2/ 27
CONTENT
1 OUTLINE.................................................................................................................................................3
1.1 MOBILE PHONE INTRODUCTION.....................................................................................................3
1.2 MOTHERBOARD COMPONENTS DISTRIBUTION...........................................................................................6
2 SIGNAL FLOW AND FAULT ANALYSIS......................................................................................................6
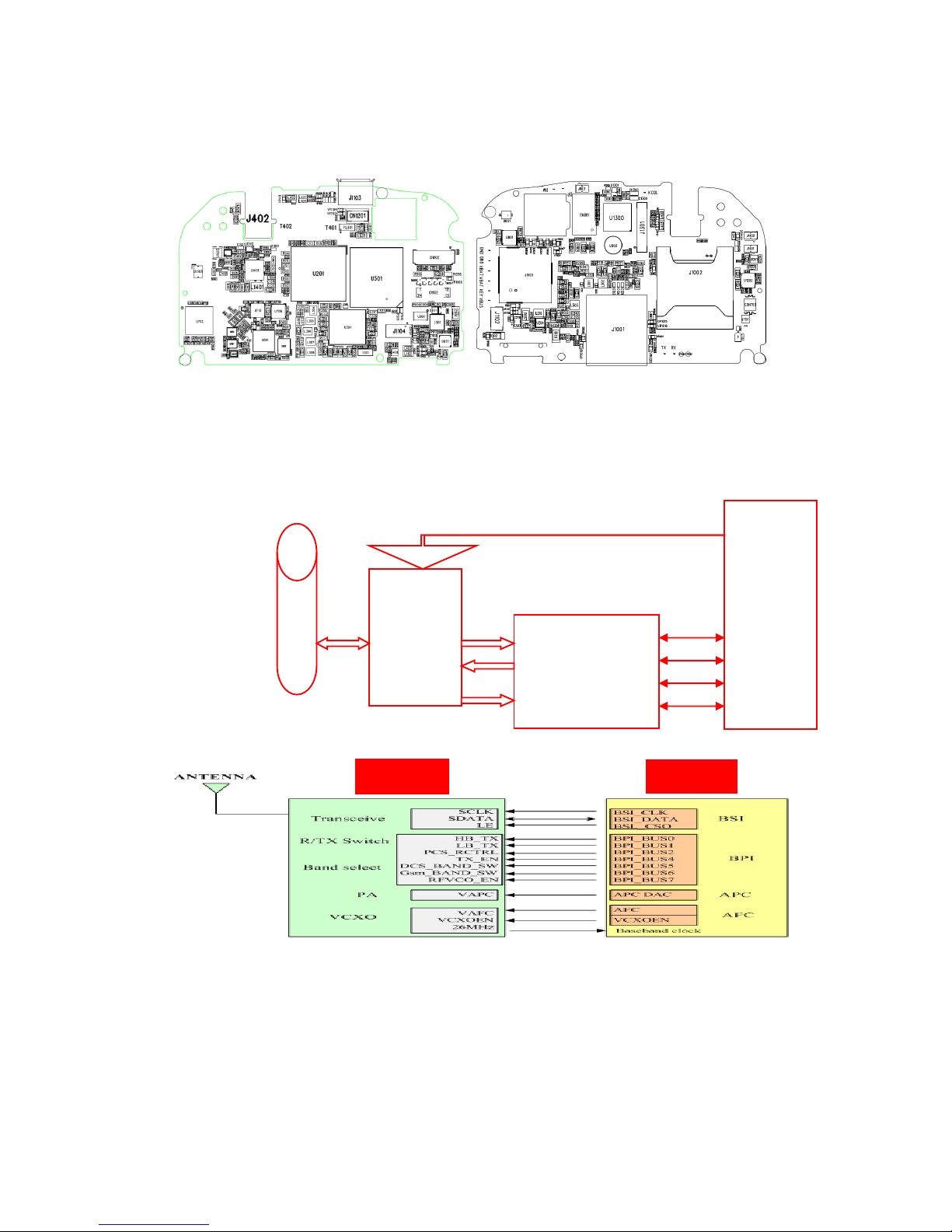
2.1 RF PART ............................................................................................................................................6
2.1.1 Block Diagram of the RF Section .............................................................................................6
2.1.2 Signal Flow OF the RF Transmitting Part..................................................................................6
2.1.2.1 Receiving and Transmit Path ............................................................................................6
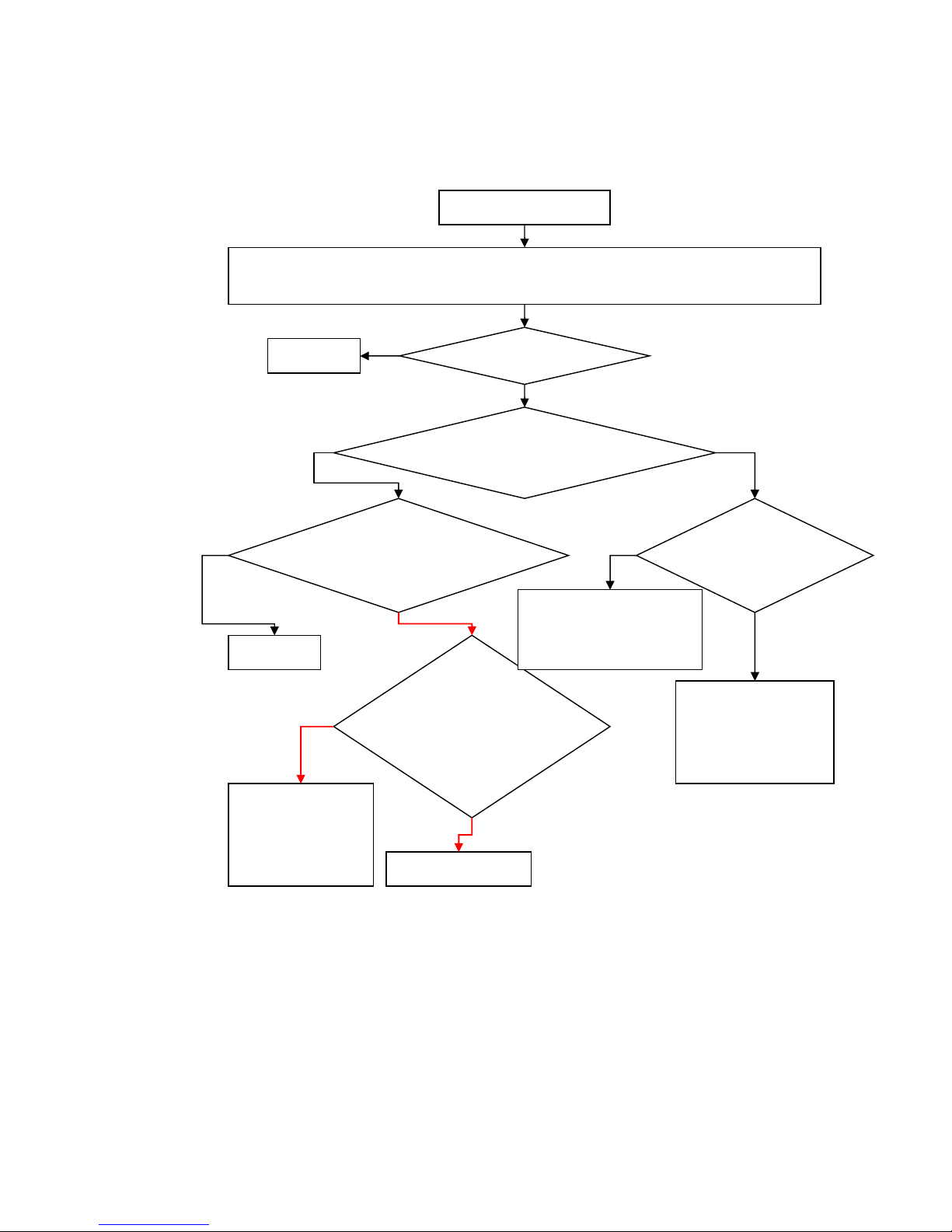
2.1.2.2 Maintenance Procedures of the Transmitting Part ..........................................................8
2.1.3 Signal Flow of the Receiving Part ............................................................................................9
2.1.3.1 Receiving Part Components .............................................................................................9
2.1.3.2 Maintenance Procedures of the Receiving Part........................................................10
2.2 BASEBAND PART................................................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Block Diagram of the Baseband Part.....................................................................................11
2.2.2 Power Management Part ......................................................................................................12
2.2.2.1 The Whole Power Supply System...................................................................................12
2.2.3 Audio Part..............................................................................................................................14
2.2.3.1 Audio CODEC Circuit......................................................................................................14
2.2.3.2 MIC, RECEIVER LOOP......................................................................................................15
2.2.3.3 HEADSET LOOP...............................................................................................................16
2.2.4 BASEBAND FAUIT ISSUES .......................................................................................................17
2.2.4.1 Analysis of the Keyboard Fault .......................................................................................18
2.2.4.2 Analysis of the Display Module Circle ............................................................................18
2.2.4.3 FM Module.....................................................................................................................19
2.2.4.4 Camera Module..............................................................................................................19
2.2.4.5 IO Interface ....................................................................................................................20
2.2.4.6 SIM Card Circuit.............................................................................................................21
2.2.4.7 T-FLASH Card Circuit .....................................................................................................21
2.2.4.8 BT Circuit.......................................................................................................................22
2.2.4.9 WIFI Circuit....................................................................................................................23
2.2.4.10 GPS Circuit...................................................................................................................24
2.2.4.11 M-sensor Circuit..........................................................................................................24
2.2.4.12 G-sensor Circuit...........................................................................................................25
2.2.4.13 IR-sensor Circuit..........................................................................................................25