B+K precision 4060B Series Owner's manual


Contents
1 About Commands & Queries 3
1.1 How They are Listed 3
1.2 How They are Described 3
1.3 When can they be used? 3
1.4 Command Notation 3
2 Common Command Introduction 4
2.1 *IDN? 5
2.2 *OPC 6
2.3 *CLS 6
2.4 *ESE 6
2.5 *ESR 6
2.6 RST 7
2.7 SRE 7
2.8 *STB? 7
2.9 *TST? 7
2.10 WAI 8
2.11 Comm_Header Command 8
2.12 Output Command 8
2.13 Basic Wave Command 9
2.13.1 Paramters 9
2.14 Modulate Wave Command 11
2.14.1 ParamtersTable 11
2.15 Sweep Wave Command 13
2.15.1 Paramters 14
2.16 Burst Wave Command 15
2.16.1 Paramters 16
2.17 Parameter Copy Command 17
2.18 Arbitrary Wave Command 17
2.18.1 Notes: 18
2.19 Sync Command 18
2.20 Number Format Command 18
2.21 Language Command 19
2.22 Conguration Command 19
2.23 Buzzer Command 19
2.24 Screen Save Command 20
2.25 Clock Source Command 20
2.26 Frequency Counter Command 20
2.27 Invert Command 21
2.28 Coupling Command 21
2.29 Voltage Overload Command 22
2.30 Store List Command 22
2.31 Arbitrary Wave Data Command 23
2.32 Virtual Key Command 24
2.33 IP Command 24
2.34 Subnet Mask Command 25
2.35 Gateway Command 25
2.36 Sampling Rate Command 25
2.37 Harmonic Command 26
2.38 Waveform Combining Command 26
3 LIMITED THREE-YEAR WARRANTY 27
4 Service Information 28

About Commands & Queries
This section lists and describes the remote control commands and queries recognized by the instrument. All commands
and queries can be executed in either local or remote state.
The description for each command or query, with syntax and other information, begins on a new page. The name
(header) is given in both long and short form, and the subject is indicated as a command or query or both. Queries
perform actions such as obtaining information, and are recognized by the question mark (?) following the header.
1.1 How They are Listed
The descriptions are listed in alphabetical order according to their short form.
1.2 How They are Described
In the descriptions themselves, a brief explanation of the function performed is given. This is followed by a presentation
of the formal syntax, with the header given in Upper-and-Lower-Case characters and the short form derived from it in
ALL UPPER-CASE characters. Where applicable, the syntax of the query is given with the format of its response.
1.3 When can they be used?
The commands and queries listed here can be used for 4060B Series arbitrary/function waveform generators.
1.4 Command Notation
The following notation is used in the commands:
< > Angular brackets enclose words that are used
placeholders, of which there are two types: the header path
and the data parameter of a command.
:= A colon followed by an equals sign separates a placeholder
from the description of the type and range of values that
may be used in a command instead of the placeholder.
Braces enclose a list of choices, one of which one must be made.
[ ] Square brackets enclose optional items.
… An ellipsis indicates that the items both to its left and right
may be repeated a number of times.
Common Command Introduction
IEEE standard denes the common commands used for querying the basic information of the instrument or executing
basic operations. These commands usually start with "*" and the length of the keywords of the command is usually 3
characters.
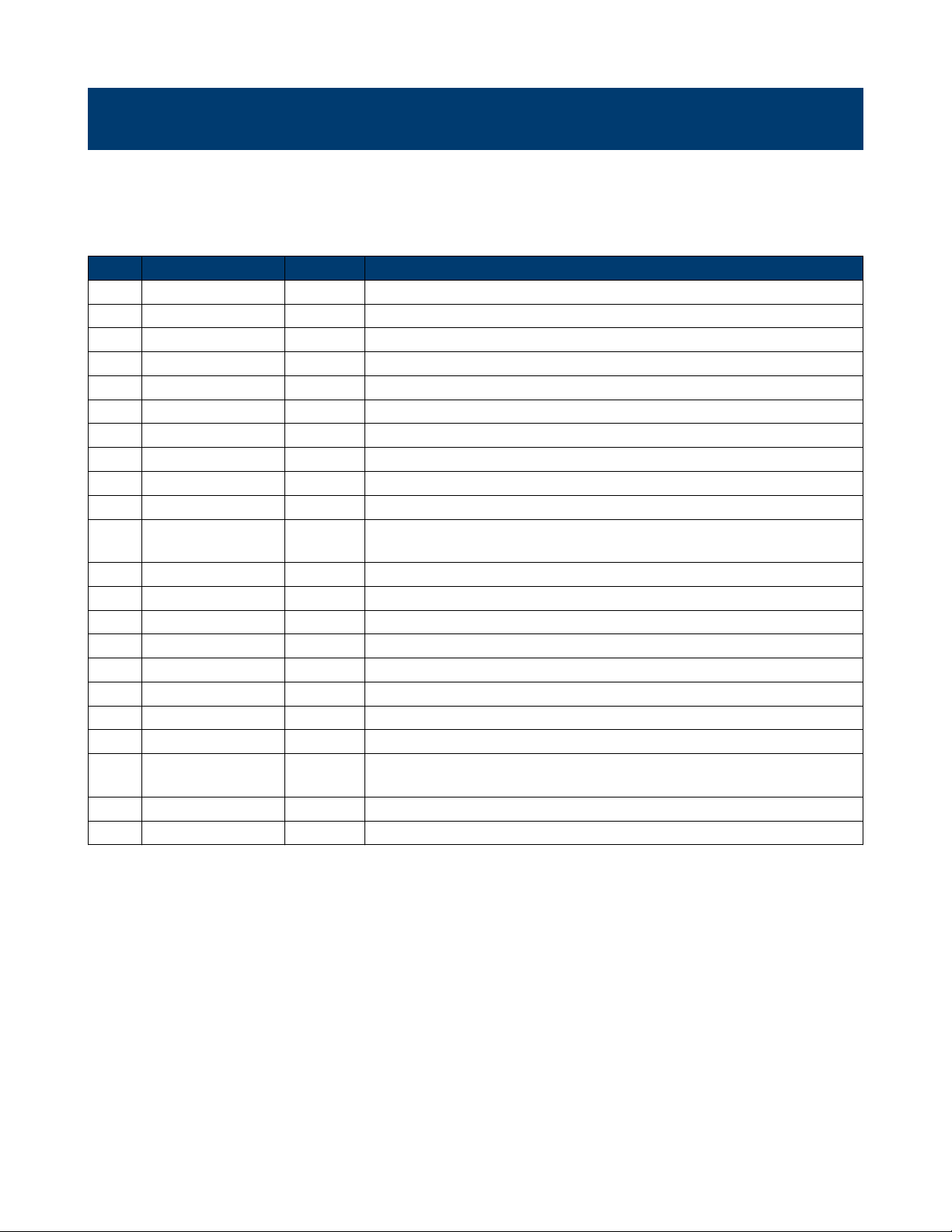
Short Long Form Subsystem What Command/Query does
*IDN *IDN SYSTEM Gets identication from device.
*OPC *OPC SYSTEM Gets or sets the OPC bit (0) in the Event Status Register (ESR).
*CLS *CLS SYSTEM Clears all the status data registers.
*ESE *ESE SYSTEM Sets or gets the Standard Event Status Enable register (ESE).
*ESR *ESR SYSTEM Reads and clears the contents of the Event Status Register (ESR).
*RST *RST SYSTEM Initiates a device reset.
*SRE *SRE SYSTEM Sets the Service Request Enable register (SRE).
*STB *STB SYSTEM Gets the contents of the IEEE 488.2 dened status register.
*TST *TST SYSTEM Performs an internal self-test.
*WAI *WAI SYSTEM Wait to continue command.
CHDR COMM_HEADER SIGNAL Sets or gets the command returned format OUTP OUTPUT SIGNAL Sets
or gets output state.
BSWV BASIC_WAVE SIGNAL Sets or gets basic wave parameters.
MDWV MODULATEWAVE SIGNAL Sets or gets modulation parameters.
SWWV SWEEPWAVE SIGNAL Sets or gets sweep parameters.
BTWV BURSTWAVE SIGNAL Sets or gets burst parameters.
PACP PARACOPY SIGNAL Copies parameters from one channel to the other.
ARWV ARBWAVE DATA Changes arbitrary wave type.
SYNC SYNC SIGNAL Sets or gets synchronization signal.
NBFM NUMBER_FORMAT SYSTEM Sets or gets data format.
LAGG LANGUAGE SYSTEM Sets or gets language. SCFG SYS_CFG SYSTEM Sets or gets the
power-on system setting way.
BUZZ BUZZER SYSTEM Sets or gets buzzer state.
SCSV SCREEN_SAVE SYSTEM Sets or gets screen save state.
Common Command Introduction 5
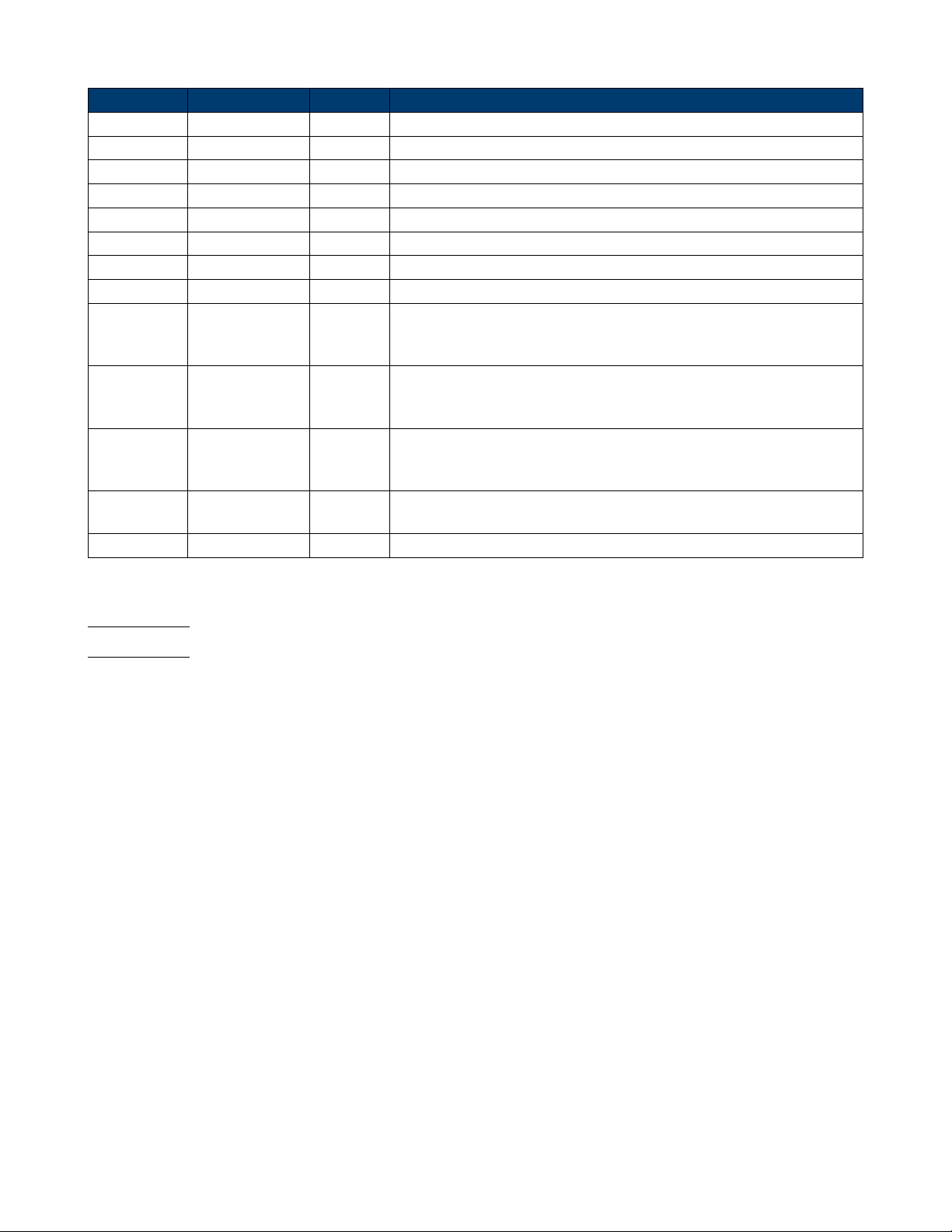
Short Long Form Subsystem What Command/Query does
ROSC ROSCILLATOR SIGNAL Sets or gets state of clock source.
FCNT FREQCOUNTER SIGNAL Sets or gets frequency counter parameters.
INVT INVERT SIGNAL Sets or gets polarity of current channel.
COUP COUPLING SIGNAL Sets or gets coupling parameters.
VOLTPRT VOLTPRT SYSTEM Sets or gets state of over-voltage protection.
STL STORELIST SIGNAL Lists all stored waveforms.
WVDT WVDT SIGNAL Sets and gets arbitrary wave data.
VKEY VIRTUALKEY SYSTEM Sets the virtual keys.
SYST:COMM:
LAN:IPAD
SYSTEM:
COMMUNICATE:
LAN:IPADDRESS
SYSTEM The Command can set and get system IP address.
SYST:COMM:
LAN:SMAS
SYSTEM:
COMMUNICATE:
LAN:SMASK
SYSTEM The Command can set and get system subnet mask.
SYST:COMM:
LAN:GAT
SYSTEM:
COMMUNICATE:
LAN:GATEWAY
SYSTEM The Command can set and get system Gateway.
SRATE SAMPLERATE SIGNAL Sets or gets sampling rate. You can only use it in TrueArb mode
HARM HARMonic SIGNAL Sets or gets harmonic information.
CMBN COMBINE SIGNAL Sets or gets wave combine information.
2.1 *IDN?
Description The *IDN? query causes the instrument to identify itself. The response comprises manufacturer,
model, serial number, software version and rmware version.
Query Format *IDN?
Response Format *IDN, <device id>,<model>,<serial number>, <software version>,
<hardware version>.
<device id>=“BK” is used to identify instrument.
<model>= A model identier less than 14 characters will contain the model number.
<serial number>:Each product has its own number, the serial number can labeled
product uniqueness.
<software version>= A serial numbers about software version.
<hardware version>=The hardware level eld, should contain information about all separately
revisable subsystems. This information can be contained in single or multiple revision codes.
Example *IDN?
Returns:
*IDN BK, 4062B, 573J19100, 2.01.01.35R3B2
value2: Hardware version. value3:
Hardware subversion. value4:
FPGA version.
value5: CPLD version.

Common Command Introduction 6
2.2 *OPC
Description The *OPC (Operation Complete) command sets the OPC bit (bit 0) in the standard Event Sta-
tus Register (ESR). This command has no other eect on the operation of the device because
the instrument starts parsing a command or query only after it has completely processed the pre-
vious command or query. The *OPC? query always responds with the ASCII character 1 because
the device only responds to the query when the previous command has been entirely executed.
COMMAND SYNTAX *OPC
Query Syntax *OPC?
Response Format *OPC 1
2.3 *CLS
Description The *CLS command clears all the status data registers.
Command Syntax *CLS
Example The following command causes all the status data registers to be cleared: *CLS
2.4 *ESE
Description The *ESE command sets the Standard Event Status Enable register (ESE). This command al-
lows one or more events in the ESR register to be reected in the ESB summary message bit (bit
5) of the STB register. The *ESE? query reads the contents of the ESE register.
Command Syntax *ESE <value>
<value> = 0 to 255.
Query Format *ESE?
Query Response *ESE <value>
Example The following instruction allows the ESB bit to be set if a user request (URQ bit 6, i.e. decimal
64) and/or a device dependent error (DDE bit 3, i.e. decimal 8) occurs. Summing these values
yields the ESE register mask 64+8=72.
*ESE?
Return:
*ESE 72
2.5 *ESR
Description The *ESR? query reads and clears the contents of the Event Status Register (ESR). The response
represents the sum of the binary values of the register bits 0 to 7.
Query Format *ESR?
Query Response *ESR <value>
<value> = 0 to 255
Example The following instruction reads and clears the content of the ESR register
*ESR?
Return:
*ESR 0
Related Commands *CLS, *ESE

Common Command Introduction 7
2.6 RST
Description The *RST command initiates a device reset. The *RST recalls the default setup.
Command Syntax *RST
Example This example resets the signal generator: *RST
2.7 SRE
Description The *SRE command sets the Service Request Enable register (SRE). This command allows the
user to specify which summary message bit(s) in the STB register will generate a service request.
A summary message bit is enabled by writing a ‘1’ into the corresponding bit location. Conversely,
writing a ‘0’ into a given bit location prevents the associated event from generating a service re-
quest (SRQ). Clearing the SRE register disables SRQ interrupts.
The *SRE? query returns a value that, when converted to a binary number represents the bit set-
tings of the SRE register. Note that bit 6 (MSS) cannot be set and it’s returned value is always
zero.
Command Syntax *SRE <value>
<value> = 0 to 255
Query Format *SRE?
Query Response *SRE <value>
Example The following instruction allows a SRQ to be generated as soon as the MAV summary bit (bit
4, i.e. decimal 16) or the INB summary bit (bit 0, i.e. decimal 1) in the STB register, or both
are set. Summing these two values yields the SRE mask 16+1 = 17.
*SRE?
Return:
*SRE 17
2.8 *STB?
Description The *STB? query reads the contents of the 488.2 dened status register (STB), and the Mas-
ter Summary Status (MSS). The response represents the values of bits 0 to 5 and 7 of the Sta-
tus Byte register and the MSS summary message.
The response to a *STB? query is identical to the response of a serial poll except that the MSS
summary message appears in bit 6 in place of the RQS message.
Query Syntax *STB?
Query Response *STB <value>
<value> = 0 to 255
Example The following reads the status byte register:
*STB?
Return:
*STB 0
Related Commands *CLS, *SRE
2.9 *TST?
Description The *TST? query performs an internal self-test and the response indicates whether the self-test
has detected any errors. The self-test includes testing the hardware of all channels. Hardware

Common Command Introduction 8
failures are identied by a unique binary code in the returned <status> number. A “0” response
indicates that no failures occurred.
Query Format *TST?
Query Response *TST <status>
<status> = 0 self-test successful
Example The following causes a self-test to be performed:
TST?
Return(if no failure):
*TST 0
Related Commands *CAL
2.10 WAI
Description The *WAI (WAIT to continue) command, requires by the IEEE 488.2 standard, has no eect on
the instrument, as the signal generator only starts processing a command when the previous com-
mand has been entirely executed.
Command Syntax *WAI
Related Commands *OPC
2.11 Comm_Header Command
Description This command is used to change the query command returned format. “SHORT” parameter re-
turns short format. “LONG” parameter returns long format. “OFF” returns nothing.
Command Syntax Comm_HeaDeR <parameter>
<parameter>={SHORT,LONG,OFF}
Query Format Comm_HeaDeR?
Query Response chdr <parameter>
Example Set query command format to long. CHDR LONG Read query command format.
CHDR?
Return:
COMM_HEADER LONG
2.12 Output Command
Description Enable or disable the output of the [Output] connector at the front panel corresponding to the
channel. The query returns “ON” or “OFF” and “LOAD”, “PLRT” parameters.
Command Syntax <channel>:OUTPut <parameter>
<channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter >={a parameter from the table below}
< load>={please see the note below.}
Parameters Value Description
ON — Turn on
OFF — Turn o
LOAD <load> value of load(defaultunite is ohm)
PLRT <NOR,INVT> value of polarity parameter

Common Command Introduction 9
Query Format <channel>:OUTPut?
Query Response <channel>:OUTP <load>
Example Turn on channel one.
C1:OUTP ON
Read channel one output state.
C1:OUTP?
Return:
C1:OUTP ON, LOAD, HZ, PLRT, NOR
Set the load to 50.
C1:OUTP LOAD, 50
Set the load to HZ.
C1:OUTP LOAD, HZ
Set the polarity normal.
C1:OUTP PLRT, NOR
Set the polarity inverted.
C1:OUTP PLRT, INVT
2.13 Basic Wave Command
Description Sets or gets basic wave parameters.
Command Syntax <channel>:BaSic_WaVe <parameter>
<channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter>:={a parameter from the table below}
2.13.1 Paramters
Note: if the command doesn’t set basic wave type, WVPT parameter will be set to current
wave type.
where:
<type>={SINE, SQUARE, RAMP, PULSE, NOISE, ARB ,DC}
<frequency>={Default unit is "Hz". Value depends on the model.}
<amplitude>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<oset>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<duty>={0% to 100%. Value depends on frequency.}
<symmetry> ={0% to 100%}
<phase>={0 to 360 if you set 400,it will set 40(400-360)}
< standard deviation >={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<mean>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<width>={Max_width < (Max_duty * 0.01) * period and Min_width >
(Min_duty * 0.01) * period.}
<rise>={Value depends on the model.}
<fall>={Value depends on the model.}
<delay>={Unit is S. Maximal is Pulse period, minimum value is 0.}
<bandwidth switch >={ON,OFF}
<bandwidth value>={value between 20MHz and 120MHz}

Common Command Introduction 10
Parameters Value Description
WVTP <type> Type of wave
FRQ <frequency> Value of frequency. If wave type is Noise or DC,
you can’t set this parameter.
PERI <period> Value of period. If wave type is Noise or DC, you
can’t set this parameter.
AMP <amplitude> Value of amplitude. If wave type is Noise or DC,
you can’t set this parameter.
OFST <oset> Value of oset. If wave type is Noise or DC, you
can’t set this parameter.
SYM <symmetry> Value of symmetry. Only when wave type is
Ramp, you can set this parameter.
DUTY <duty> Value of duty cycle. Only when wave type is
Square and Pulse, you can set this parameter.
PHSE <phase> Value of phase. If wave type is Noise or Pulse or
DC, you can’t set this parameter.
STDEV <standard deviation > Value of Noise wave standard deviation. Only
when wave type is Noise, you can set this
parameter.
MEAN <mean> Value of Noise wave mean. Only when wave type
is Noise, you can set this parameter.
IDTH <width> Value of width. Only when wave type is Pulse,
you can set this parameter.
RISE <rise> Value of rise time. Only when wave type is Pulse,
you can set this parameter.
FALL <fall> Value of fall time. Only when wave type is Pulse,
you can set this parameter
DLY <delay> Value of delay. Only when wave type is Pulse, you
can set this parameter.
HLEV <high level> Value of high level. If wave type is Noise or DC,
you can’t set this parameter.
LLEV <low level> Value of low level. If wave type is Noise or DC,
you can’t set this parameter.
BANDSTATE <switch > <bandwidth> State of noise bandwidth switch. Only when wave
type is Noise, you can set this parameter.
BANDWIDTH <bandwidth value> Value of noise bandwidth. Only when wave type is
noise, you can set this parameter.
Query Format <channel>:BaSic_WaVe?
<channel>={C1, C2}
Query Response <channel>:BSWV<type>,<frequency>,<amplitude>,<oset>, <duty>,<symmetry>,
<phase>,<variance>,<mean>,<width>, <rise>, <fall>, <delay>.
Example Change channel one wave type to ramp.
C1:BSWV WVTP, RAMP
Change frequency of channel one to 2000 Hz.
C1:BSWV FRQ, 2000
Set amplitude of channel one to 3Vpp.
C1:BSWV AMP, 3
Read channel basic wave parameters from device.
C1:BSWV?
Return:

Common Command Introduction 11
C1:BSWV WVTP, SINE,FRQ,100HZ,PERI,0.01S,AMP,2V, OFST,0V,HLEV,1V,LLEV,-1V,PHSE,0
Set noise bandwidth value of channel one to 100MHz
C1:BSWV BANDWIDTH, 100000000
2.14 Modulate Wave Command
Description Sets or gets modulation parameters.
Command <channel>:MoDulateWaVe<parameter>
Syntax <channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter>={a parameter from the table below}
2.14.1 ParamtersTable
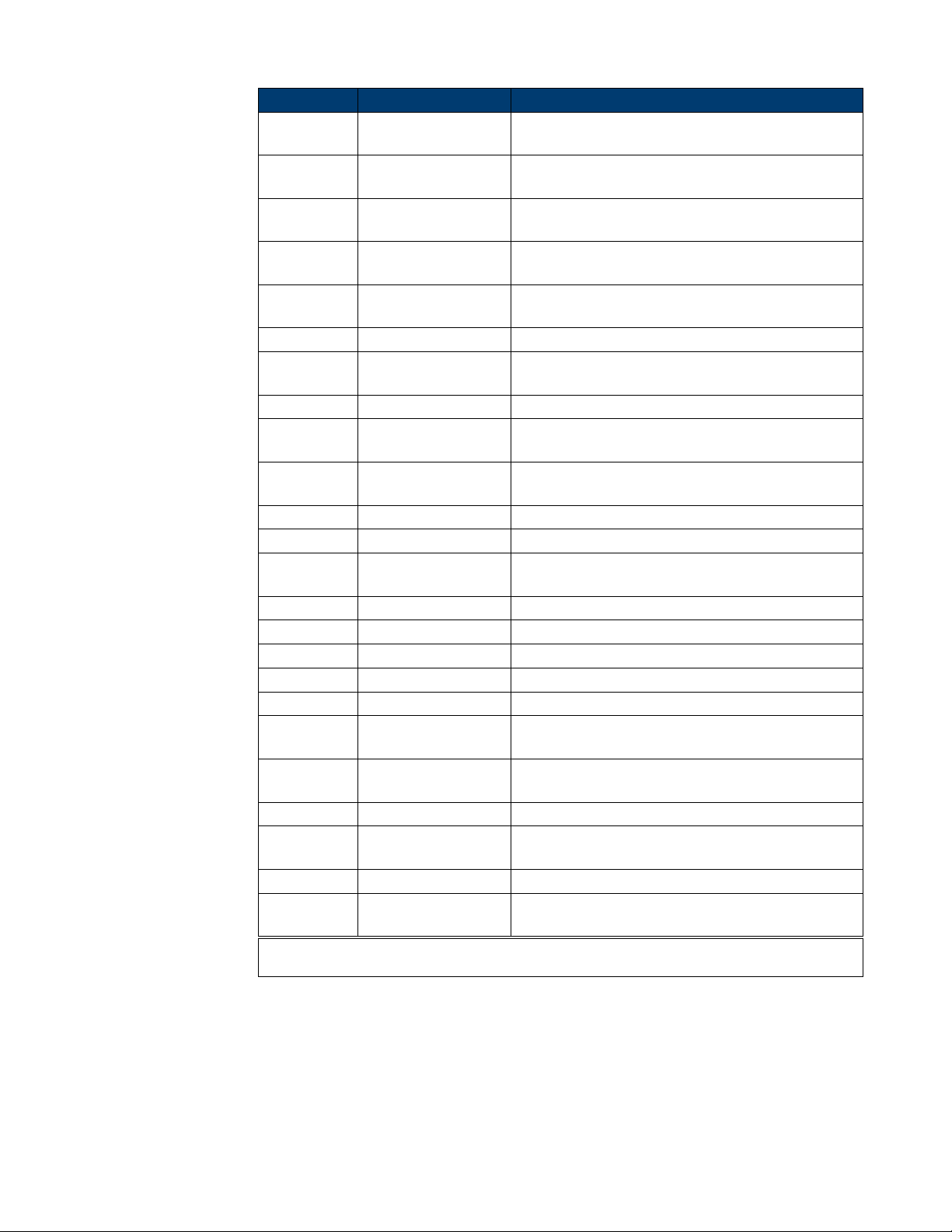
Parameters Value Description
STATE <state> Turn on or o modulation. Note: if you want
to set or read other parameters of modulation,
you must set STATE to ON at rst.
AM, SRC <src> AM signal source.
AM, MDSP <mod wave shape> AM modulation wave. Only when AM sign al
source is set to INT, you can set the
parameter.
AM, FRQ <AM frequency> AM frequency. Only when AM signal sour ce
is set to INT, you can set the paramet er.
AM, DEPTH <depth> AM depth. Only when AM signal source is set
to INT, you can set the parameter.
DSBAM, SRC <src> DSBAM signal source.
DSBAM, MDSP <mod wave shape> DSBAM modulation wave. Only when AM
signal source is set to INT, you can set the
parameter.
DSBAM, FRQ <DSB-AM>< frequency> DSBAM frequency. Only when AM signal
source is set to INT, you can set the
parameter.
FM, SRC <src> FM signal source.
FM, MDSP <mod wave shape> FM modulation wave. Only when FM signal
source is set to INT, you can set the
parameter.
FM, FRQ <FM frequency> FM frequency. Only when FM signal source is
set to INT, you can set the parameter.
FM, DEVI <FM frequency deviation > FM frequency deviation. Only when FM
signal source is set to INT. you can set the
parameter.
PM, SRC, <src> PM signal source.
Common Command Introduction 12
Parameters Value Description
PM, MDSP <mod wave shape> PM modulation wave. Only when PM signal source
is set to INT, you can set the parameter.
PM, FRQ <PM frequency> PM frequency. Only when PM signal source is set to
INT, you can set the parameter.
PWM, FRQ <PWM frequency> PWM frequency. Only when carrier wave is PULSE
wave, you can set the parameter.
PWM, DEVI <PWM dev> Duty cycle deviation. Only when carrier wave is
PULSE wave, you can set the parameter.
PWM, MDSP <mod wave shape> PWM modulation wave. Only when carrier wave is
PULSE wave, you can set the parameter.
PWM, SRC <src> PWM signal source.
PM, DEVI <PM phase oset> PM phase deviation. Only when PM signal source is
set to INT, you can set the parameter.
ASK, SRC <src> ASK signal source.
ASK, KFRQ <ASK key frequency> ASK key frequency. Only when ASK signal source is
set to INT, you can set the parameter.
FSK, KFRQ <FSK key frequency> FSK key frequency. Only when FSK signal source is
set to INT, you can set the parameter.
FSK, HFRQ <FSK hop frequency> FSK hop frequency.
FSK, SRC <src> FSK signal source.
PSK, KFRQ <FSK key frequency> PSK key frequency. Only when PSK signal source is
set to INT, you can set the parameter.
PSK, SRC <src> PSK signal source.
CARR, WVTP <wave type> Carrier wave type.
CARR, FRQ <frequency> Value of carrier frequency.
CARR, AMP <amplitude> Value of carrier amplitude.
CARR, OFST <oset> Value of carrier oset.
CARR, SYM <symmetry> Value of carrier symmetry. Only ramp can set this
parameter.
CARR, DUTY <duty> Value of duty cycle. Only square and pulse can set
this parameter.
CARR, PHSE <phase> Value of carrier phase.
CARR, RISE <rise> Value of rise time. Only Pulse can set this
parameter.
CARR, FALL <fall> Value of fall time. Only Pulse can set this parameter.
CARR,DLY <DELAY> Value of carrier delay.Only PULSE can set this
parameter.
Note: If carrier wave is Noise you can’t set to turn on modulation.
If you want to set AM, FM, PM, CARR and STATE the rst parameter have to be one of them.
where: <state>={ON, OFF}
<src>={INT, EXT}
<mod wave shape>={SINE, SQUARE, TRIANGLE, UP RAMP, DNRAMP, NOISE, ARB}
<am frequency>={Default unit is "Hz". Value depends on the model.} <depth>={0% to 120%}
<fm frequency>={Default unit is "Hz". Value depends on the model.} <fm frequency devia-
tion > ={0 to carrier frequency, Value depends on the dierence between carrier frequency and
bandwidth frequency.} <pm frequency> ={Default unit is "Hz", Value depends on the model.}
<pm phase deviation >={0 to 360.} <pwm frequency>={Default unit is "Hz", Value depends
on the model.}

Common Command Introduction 13
<pwm dev>={Default unit is "%",value depends on carrier duty cycle} <ask key frequency>={De-
fault unit is "Hz", Value depends on the model.}
<fsk frequency>={Default unit is "Hz", Value depends on the version.} <fsk jump frequency>={the
same with basic wave frequency}
<wave type>={SINE ,SQUARE, RAMP, ARB, PULSE}
<frequency> ={Default unit is "Hz", Value depends on the model.}
<amplitude> ={Default unit is "V", Value depends on the model.}
<oset> ={Default unit is "V", Value depends on the model.}
<duty>={0% to 100%.}
<symmetry>={0% to 100%}
<rise>={Value depends on the model.}
<fall>={Value depends on the model.}
<delay>={Default unit is "S".}
Note: There are some parameters Value depends on the model, You can read version
datasheet to get specic parameters
Query Format <channel>:MoDulateWaVe?
<channel>={C1, C2}
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>:MDWV <parameter>
<parameter> ={Return all parameter of the current modulation parameters.}
Example Set channel one modulation type to AM.
C1:MDWV AM
Set modulation shape to AM, and set AM modulating wave type to sine wave.
C1:MDWV AM, MDSP, SINE
Read channel one modulation parameters of which STATE is ON.
C1:MDWV?
Return:
C1:MDWV STATE,ON,AM,MDSP,SINE,SRC,INT,FRQ,100HZ,
DEPTH,100,CARR,WVTP,RAMP,FRQ,1000HZ,AMP,4V,OFST,0V,PHSE, 0, SYM, 50 Read chan-
nel one modulate wave parameters of which STATE is OFF. C1:MDWV?
Return:
C1:MDWV STATE, OFF
Set channel one FM frequency to 1000Hz
C1:MDWV FM, FRQ, 1000
Set channel one carrier shape to SINE.
C1:MDWV CARR, WVTP, SINE
Set channel one carrier frequency to 1000 Hz.
C1:MDWV CARR, FRQ,1000
RELATED COMMANDS ARWV, BTWV, SWWV, BSWV
2.15 Sweep Wave Command
Description Sets or gets sweep parameters.
Command Syntax <channel>:SWeepWaVe <parameter>
Common Command Introduction 14
<channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter>={a parameter from the table below}
2.15.1 Paramters
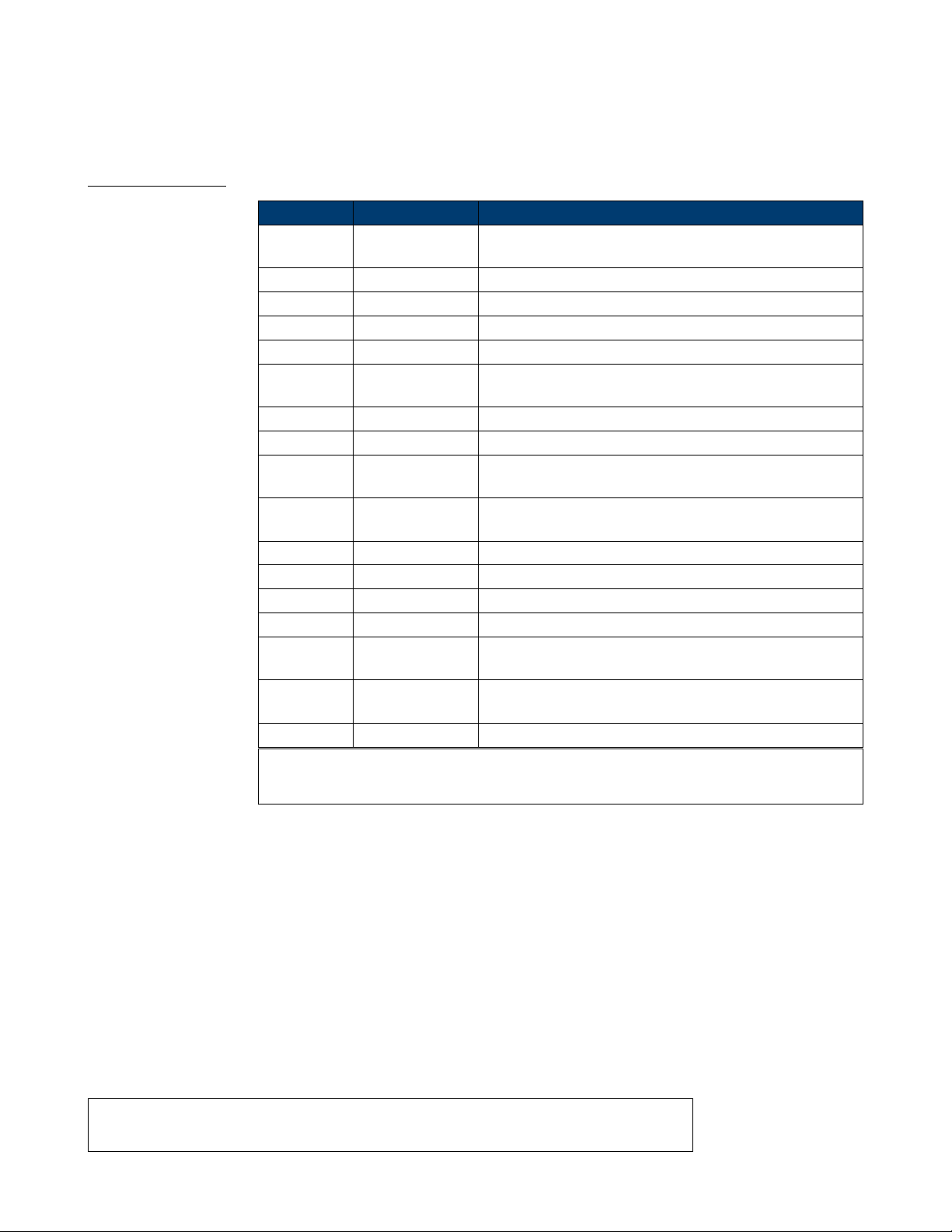
Parameters Value Description
STATE <state> Turn on or o sweep. Note: if you want to set or read
other parameters you must set STATE to ON at rst.
TIME <time> Value of sweep time.
STOP <stop frequency> Value of stop frequency.
START <start frequency> Value of start frequency.
TRSR <trigger src> Trigger source.
TRMD <trigger mode> State of trigger output. If TRSR is EXT, the parameter is
invalid.
SWMD <sweep mode> Sweep style.
DIR <direction> Sweep direction.
EDGE <edge> Value of edge. Only when TRSR is EXT, the parameter is
valid.
MTRIG <manual trigger> Make a manual trigger. Only when TRSR is MAN, the
parameter is valid.
CARR,WVTP <wave type> Carrier type.
CARR, FRQ <frequency> Value of carrier frequency.
CARR, AMP <amplitude> Value of carrier amplitude.
CARR, OFST <oset> Value of carrier oset.
CARR, SYM <symmetry> Value of carrier symmetry, Only Ramp can set this
parameter.
CARR,DUTY <duty> Value of carrier duty cycle. Only Square can set this
parameter.
CARR,Phase <phase> Value of carrier phase.
Note: If carrier is Pulse or Noise you can’t turn on sweep.
If you want to set CARR and STATE, the rst parameter has to be one of them.
where:
<state>={ON, OFF}
<time>={Default unit is "S". Value depends on the model.} <stop frequency> ={the same
with basic wave frequency}
<start frequency> ={the same with basic wave frequency}
<trigger src>={EXT, INT, MAN}
<trigger mode>={ON, OFF}
<sweep mod>={LINE, LOG}
<direction>={UP, DOWN}
<edge>={RISE, FALL} <wave type>={SINE ,SQUARE, RAMP, ARB}
<frequency> ={Default unit is "Hz". Value depends on the model.}
<amplitude> ={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<oset> ={Default unit is "V", Value depends on the model.}
<duty>={0% to 100%.}
<symmetry>={0% to 100%}
Note: There are some parameters Value depends on the model, You can read version
datasheet.
Query Format <channel>:SWeepWaVe? <channel>={C1, C2}

Common Command Introduction 15
Query Response <parameter> ={Return all parameters of the current sweep wave.}
Example Set channel one sweep time to 1 S.
C1:SWWV TIME, 1
Set channel one sweep stop frequency to 1000 Hz.
C1:SWWV STOP, 1000
Read channel one sweep parameters of which STATE is ON.
C2:SWWV?
Return:
C2:SWWV STATE, ON, TIME, 1S, STOP, 100HZ, START,
100HZ, TRSR, MAN,TRMD, OFF, SWMD, LINE, DIR, UP,
CARR, WVTP, SQUARE,
FRQ, 1000HZ, AMP, 4V, OFST, 0V, DUTY, 50, PHSE, 0
Read channel two sweep parameters of which STATE is OFF.
C2:SWWV?
Return:
C2:SWWV STATE, OFF
2.16 Burst Wave Command
Description Sets or gets burst wave parameters.
Command Syntax <channel>={C1, C2} <parameter>={a parameter from the table below}
Note: If you want to set CARR and STATE, the rst parameter has to one of them
where: <state>={ON, OFF}
<period>={Default unit is “S”. Value depends on the model.}
<start phase>={0 to 360}
<gate ncycle>={GATE, NCYC}
<trigger source>={EXT, INT, MAN}
<delay>={Default unit is "S", Value depends on the model.}
<polarity>={NEG, POS}
<trig mode >={RISE, FALL, OFF} <edge>={RISE, FALL} <circle time> ={Value depends
on the Model (“INF” means innite).}
<wave type>={SINE ,SQUARE, RAMP, PULSE, NOISE, ARB}
<frequency> ={Default unit is "HZ". Value depends on the model.}
<amplitude>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<oset>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<duty>={0% to 100%.}
<symmetry> ={0% to 100%}
<phase>={0 to 360}
< standard deviation >={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the
model.}
<mean>={Default unit is "V". Value depends on the model.}
<width> ={Max_width < (Max_duty * 0.01) * period and
Min_width > (Min_duty * 0.01) * period.}
<rise>={Value depends on the model.}
<fall>={Value depends on the model.}
<delay>={Default unit is “S”.}
Note: There are some parameters Value depends on the model, You can read version
datasheet to get specic parameters.
Common Command Introduction 16
2.16.1 Paramters
Parameters Value Description
STATE <state> Turn on or o burst. Note: If you want to set orread
other parameters of burst, you must set state to ON
at rst. And when trigger source is EXT, you can’t
set it.
PRD <period> Value of burst period. When carrier is NOISE wave,
you can’t set it.
STPS <start phase> Start phase of carrier. When carrier is NOISE or
PULSE wave, you can’t set it.
GATE_NCYC <gate Ncycle> Set the burst mode to GATE or NCYC. When ca
rrier is NOISE, you can’t set it.
TRSR <trigger source> Set the trigger source.
DLAY <delay> Value of delay. When carrier is NOISE wave, you
can’t set it. When NCYC is chosen you can set it.
PLRT <polarity> Value of polarity. When GATE is chosen you can set
it. When carrier is NOISE, it is the only parameter.
TRMD <trig mode> Value of trigger mode. When carrier is NOISE wave,
you can’t set it. When NCYC is chosen you can set
it. When TRSR is set to EXT, you can’t set it.
EDGE <edge> Value of edge. When carrier is NOISE wave, you
can’t set it. When NCYC is chosen and TRSR is set
to EXT, you can set it.
TIME <circle time> Value of Ncycle number. When carrier is NOISE
wave, you can’t set it. When NCYC is chosen you
can set it.
MTRIG <manual trig> Manual trigger. When TRSR is set to MAN, it can
be set.
CARR,WVTP <wave type> Value of carrier type.
CARR, FRQ <frequency> Value of carrier frequency
CARR, AMP <amplitude> Value of carrier amplitude.
CARR, OFST <oset> Value of carrier oset.
CARR, SYM <symmetry> Value of symmetry. Only Ramp can set this
parameter.
CARR,DUTY <duty> Value of duty cycle. Only Square or Pulse can set
this parameter.
CARR, PHSE <phase> Value of carrier phase.
CARR, RISE <rise> Value of rise edge. Only when carrier is Pulse, the
Value is valid.
CARR, FALL <fall> Value of fall edge. Only when carrier is Pulse, the
Value is valid.
CARR,STDEV <standard deviation > Value of standard deviation. Only when carrier is
Noise, the Value is valid.
CARR,MEAN <mean> Value of mean. Only when carrier wave is Noise, the
Value is valid.
CARR,DLY <delay> Value of delay. Only whencarrier is Pulse, the
parameter is valid

Common Command Introduction 17
Query Format <channel>:BursTWaVe? <parameter>
<channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter>=<period>……
Query Response
<channel>:BTWV <type>,<state>,<period>……
Example Set channel one burst period to 1S.
C1:BTWV PRD, 1
Set channel one burst delay to 1s C1:BTWV DLAY, 1 Set channel one burst to innite C1:BTWV
TIME, INF
Read channel two burst parameters of which STATE is ON.
C2:BTWV?
Return:
C2:BTWV STATE,ON,PRD,0.01S,STPS,0,TRSR,INT,
TRMD,OFF,TIME,1,DLAY,2.4e-07S,GATE_NCYC,NCYC,
CARR,WVTP,SINE,FRQ,1000HZ,AMP,4V,OFST,0V,PHSE,0
Read channel two burst parameters of which STATE is OFF.
C2:BTWV?
Return:
C2:BTWV STATE, OFF
2.17 Parameter Copy Command
Description Copies parameters from one channel to another.
Command Syntax ParaCoPy <destination channel>, <src channel>
<destination channel>={C1, C2}
<src channel>={C1, C2}
Note: the parameters C1 and C2 must be set to the device together.
Example Copy parameters from channel one to channel two.
PACP C2, C1
Related Commands ARWV, BTWV, MDWV, SWWV, BSWV
2.18 Arbitrary Wave Command
Description Sets and gets arbitrary wave type.
Command Syntax <channel> ARWV(ArbWaVe) INDEX,<value1>, NAME,<value2>
<channel>={C1, C2}
<value1>: the table below shows what the index number mean.)
< value2>: see table below.
Query Format <channel>:ARbWaVe?
<channel>={C1, C2}
Query Response <channel>:ARWV <index>
Example Set StairUp arbitrary wave output by index.
C1:ARWV INDEX, 2
Read system current wave.
ARWV?
Return:
ARWV INDEX,2,NAME,StairUp

Common Command Introduction 18
Set Cardiac arbitrary wave output by name.
ARWV NAME, Cardiac
2.18.1 Notes:
Index Name Index Name Name Index Name Index
0 Sine 12 Logfall 24 Gmonopuls 36 Triang
1 Noise 13 Logrise 25 Tripuls 37 Harris
2 StairUp 14 Sqrt 26 Cardiac 38 Bartlett
3 StairDn 15 Root3 27 Quake 39 Tan
4 Stairud 16 X^2 28 Chirp 40 Cot
5 Ppulse 17 X^3 29 Twotone 41 Sec
6 Npulse 18 Sinc 30 Snr 42 Csc
7 Trapezia 19 Gaussian 31 Hamming 43 Asin
8 Upramp 20 Dlorentz 32 Hanning 44 Acos
9 Dnramp 21 Haversine 33 Kaiser 45 Atan
10 Exp_fall 22 Lorentz 34 Blackman 46 Acot
11 Exp_rise 23 Gauspuls 35 Gausswin 47 Square
Note: About the table: This table is just an example, the index may depend on the model,
you can execute “STL?” command to get them accurately.
2.19 Sync Command
Description Sets synchronization signal.
Command Syntax <channel>:SYNC <parameter>
<channel>={C1, C2}
<parameter>={ON, OFF}
Query Format <channel>:SYNC?
<channel>={C1, C2}
Query Response <channel>:SYNC <parameter>
Example Turn on sync function of channel one.
C1:SYNC ON
Read state of channel one sync.
C1:SYNC?
Return:
C1:SYNC OFF
2.20 Number Format Command
Description Sets or gets number format.
Command Syntax NBFM(NumBer_ForMat) <parameter>
<parameter> ={a parameter from the table below.}

Common Command Introduction 19
Parameters Value Description
PNT <pnt> Point format
SEPT <sept> Separator format
Where:
<pnt>={Dot, Comma}.
<sept> ={Space, O, On}.
Query Format NBFM (NumBer_ForMat)?
Query Response NBFM <parameter>
Example Set point format to DOT.
NBFM PNT, DOT
Set Separator format to ON.
NBFM SEPT,ON
Read number format.
NBFM?
Return:
NBFM PNT, DOT, SEPT, ON
2.21 Language Command
Description Sets or gets system language.
Command Syntax LAGG(LAnGuaGe) <parameter> <parameter>={EN, CH, RU}
Query Format LAGG (LAnGuaGe)?
Query Response LAGG <parameter>
Example Set language to English. LAGG EN Read language LAGG? Return: LAGG EN
2.22 Conguration Command
Description Sets or gets the power-on system setting..
Command Syntax SCFG(Sys_CFG)<parameter> <parameter>={DEFAULT, LAST}
Query Format SCFG (Sys_CFG)?
Query Response SCFG <parameter>
Example Set the power-on system setting to LAST. SCFG LAST
2.23 Buzzer Command
Description Turns on or o the buzzer.
Command Syntax BUZZ(BUZZer) <parameter> <parameter>={ON, OFF}
Query Format BUZZ (BUZZer)?
Query Response BUZZ <parameter>
Example Turn on the buzzer. BUZZ ON
Common Command Introduction 20
2.24 Screen Save Command
Description Turns o or sets screen save time (default unit is minutes).
Command Syntax SCSV (SCreen_SaVe) <parameter> <parameter>={OFF, 1, 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 300}
Query Format SCSV (SCreen_SaVe)?
Query Response SCreen_SaVe <parameter>
Example Set screen save time to 5 minutes. SCSV 5 Read the current screen save time. SCreen_SaVe?
Return: SCSV 5MIN
2.25 Clock Source Command
Description Sets or gets the clock source.
Command Syntax ROSC (ROSCillator) <parameter> <parameter>={INT, EXT}
Query Format ROSC (ROSCillator)?
Query Response ROSC <parameter>
Example Set internal time base as the clock source. ROSC INT
2.26 Frequency Counter Command
Description Sets or gets frequency counter parameters.
Command Syntax <parameter>={a parameter from the table below}
Parameters Value Description
STATE <state> State of frequency counter.
FRQ <frequency> Value of frequency. Can’t be set.
PW <position width> Value of positive width. Can’t be set.
NW <negative width> Value of negative width. Can’t be set.
DUTY <duty> Value of duty cycle. Can’t be set.
FRQDEV <freq deviation> Value of freq deviation. Can’t be set.
REFQ <ref freq> Value of reference freq.
TRG <triglev> Value of trigger level.
MODE <mode> Value of mode.
HFR <HFR> State of HFR.
where: < state >={ON, OFF}
<frequency>={Default unit is "Hz". Value range depends on the model.}
< mode >={AC, DC}
<HFR>={ON, OFF}
Query Format FCNT (FreqCouNTer)?
Query Response FCNT < state ><frequency><duty><ref freq><triglev>
<position width><negative width> <freq deviation><mode><HFR>
Example Turn frequency counter on:
FCNT STATE,ON
Set reference freq to 1000Hz:
FCNT REFQ,1000
Other manuals for 4060B Series
1
Table of contents
Other B+K precision Laboratory Equipment manuals



















