puts the oscillator in Sync or Low
modes. Sync mode is low frequency mode with
beat divisions as the frequency. Low mode is also
low frequency, with a frequency four octaves below
the 32’ setting. Note: 8’ is at the same octave as
the keyboard.
•Shape - The shape knob controls the pulse
width of the rectangular shape and the variable
waveform shape of the VK-1 waveform. The shape
knob only affects those two waveform sources, not
the base shapes.
•Sync - Sync allows you to sync an oscillator to Oscillator 1’s output using either a hard sync
or a reverse sync algorithm.
•Modulation Inputs
Frequency 1
Pitch in semitones (typically keyboard Note)
Frequency 2
Pitch in semitones
Linear FM
Linear pitch, useful for audio rate FM
Shape
Shape of rectangular and VK-1 waveforms, useful for pulse width modulation
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

8
Oscillator Tweaks
On the back of the devices there are a few settings to
subtly tweak the oscillators.
•CPU - Can save CPU at the cost of less accurate Linear FM and some loss of clarity on very
low notes
•Mode - Allows you to choose waveforms from two hardware modular oscillators, the 921 or the
Mini, or use clean waveforms.
•Jitter - Controls the amount of jitter in the oscillator’s frequency
•Drift - Controls the amount of slow frequency drift
•Tracking - There is a knob located in each oscillator column for subtly tweaking the keyboard
tracking for results like an uncalibrated analog synth.
Waveforms
There are several waveforms generated simultaneously for each oscillator. They can be chosen
in the modulation parameter (or signal) displays.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sine
Classic sine wave, has noticeable warmth in the 921 and Mini modes
Triangular
This waveform can sound noticeably different in the 921 and Mini modes
Sawtooth
The sawtooth from the different modes are almost identical
Rectangular
A pulse with its width set by the shape knob, slightly less harsh for 921 and Mini
VK-1
This oscillator has become a modern classic, variable shape is determined by
the shape knob

9
Mixer
The middle Mixer section provides a mixer with four inputs and a drive control.
•Input and Amount - The input can be chosen from any of the common
modulation sources. Typically, you would use one of the oscillator waveforms. A
gain control is provided to control the source level.
•Drive - The drive algorithm provides saturation, soft clipping, or analog
modeled hard clipping from the CP-3 mixer. Note: The mode is selected on the
back.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

10
Filters
The middle right Filters section provides a dual filter module. The filters are
Zero Delay Feedback with accurate analog saturation.
•Frequency - This knob controls the cutoff frequency of the filter.
•Resonance - This knob controls the amount of resonance (or peaking at
the cutoff frequency).
•Modifier – When the filter is in Dual LP mode, this controls the difference in
frequency between individual filters for the left and right channels. When the
filter is in HP / LP mode, this controls the difference in frequency between two
series filters that create a band pass effect. In Notch mode, this cross-fades
between lowpass and highness filters to create the notch response.
•Poles - Poles determine the cutoff slope of the filter. You can think of more
poles as stronger filtering.
•Mode - You can choose between Dual Lowpass (stereo lowpass), Highpass
/ Lowpass (effective bandpass), and Notch
•Algorithm - This switch lets you choose between less CPU usage or higher
quality processing and saturation.
•Drive - This knob adjusts the gain into the filter for subtle warmth and grit.
Note: this is located on the back of the device.
•Compensation - This knob adjusts the gain of the filter output compared to
the resonance knob. High compensation will result in more output gain when
resonance is turned up. Note: this is located on the back of the device.
•Modulation/Signal Inputs
Frequency 1
Cutoff frequency (typically an envelope)
Frequency 2
Cutoff frequency
Frequency 3
Cutoff frequency
Signal
Input signal to the filters (typically the mixer output)
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

11
Envelopes
The two envelopes provide a modulation signal that typically
would be used to shape filter cutoff or volume. In VK-2, the
envelopes can shape anything that has a modulation input. The
envelopes are typical ADSR analog-style envelopes common in
many synthesizers.
•Attack - Adjusts the attack time of the envelope
•Decay - Adjusts the decay time of the envelope
•Sustain - Adjusts the sustain level of the envelope
•Release - Adjusts the release time of the envelope
•Velocity - You can add velocity sensitivity to the envelope,
this will makes its amplitude depend on velocity.
•Curve - Curve allows you to adjust the curvature of the
envelope stages. Note: 100% curvature models an analog
envelope.
!
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.
Attack
Decay
Release
Sustain

12
•Mode - You can choose one of several modes for the envelope operation
•Legato - If with no other notes are held, the Envelopes trigger when a note is played. If
other notes are held, the envelopes do not trigger.
•Retrigger - Envelopes trigger any time a note is played
•Loop AD - The attack and decay portions loop while a key is held, then the release
stage happens as usual
•Loop ADR - The attack, decay, and release stages all loop continuously
•Loop S - The attack, decay, and release stages all loop continuously with times
controlled in beat divisions
•CV Inputs - One of the CV inputs is used as a gate for the envelope
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

13
Amp
The right Amplifier section provides a voltage controlled amplifier. It is typically
used after the filters in the signal path as the output stage of the synth. Note,
the effects are connected just prior to the Amp section output in the signal
path.
•Level - Output level of the synth, pre-effects
•Mode - You can set the amp to operate on a linear scale or a dB scale.
Typically, you would use a linear scale.
•Drive - The drive algorithm provides saturation, soft clipping, or analog
modeled hard clipping from the CP-3 mixer. Note: The mode is selected on
the back.
•Modulation/Signal Inputs
Control 1
Amplifier level (typically an envelope)
Control 2
Amplifier level
Pan
Left/right panning
Signal
Input signal to the amp (typically the filters output)
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

14
Mod Busses / LFOs
The two Mod Busses and two LFOs provide low frequency modulation signals for use in
destinations throughout the synth.
Mod Busses
Mod Busses are like VCAs (voltage controlled amplifiers) with the scale signal acting as the
control input. Each Mod Bus has a source, scale, and scale amount. The bus’s input signal
(source) is scaled by the scale value. The amount of scaling is controlled by the scale amount.
Note: This is not like a mod matrix, the destination is not chosen here, it is instead chosen in a
modulation parameter display elsewhere on the synth.
•Source - Input signal
•Scale - Amplitude control
•Amount - Scale amount
LFOs
Each LFO has multiple waveforms that can be chosen at the destination.
•Rate - Adjusts the rate in hertz, or allows you to select a beat division in synced mode.
•Mode - This lets you select one of four operating modes for the LFO.
•Free – The LFO is free running with frequency in hertz.
•Reset – The LFO resets to the beginning of its waveform when a key is pressed.
•One Shot – When a key is pressed, the LFO goes one time through its waveform and
stops
•Sync – The LFO runs continuously, synced to the transport, with its frequency set to a
beat division
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

15
There are several waveforms generated simultaneously for each LFO. They can be chosen in
the modulation parameter (or signal) displays.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.
Sine
Classic sine wave
Triangle
Classic triangle
Ramp
Upward sawtooth
Sawtooth
Downward sawtooth
SH 1
Classic sample and hold
SH 2
Smoothed sample and hold

16
Effects
VK-2 has five on-board effects that allow you to add depth and interest to your
patch. The effects are connected to the Amp section. The effects are enabled
and re-ordered using the display. Click to enable/disable. Drag to reorder them
in any order. The included effects are chorus, equalizer, phaser, distortion, delay,
and reverb.
•Chorus – Adds thickness by mimicking the sound of unison
•Phaser – Offers the distinct phasing effect with a wide range of options
•Distortion – Allows you to create grit or bit crushing effects.
•Delay – Provides various echo effects
•Reverb – Adds a hall-like space to the sound
Chorus
The Chorus unit provides a Roland
Dimension D influenced chorus
effect that can add stereo width and
richness to your patch. It offers an
additional feedback control.
•Delay – Adjusts the mid-point for the delay taps
•Rate – Adjusts how fast the delay taps move
•Depth – Adjusts how far the delay taps move
•Feedback – Adjusts feedback in the delay lines
•Mix – Sets the wet/dry mix for the effect
Phaser
The phaser offers up to 6 notches,
with configurable notch width and
feedback, for a wide range of
phasing sounds.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

17
•Notches - Number of notches in the frequency response, more create a thicker sound
•Notch width - Bandwidth of the notches
•Frequency - Frequency range of the effect, controlling the low end frequency of the LFO
•Mod Amount - Adjusts the LFO strength
•Feedback - Amount of feedback present in the effect
•Rate - Rate of the LFO that controls the frequency of the all-pass filters
•Offset - LFO offset between the left and right panned effects
•Mix - Sets the wet/dry mix for the effect
Distortion
The Distortion effect can add
anything from warmth, to grit, to
crushing mayhem.
•Drive - Gain into the distortion algorithm that results in more distortion
•High Cut - Lowpass filter
•Low Cut - Highpass filter
•Type - Chooses between several distortion algorithms
•Level - A post-distortion gain setting
•Mix - Sets the wet/dry mix for the effect
Delay
The delay unit offers a repeating
echo. It has quite a few additional
parameters that can spice up the
effect.
•Delay Mode – At the lowest setting, the delay is in normal mode, otherwise it is in ping pong
mode
•Normal - Input signal is delayed with no panning effect
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

18
•Ping Pong – Echoes bounce between left and right channels starting with left, spread
controls panning amount
•Time – Adjusts the delay time in beat divisions
•Rate – Adjusts the delay time for the right channel
•Tone – Adjusts filtering inside the feedback path. Turning the knob to the left of center
creates lowpass filtering. Turning the knob to the right of center creates highpass filtering.
•Drive – Adjusts a subtle distortion effect on the delayed signal
•Feedback – Controls how fast the echoes decay
•Mod Amount – Turning up the Mod Amount creates a changing delay time with a slight offset
between left and right delay times
•Mod Rate – Adjusts the rate of the modulation set by Mod Amount
•Mix – Sets the wet/dry mix for the effect
Reverb
The reverb effect adds a hall-like
spatialization effect to the sound.
•Low Time – Adjusts the T60 decay time for the low-range frequencies
•Mid Time – Adjusts the T60 decay time for the mid-range frequencies
•Crossover – Adjusts the cross-over frequency between mid and low range
•Damping – Sets the frequency of high frequency damping
•Delay – Adds a delay to the signal to simulate a larger space
•Mod Amount – Adds subtle variation in the decay times
•Mod Rate – Adjusts the modulation rate of the decay times
•Mix – Sets the wet/dry mix for the effect
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

19
Connections
Oscillator Connections
•Outputs are available for each of the oscillator waveform shapes.
•Individual inputs are available for the same parameters that can be modulated using displays
on the front panel.
Mixer Outputs
Connections are available from the mixer in both audio and CV format.
Filter Connections
•Audio outputs are available for the filtered signal.
•Filter frequency and resonance have individual modulation inputs.
•The audio input signal should be connected to the Signal inputs.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.

20
Envelope Outputs
A CV output is available for each envelope.
LFO Outputs
The individual waveforms from the LFOs are available as CV outputs.
Amp Connections
•Audio and CV outputs are available for the amplified signal.
•Control (gain) and pan have individual modulation inputs.
•The audio or CV input signal should be connected to the Signal inputs.
Performance CV Inputs
The Performance CV Input group lets you control VK-2 with an external triggering device such
as the Matrix Pattern Sequencer. VK-2 supports the PolyCV protocol for polyphonic triggering.
•Gate – Controls triggering velocity
•Note – Controls triggering note
•PW – Pitch Wheel input
•MW – Mod Wheel input
•AT – Aftertouch input
•Sust – Sustain pedal input
Global Inputs
The Global CV and Audio Inputs located at the bottom let you route inputs to any of the
modulation parameters using their destination displays.
Modulation Bus Outputs
Outputs from the Mod Busses are available in both audio and CV format.
© 2017 Blamsoft, Inc. All rights reserved.
Table of contents
Other Blamsoft Synthesizer manuals
Popular Synthesizer manuals by other brands

Freedom Enterprise
Freedom Enterprise Inter Continental Capacitive Ballistic Synth owner's manual

Korg
Korg DS-8 Service manual

Xaoc Devices
Xaoc Devices JENA Operator's manual

Korg
Korg MiniKorg-700S owner's manual

Satel
Satel SM-2 Quick start manual

RADIKAL TECHNOLOGIES
RADIKAL TECHNOLOGIES Spectralis user manual