BrickElectric BEM11000 User manual

www.BrickElectric.com
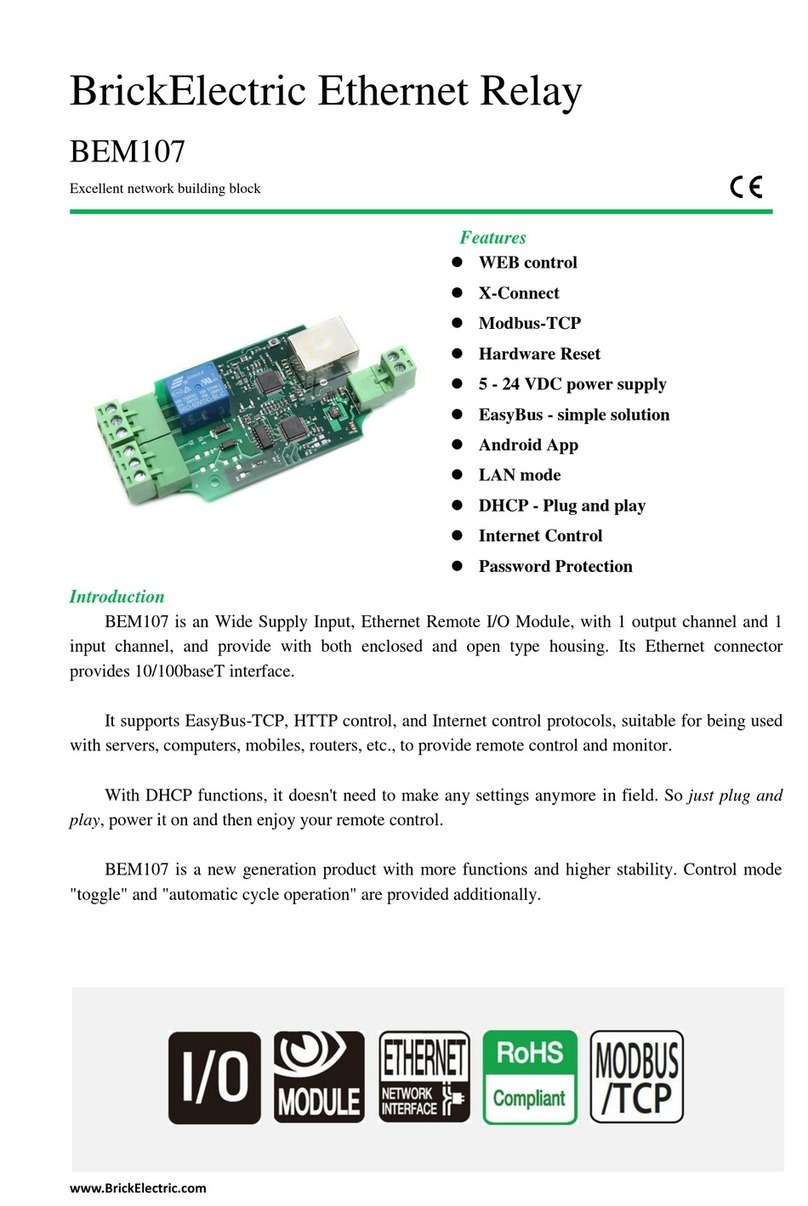
BrickElectric Ethernet I/O
BEM11000
Excellent network building block
Features
⚫WEB control
⚫Modbus-TCP
⚫X-Connect
⚫Hardware Reset
⚫IEEE 802.3at / 802.3af POE Compatible
⚫EasyBus - simple solution
⚫Windows Desktop App
⚫LAN mode
⚫DHCP / DNS
⚫Password Protection
⚫2 CH Relay Outputs
⚫SNMP V1 / V2C
Introduction
BEM11000 is POE Supply Input, Ethernet Remote I/O Module, with 2 output Relays channels
remote control module. Its Ethernet connector provides 10/100baseT interface.
It supports EasyBus –simple solution, HTTP, SNMP, Auto ping and Modbus-TCP control
protocols, suitable for being used with servers, computers, mobiles, routers, etc., to provide remote
control and monitor.
With DHCP / DNS functions, it can be configured together with servers very flexible.
BEM11000 is a new generation product with more functions and higher stability.

www.BrickElectric.com
Table of Contents
1. Device Overview............................................................................................................................3
1.1 General Ratings ...................................................................................................................3
1.2 Connection Diagram............................................................................................................3
2. Specifications ................................................................................................................................3
2.1 Recommended Operating Conditions.................................................................................3
2.2 Default Software Settings....................................................................................................4
3. Easy Start.......................................................................................................................................5
3.1 HTTP Mode..........................................................................................................................5
3.2 LAN Mode............................................................................................................................6
4. General Functionality....................................................................................................................7
4.1 Basic Network Communications .........................................................................................7
4.2 Save Parameters..................................................................................................................7
4.3 Reboot.................................................................................................................................7
4.3 DHCP Function ....................................................................................................................8
4.4 Static IP Address..................................................................................................................8
4.5 Relay outputs control..........................................................................................................9
4.7 Http port setting................................................................................................................11
4.8 Hardware reset button......................................................................................................12
4.9 Identification & customized information ..........................................................................12
4.10 Easybus Server/Client Mode ...........................................................................................13
5. Auto ping and reboot mode........................................................................................................17
6. X-Connect....................................................................................................................................23
6.1 X-Connect Map Setting......................................................................................................23
6.2 X-Connect Map Parameter List..........................................................................................24
7. Modbus-TCP................................................................................................................................26
8. SNMP...........................................................................................................................................27
8.1 SNMP commands example................................................................................................27
9. Program Reference......................................................................................................................28
9.1 Easybus Specifications.......................................................................................................28
10. Support & Contact us................................................................................................................33

www.BrickElectric.com
1. Device Overview
1.1 General Ratings
Power Consumption
3W max.
Operation Temperature
-30℃to +85℃
Module Size
91mm x 53mm x 18mm
Weight
-
1.2 Connection Diagram
Fig. 1.1
2. Specifications
2.1 Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameters
At T = 25℃, unless otherwise specified.
Symbol
Values
Unit
Min.
Typ.
Max.
POE Supply Voltage (IEEE 802.3af/at)
Vs
44
48
57
V
Relay Rating
-
250VAC/10A
-
125VAC/10A
24VDC/10A
12VDC/10A

www.BrickElectric.com
2.2 Default Software Settings
Default Settings
⚫IP Setting:
IP address: 192.168.1.105
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.1
DHCP: disable
⚫Latest Firmware Version
V100.0-02
You can download latest firmware for
free.
⚫HTTP function
State: Enable
Port: 80
⚫TCP function
State: Enable
Port: 5000

www.BrickElectric.com
3. Easy Start
A Practical step-by-step operation guide for starters
This part is a step-by-step tutorial explaining how to start with BEM11000. We'll not discuss too
much details here. The only idea here is to make it work by minimum steps. For more
information, please refer to later chapters.
3.1 HTTP Mode
1. Connect BEM11000 with your routers or computer via a standard Ethernet POE cable. (see
fig.1.1 at page 2)
2. Open any Browser, for example Chrome is used here as demonstration. Please enter URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[45]=2. Relay channel 1 will be toggled, and a message will be
returned to your browser. Congratulations!

www.BrickElectric.com
3.2 LAN Mode
1. Connect BEM module with your routers or computer by Ethernet POE cable. (see fig.1.1 at
page 2)
2. Open any TCP test tool (if you don't have any, or you don't know what a TCP test tool is, you
can use BE-Manager, it is within our software package). Open it and see the following Fig.1.2:
Fig.1.2
3. Click "Connect" button, and wait for module connected. Then, it is able control the relay
module. Click "CH1 OFF" button, and the relay channel 1 will be switched on. See Fig.1.3
Fig.1.3

www.BrickElectric.com
4. General Functionality
4.1 Basic Network Communications
The main method of communication to BEM11000 is a standard Ethernet communication.
This communication protocol makes use of Network Sockets or HTTP protocol to create
point to point tunnels that data can flow through bi-directionally. In this way, the computer
that is controlling the relay can send commands and shortly thereafter receive the
response through the same Socket/Web Page.
Communications
In most programming languages, all you need to do to open a socket is to import the
appropriate plug-in, build the socket object, and connect the socket using the IP Address
and Port Number of the target device.
MAC Address
You can find the MAC Address of the module at the simple start manual delivered together
with module package. You can also change the MAC address to use your own MAC
address.
4.2 Save Parameters
After power cycle, BEM11000 will lose its parameter modifications if you don't actively
require it to save modified parameters into internal nonvolatile memory. For examples, IP
Address, Gateway address and Net mask.
Assuming module current IPAddress is 192.168.1.105 for all the following commands.
Save parameters
To save parameters:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[28]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[28]=1;
4.3 Reboot
Send the module a restart signal so it will restart itself. Some parameters modifications
are only effective after a reboot or power cycle. Parameters modifications will be lost if
you don't save them before reboot or power cycle operation.
Assuming module current IPAddress is 192.168.1.105 for all the following commands.
Reboot
To reboot device:

www.BrickElectric.com
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[61]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[61]=1;
4.3 DHCP Function
BEM11000 supports both DHCP and static IP Addressing. For communication reliability,
we recommend using a Static IP Address when you feel comfortable doing so. This will
ensure that the device will always be where you expect it to be, when you try to connect to
it.
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and basically means that your
router will assign the first available IP Address in the list of IP Addresses Range to your
device. This technology makes network devices very easy to use, but it is not as reliable
because in certain circumstances it will cause the IP Address it assigns to change. DHCP
mode is recommended when you only use Internet control, or your local software is able
to detect module IP changes.
Assuming module current IPAddress is 192.168.1.105 for all the following commands.
Enable/Disable DHCP
Note: modification only effective after parameter saving and module reboot.
To Enable DHCP:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[0]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[0]=1;
To Disable DHCP and use static IP:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[0]=0
Socket command text:
setpara[0]=0;
4.4 Static IP Address
This technology is the antithesis of DHCP in that it is manually set IP address and does
not dynamically change without direct action. The disadvantage of this method is that, if
done incorrectly, can make the module unreachable through any standard means. This
usually happens when an IPAddress is statically set to an IPAddress outside of the range
of the router, or another device on the network obtains this IP address via DHCP. If this
happens, see the section of this guide titled “Reset Function”. This method is the preferred
and more reliable way to handle network IP Address allocation. For improved reliability,
the IPAddress assigned to this Module should be reserved on your router.

www.BrickElectric.com
To work correctly in static IP address mode, you need to set correct IP address, gateway
address and subnet mask. The following content describes how to modify each of them.
If module is currently in DHCP mode, to set a new static IP address you need to
disable DHCP mode at first. After settings are done, please save parameters and
reboot the device to make it effective.
Assuming module current IPAddress is 192.168.1.105 for all the following commands.
Set static IP Address
Note: modification only effective after parameter saving and module reboot.
To set static IPAddress to 192.168.2.100:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[1]=192
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[2]=168
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[3]=2
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[4]=100
Socket command text:
setpara[1]=192;setpara[2]=168;setpara[3]=2;setpara[4]=100;
Set static Gateway Address
Note: modification only effective after parameter saving and module reboot.
To set static Gateway Address to 192.168.2.1:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[5]=192
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[6]=168
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[7]=2
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[8]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[5]=192;setpara[6]=168;setpara[7]=2;setpara[8]=1;
Set static Net Mask
Note: modification only effective after parameter saving and module reboot.
To set static net mask to 255.255.255.0
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[9]=255
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[10]=255
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[11]=255
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[12]=0
Socket command text:
setpara[9]=255;setpara[10]=255;setpara[11]=255;setpara[12]=0;
4.5 Relay outputs control
In the following contents, assuming current IP Address is 192.168.1.105. If you need to

www.BrickElectric.com
switch different channels please replace parameter index to the value you need. For
example, if you want control ch2, you may replace “setpara[45]” with "setpara[46]".
Normal ON/OFF/TOGGLE
Normal on/off/toggle operation changes the relay output status immediately after receiving
commands. No timing features included.
Switches
To switch off ch1 output:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[45]=0
Socket command text:
setpara[45]=0;
To switch on ch1 output:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[46]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[46]=1;

www.BrickElectric.com
To toggle (opposite to previous status) ch1 output:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[45]=2
Socket command text:
setpara[45]=2;
Read Switch Mode
Read current relay output status for feedback control. Module will return the current status
in web content or socket text, depending on how do you send the command.
To read relay ch1 current status:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/getpara[45]=1
Socket command text:
getpara[45]=1;
4.7 Http port setting
In default conditions, HTTP port is always 80 if you enter directly in web browser a URL
without any additional parameters. But in some applications different port number is
needed for port forwarding or any other reasons. For example, you can force your web
browser to access http content at port 8080, to do so you need to enter http://url:8080.
This module is able to customize http access port to realize such functions. In the
following contents, assuming current IPAddress is 192.168.1.105.
Change Http Port
To change http port to 8080:
Web access URL:

www.BrickElectric.com
http://192.168.1.105/ webport=8080
Socket command text:
webport=8080;
4.8 Hardware reset button
Hardware reset button is used for situations when you want to reset the device to factory
settings. For example, if you set incorrect IP Address and the device is no longer
detectable in your network. Two different level of reset are provided in this module.
Level-1 only reset parameters, i.e. network settings, time settings and so on, while Level-2
will reset on-chip app, i.e. for firmware updating/reload.
Hardware reset Level-1 (Parameter reset)
To reset parameters, press the hardware reset button in above pictures until green and
red LEDs are both on, then release the button. Module will set all parameters to their
default values.
Hardware reset Level-2 (Firmware update/reload)
To update firmware, press the hardware reset button in above pictures until green and red
LEDs are both on, then continue to press the button for 10 seconds. Module will erase its
firmware and try to download latest firmware from Internet. Please connect to internet
when you do this operation.
4.9 Identification & customized information
When more than one module is installed in the field, it is necessary to be able to read the
identification information from module, for example serial number. Except for several
pre-defined parameters in system, additionally a device name which can be set by user is
supported.
Read serial number
You can read serial number by reading the sticker on the device, but you can also read
device serial number by communication.
To read device serial number:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[19]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[19]=1;
Customized device name
In some applications, customer may want to set up their own name for better identification
of the device. For this purpose, device name can be customized, with a maximum length
of 15 letters.
To read device name:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[25]=1;

www.BrickElectric.com
Socket command text:
getpara[25]=1;
To change device name to "MYDEVICE":
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[25]=MYDEVICE
Socket command text:
setpara[25]=MYDEVICE;
Read device type
you can read device type by communication, for the purpose of better identification the
device.
To read device type:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[22]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[22]=1;
Read device firmware version
you can read device firmware version by communication, for the purpose of better
identification the device, or diagnosis.
To read device firmware version:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[24]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[24]=1;
4.
10
Easybus Server/Client Mode
EasyBus supports both TCP Server and TCP Client mode, both mode has its application
advantage. Additionally, one configurable communication watchdog can be setup to
monitor the connection between Ethernet relay module and its server/client.
EasyBus Server Mode
By default, relay modules are setup in EasyBus Server Mode. Which means relay
module listens to its port 5000(by default) and by actively connecting to module ip / port
number you can create a TCP connection between your software and relay module.
Unlike http interface, each module supports only one TCP channel at the same time. If
you want to connect to the module by another software, the previous TCP connection has
to be disconnected at first. If you wish to connect multiple software to relay module at the
same time, please reference to HTTP access mode, which allows multiple software
connection at the same time.
To read relay module EasyBus mode:
Web access URL:

www.BrickElectric.com
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[132]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[132]=1;
Tips:
Response 0 means: TCP Server Mode
Response 1 means: TCP Client Mode
Response 2 means: UDP mode
To set relay module to TCP Server Mode:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[132]=0;
Socket command text:
setpara[132]=0;
EasyBus Server Local Port Number
This parameters setup the local listening port number at relay module. To read relay
module EasyBus Server Local Port Number:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[131]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[131]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Server Local Port Number, for example to 5000:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[131]=5000;
Socket command text:
setpara[131]=5000;
EasyBus Client Mode
For applications, it is better to listen at the server and let the relay module be the TCP
client and actively connecting to one server (for example, if DHCP mode is activated).
Each relay module supports only one TCP connection to server, that means only one
server can be connected in the same time.
To set relay module to TCP Client Mode:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[132]=1;
Socket command text:
setpara[132]=1;
EasyBus Client Remote IP address
This parameter setup the remote server IP address for relay module to connect. To read
relay module EasyBus Client Remote IP address:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[117]=1& getpara[118]=1& getpara[119]=1& getpara[120]=1;

www.BrickElectric.com
Socket command text:
getpara[117]=1; getpara[118]=1; getpara[119]=1; getpara[120]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Client Remote IP address, for example to 192.168.1.100:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/
setpara[117]=192&setpara[118]=168&setpara[119]=1&setpara[120]=100;
Socket command text:
setpara[117]=192; setpara[118]=168; setpara[119]=1; setpara[120]=100;
EasyBus Client Remote Port Number
This parameter setup the remote server port number for relay module to connect. To read
relay module EasyBus Client Remote Port Number:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[130]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[130]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Client Remote Port Number, for example to 5000:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[130]=5000;
Socket command text:
setpara[130]=5000;
EasyBus Client DNS Enable
For some applications, the remote server IP address is assigned by DHCP, so to get the
actual address of server, DNS host name is used and in this case a properly setup DNS
service must be provided to locate at the server. An enable bit is necessary to enable this
DNS function, by default this function is disabled. To read relay module EasyBus Client
DNS Enable:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[129]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[129]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Client DNS Enable to be enabled:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[129]=1;
Socket command text:
setpara[129]=1;
EasyBus Client Remote Host Name
For some applications, the remote server IP address is assigned by DHCP, so to get the
actual address of server, DNS host name is used and in this case a properly setup DNS

www.BrickElectric.com
service must be provided to locate at the server. To read relay module EasyBus Client
Remote Host Name:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[128]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[128]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Client Remote Host Name, for example to BrickElectric.com:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[128]=BrickElectric.com;
Socket command text:
setpara[128]=BrickElectric.com;
EasyBus Client Watchdog
In most of networks, router will kill a TCP connection if it is unused for some time period,
an practical time will be 120 seconds. This behavior saves resource for the entire network
but if you really want to keep a long connection between relay module and server, this
behavior will create troubles. Another problem is when the connection is accidently broken,
or the server is unreachable or rebooted at certain moment, the TCP connection will be
lost. You can actively access http interface to reboot the relay module, so it will try to
connect to server again, but you can also use the additional watchdog provided by relay
module, so it will automatically reconnect to the server when no response is received after
some time. The length of this waiting time is also configurable.
If this watchdog is enabled, it is important that your server continuously send
message to the module, otherwise it will automatically disconnect and reconnect
again.
To read relay module EasyBus Client Watchdog:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ getpara[127]=1;
Socket command text:
getpara[127]=1;
To set relay module EasyBus Client Watchdog to enable:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/ setpara[127]=1;
Socket command text:
setpara[127]=1;
Tips:
The higher the value of this parameters, the longer the server un-response time will be
allowed. In good network environment this is recommended so it will save the traffic in
total. For example, setpara[127] = 2, or setpara[127] = 3, 4 … 9999.

www.BrickElectric.com
5. Auto ping and reboot mode
Auto ping is an automatic system for rebooting IP equipment without human intervention.
Auto ping works by running a pre-set commands sequence when a device becomes
unresponsive to IP pings. You can input customized pre-set commands sequence to
realize flexible action according to your requirement, like power cycling or specific timing
functions.
BEM11000 has a 2 independent auto ping channels watchdog which can monitor 2
external servers/controllers on network at the same time. Auto ping monitor channels
are completely independent from relay channels, you can map either one or both relay
channel to each auto ping channel freely.
To use auto ping function, you need to follow these steps:
(1).Assign auto ping mode select, default is fixed IP mode.
(2). Configure Fixed IP or Domain Name, default is your gateway IP.
(3). Configure programmable reboot sequence, default is no action.
(4). Set time between pings, default is 5 seconds.
(5). Set max ping failures before reboot, default is 3 failures.
(6). Set delay time after reboot actions, default is 20 seconds.
(7). Start auto ping function, default is not start.
(1). Auto ping mode select
Two modes are available for auto ping function:
1.Fixed IP Mode(mode 0).
In Fixed IP Mode you can set fixed IP address for auto ping.
2.Name Server Mode(mode 1).
In Name Server Mode you can set a domain name for auto ping, and auto ping function
will get actual IP address from your DNS server.
Change mode to Fixed IP Mode(mode 0) for auto ping:
Auto Ping Channel 1:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[149]=0
Socket command text:
setpara[149]=0;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[150]=0
Socket command text:
setpara[150]=0;

www.BrickElectric.com
Change mode to Name Server Mode(mode 1) for auto ping:
Auto Ping Channel 1:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[149]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[149]=1;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
Web access URL:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[150]=1
Socket command text:
setpara[150]=1;
(2.a) Configure auto ping monitor target IP
If Fixed IP Mode is selected, auto ping target IP(external device's IP) address should be
assigned manually before start auto ping.
Change monitor target IP address to 192.168.1.100.
Auto Ping Channel 1:
Web access URL:
Write:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[101]=192&setpara[102]=168&setpara[103]=1&setpara[104]
=100
Read:
http://192.168.1.105/getpara[101]=192&getpara[102]=168&getpara[103]=1&getpara[104]
=100
Socket command text:
Write: setpara[101]=192;setpara[102]=168;setpara[103]=1;setpara[104]=100;
Read: getpara[101]=192;getpara[102]=168;getpara[103]=1;getpara[104]=100;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
Web access URL:
Write:
http://192.168.1.105/setpara[105]=192&setpara[106]=168&setpara[107]=1&setpara[108]
=100
Read:
http://192.168.1.105/getpara[105]=192&getpara[106]=168&getpara[107]=1&getpara[108]
=100
Socket command text:
Write: setpara[105]=192;setpara[106]=168;setpara[107]=1;setpara[108]=100;
Read: getpara[105]=192;getpara[106]=168;getpara[107]=1;getpara[108]=100;

www.BrickElectric.com
(2.b) Configure auto ping monitor target domain name
If Name Server Mode is selected, auto ping monitor target IP will be assigned by your
DNS server. The target domain name should be set manually before start auto ping.
Change domain name to "www.example.com"
Auto Ping Channel 1:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/setpara[133]=www.example.com
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[133]=any.input.here
Socket command text:
Write: setpara[133]= www.example.com;
Read: getpara[133]= any.input.here;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/setpara[134]=www.example.com
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[134]=any.input.here
Socket command text:
Write: setpara[134]= www.example.com;
Read: getpara[134]= any.input.here;
(3) Configure auto ping programmable reboot sequence
In case of remote IP device becomes unresponsive, auto ping function will run a pre-set
reboot sequence to make a customized reboot action according to your application.
For this function, the following commands are supported to generate a reboot sequence:
1. Programmable mark, for example:
Start program input : program = 1;
Stop program input : program = 0;
2. All switch relay output commands, for example:
Switch on relay channel 1 : k01 = 1;
Switch off relay channel 1 : k01 = 0;
Toggle relay channel 2 : k02 = 2;
And so on...
3. Timing commands, waitms and wait, for example
Wait 10 seconds : wait = 10;
Wait 500 milliseconds : waitms = 500;
For example, in my application I need auto ping to power off the device, and then wait for
5 seconds, and then power it on again. I'm using k01 to supply power to my device, so my
reboot sequence is: k01=0;wait=5;k01=1; and plus the programmable mark(if you don't
insert programmable mark, your sequence will be running immediately rather than saving
into preset program and wait to be triggered)

www.BrickElectric.com
Auto Ping Channel 1:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/program=1&k01=1&wait=5&k01=0&program=0
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[141]=1
Socket command text:
Write: program=1;k01=1;wait=5;k01=0;program=0;
Read: getpara[141]=1;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/program=2&k01=1&wait=5&k01=0&program=0
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[142]=1
Socket command text:
Write: program=2;k01=1;wait=5;k01=0;program=0;
Read: getpara[142]=1;
(4) Set time between pings
This is the time between each "ping" check of the IP address.Auto ping function waits this
amount of time for a valid ICMP response and then send next ICMP message. Available
options are from 1 millisecond to 65535 seconds. Normally 60 seconds should be useful
for most applications.
To setup time you need to set 2 parameters, time unit and time.
Auto Ping Channel 1:
1. To set time unit to millisecond : setpara[45]=0;
2. To set time unit to second : setpara[45]=1;
3. To set time value to 60: setpara[81]=60;
I want to setup time between pings to 60 seconds, for example:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/setpara[45]=1&setpara[81]=60
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[45]=1&getpara[81]=1
Socket command text:
Write: setpara[45]=1;setpara[81]=60;
Read: getpara[45]=1;getpara[81]=1;
Auto Ping Channel 2:
1. To set time unit to millisecond : setpara[46]=0;
2. To set time unit to second : setpara[46]=1;
3. To set time value to 60: setpara[82]=60;
I want to setup time between pings to 60 seconds, for example:
Web access URL:
Write: http://192.168.1.105/setpara[46]=1&setpara[82]=60
Read: http://192.168.1.105/getpara[46]=1&getpara[82]=1
Socket command text:
Table of contents
Other BrickElectric Relay manuals