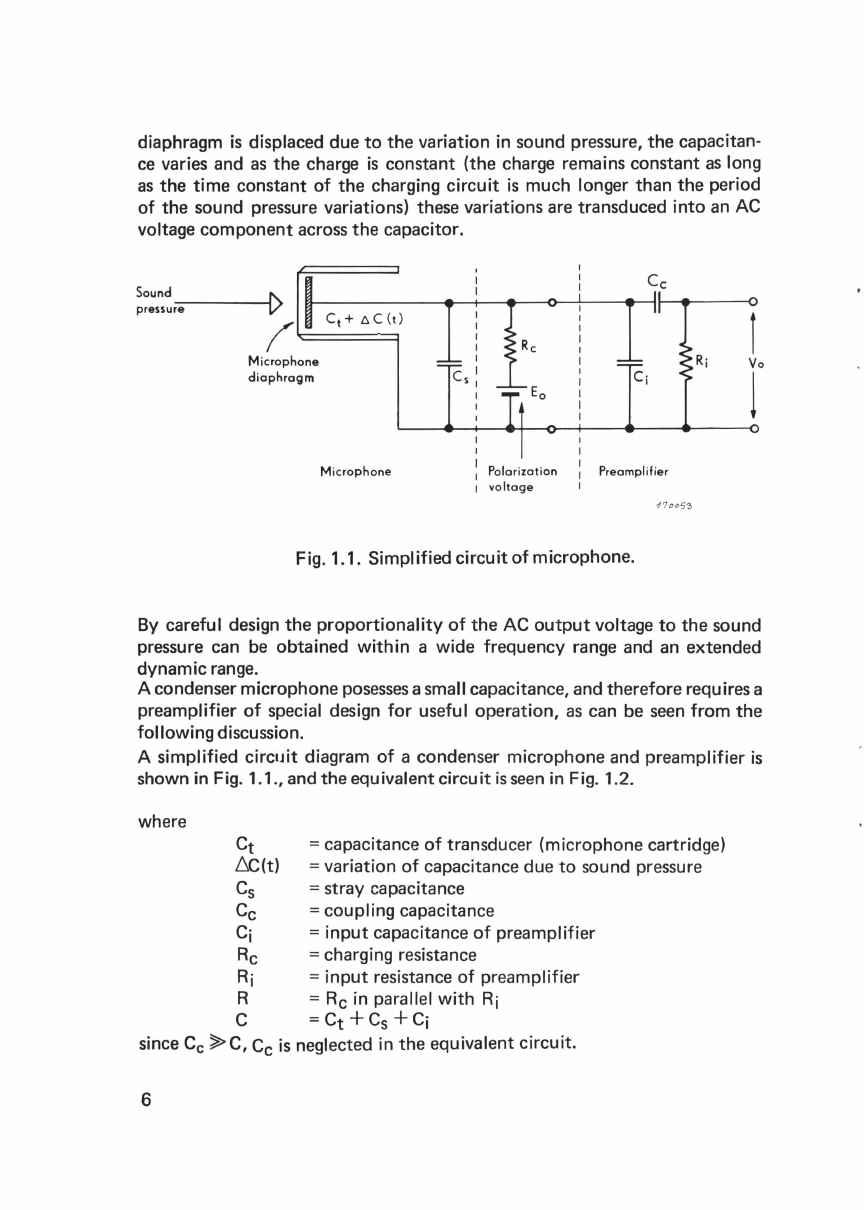
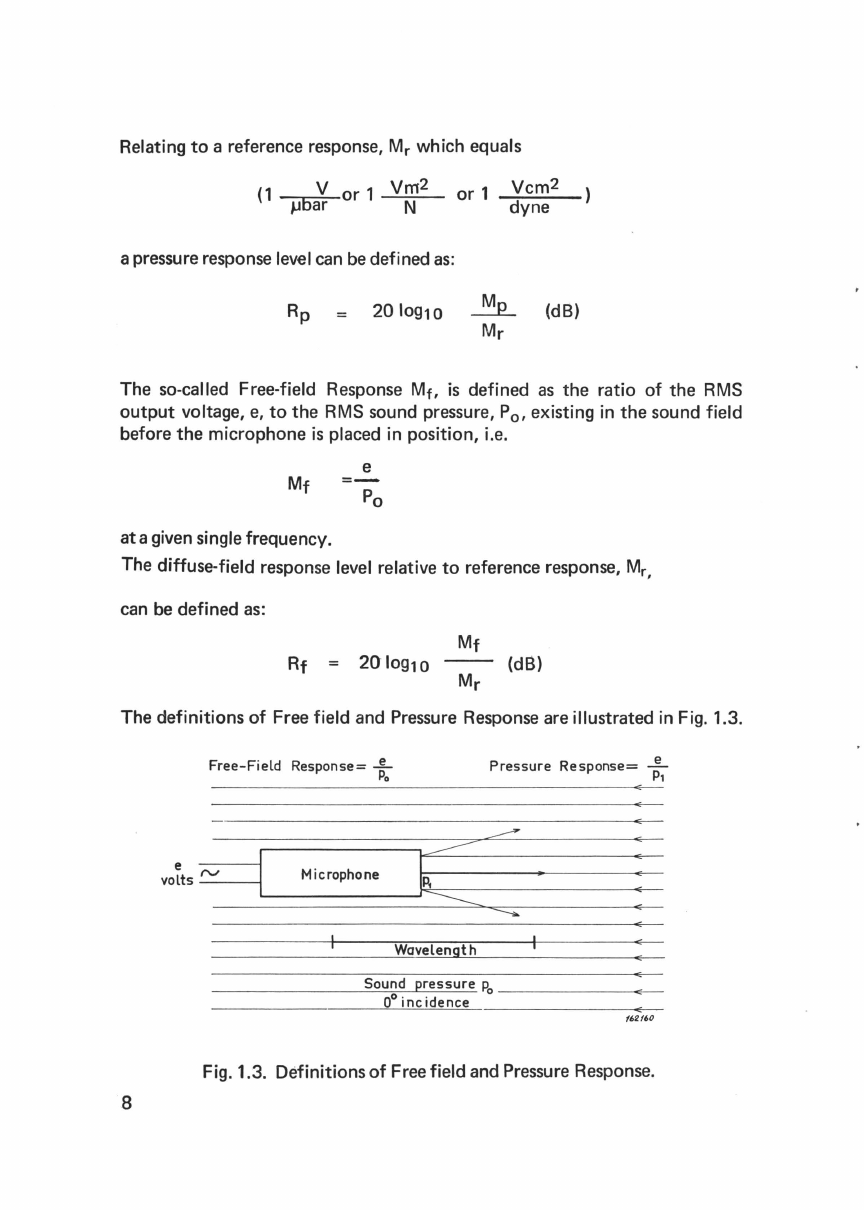
1.
Introduction
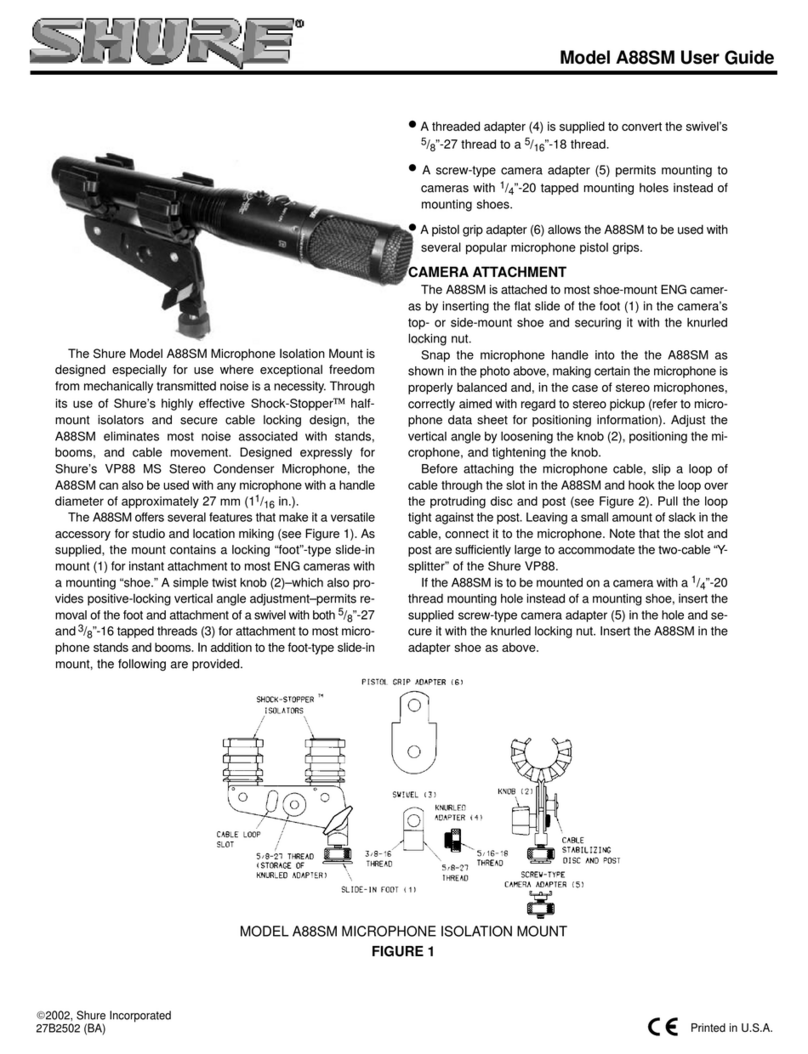
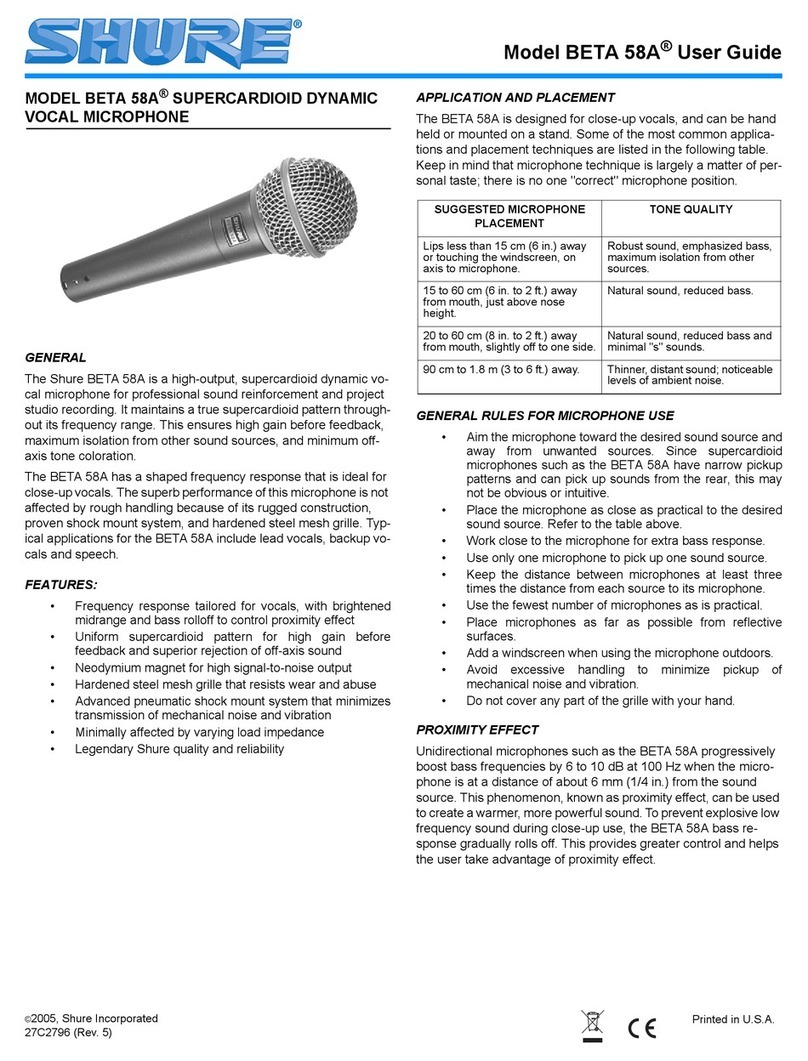
1.1. Purpose
of
the half-inch Condenser Microphone
There
are
many
different
types
of
microphoneand signal conditioners
used
to
measure sound pressure levels. In the
majority
of
cases,
the
condenser micro-
phone
is
the
type
to
be
preferred, since
it
features high
stability
and
flat
frequency characteristics combined
with
reasonably high sensitivity. Itssmall
size minimizes the disturbance
of
the sound field due
to
the
presence
of
the
microphone.
The condenser microphone
type
4148
is
designed
for
precision sound pressure
measurements
wi
th the Precision Sound Level meter 2206 and
needs
only
a
low
polarizationvoltage
of
28 V instead
of
the
norrnal200
V.
Despite
the
low
polarization voltage, a sensitivity about 12.5
mV
per Nfm2
(-38 dB ± 2 dB
re
1 V per
Nfm2)
is
obtained, which
is
comparable
with
that
of
similarly sized microphones needing higher polarization voltages.
Without
seriously affecting
the
frequency response, the sensitivity
can
be
varied
from
12.5
mV
per N/m2
to
60
mV
per Nfm2 simply
by
varying the
polarization voltage between
28
and 120 V DC. The microphone
has
a
flat
frequency response between 4 Hz and
16kHz
and a wide dynamic range. Its
most outstanding feature
is
excellent long-term
stability
under a great range
of
environment
al
conditions.
An
excellent battery driven precision sound measuring system
is
obtained in
conjunction
wi
th a precision sound level meter Type 2206
or
a sound level
meter Type 2205 plus adaptor
UA
0208
or
with
F.E.T.- preamplifier Type
2619 and a measuring voltmeter.
An
extensive
range
of
accessories provides great measuring versatility.
1.2. Principle
of
Condenser Microphone
A capacitive transducer converts energy
from
mechanical
to
electrical form,
or
vice
versa.
The conversion
is
effected
by
mechanically inducing changes in
electrical capacitance between
two
conducting plates separated
by
an
insula-
tor
and detecting the capacitance changes electrically. The condenser micro-
phone
is
a transducer operating on this principle.
It
consists basically
of
a
thin
metal diaphragm mounted in close
proximity
to
a rigid back plate
forming
a capacitor
with
air
as
insulator between the conductors. A
DC
voltage, the so-called polarization voltage, charges the system.
When
the
5