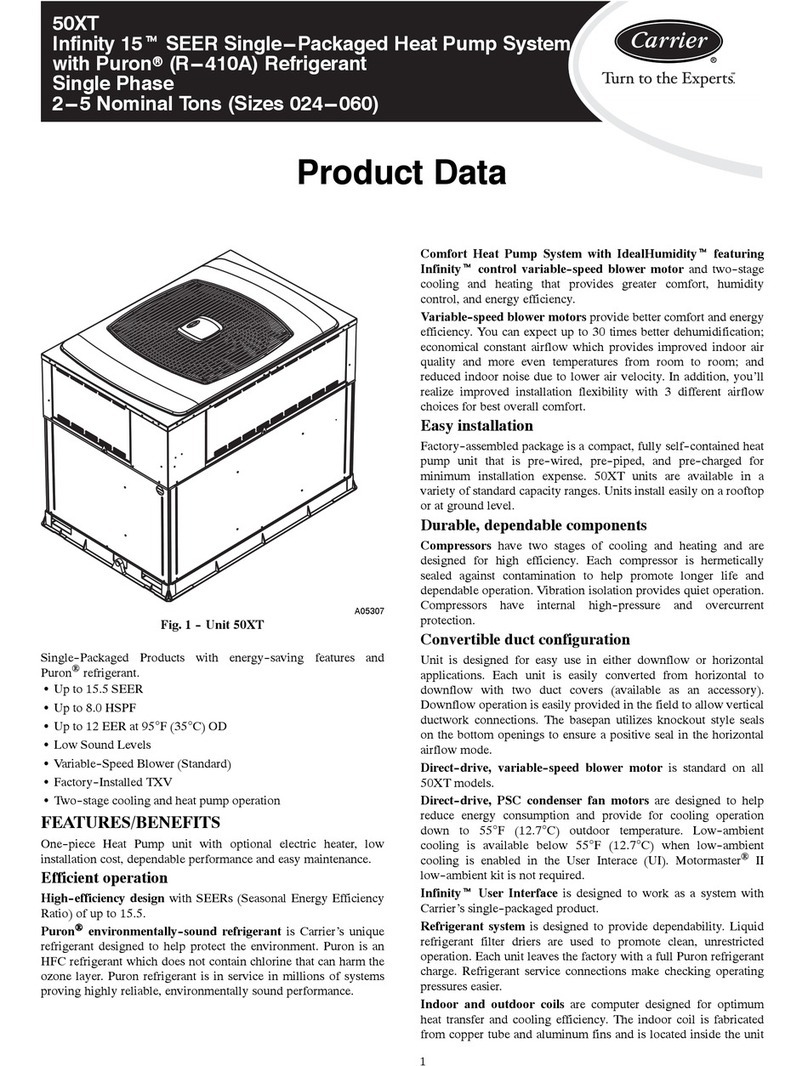
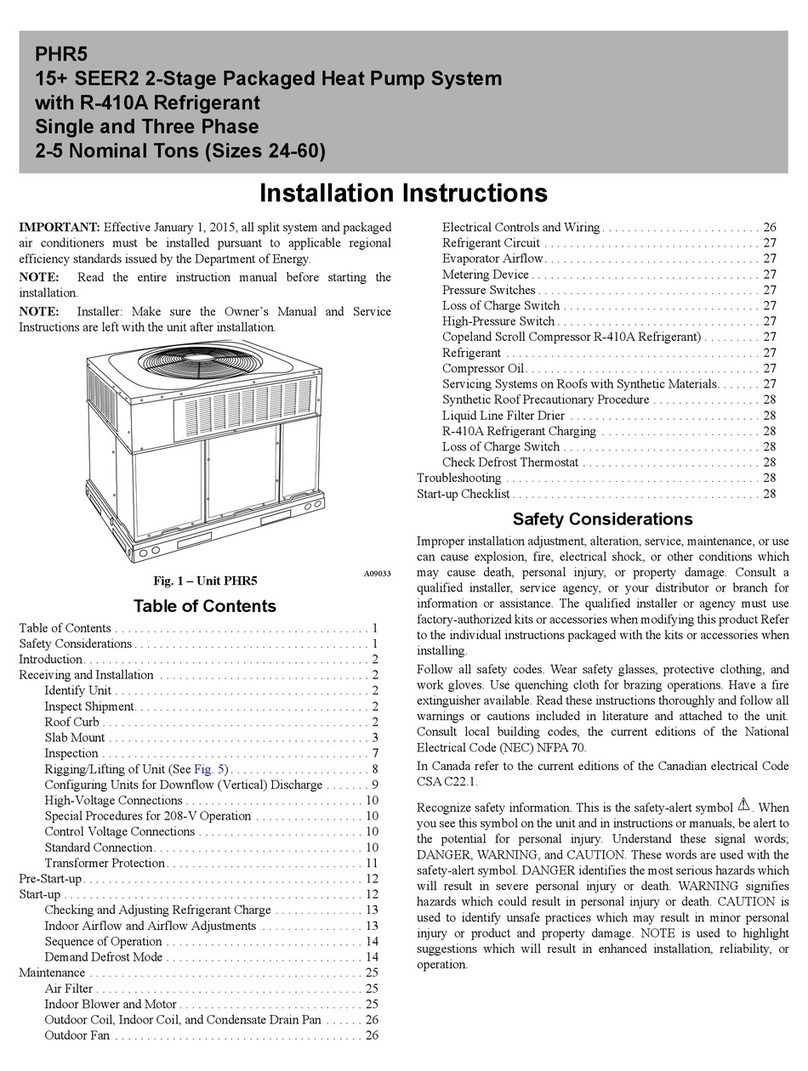
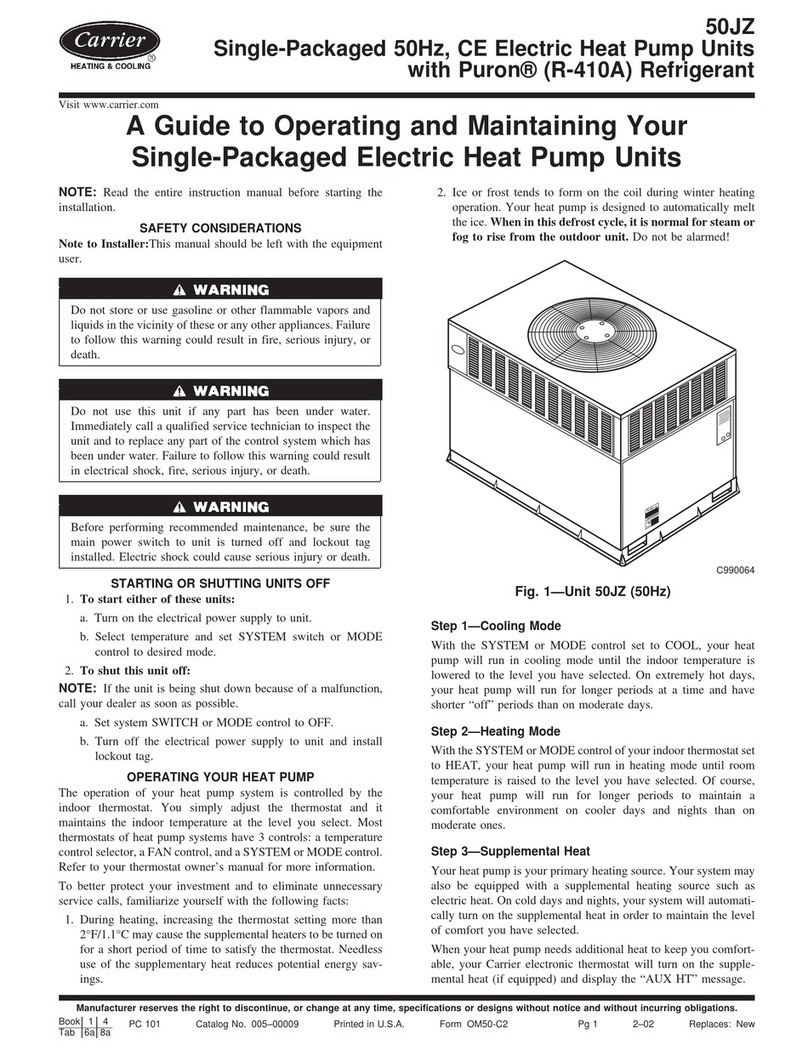
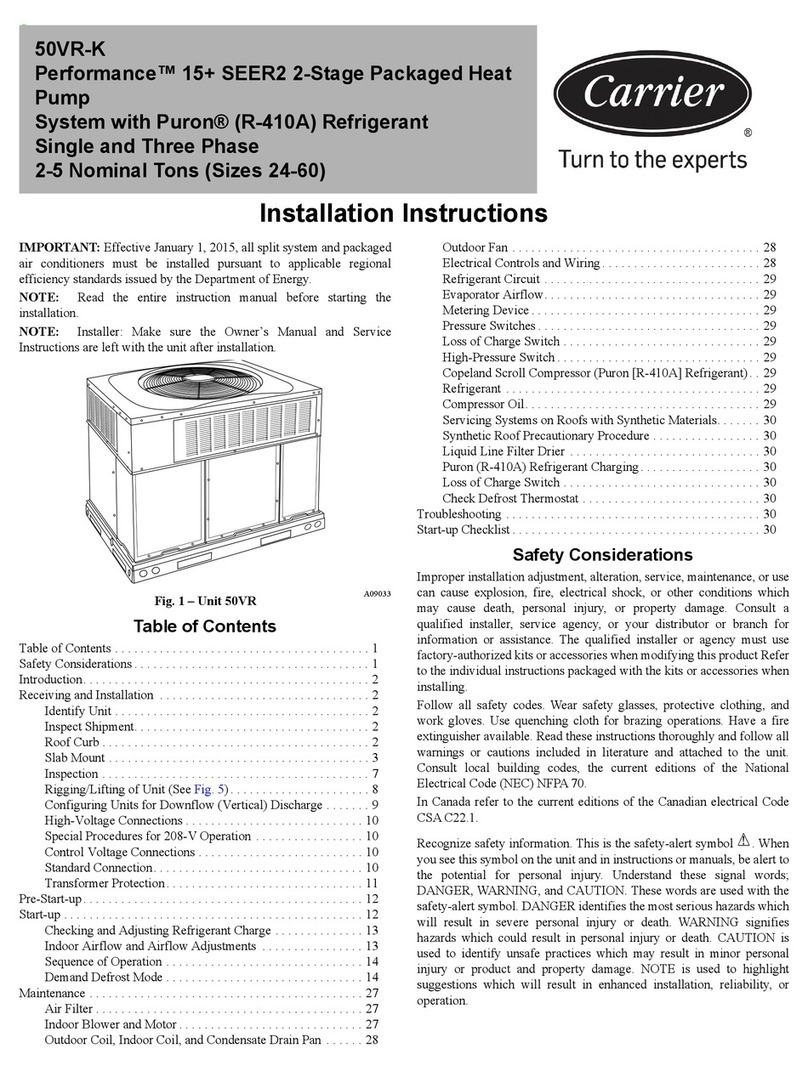
12 - HYDRAULIC CONNECTIONS
AQUASNAP 30WI 700V 800V 900V 1000V 1100V 1200V 1400V 1600V 1800V 2100V 2400V
Chilled water inlet/outlet BCDiameter DN 100 PN 16 -
VICTAULIC DN 125 PN 16 - VICTAULIC DN 150 PN 16
VICTAULIC
Cooling water inlet/outlet
DEDiameter DN 100 PN 16 -
VICTAULIC DN 125 PN 16 - VICTAULIC DN 150 PN 16
VICTAULIC
Hydraulic connections must be made in accordance with the
diagram delivered with the unit. This diagram shows the positions
and dimensions of the water inlets and outlets on the exchangers.
Follow the requirements below when making these connections:
-Ensure the inlet and outlet pipes are connected in the
direction shown on the unit.
-In order to meet the operating conditions (ow rates, pressure
loss), a sizing calculation must be performed. The diameter
of the pipes may therefore be different to that specied on
the exchanger.
-The pipes and tubes should not transmit any axial or radial
forces to the exchangers or any vibrations.
-The water must be analysed and, if necessary, treated (we
recommend contacting a qualied water treatment specialist).
The analysis will reveal whether the water is suitable for use with
the various materials it will come into contact with and prevent the
formation of electrolytic couples:
• 99.9% copper tubes brazed with copper and silver
• Threaded bronze couplings or at steel anges, depending
on the unit model
• Plate heat exchangers and AISI 316 - 1.4401 stainless steel
connections brazed with copper and silver
-The water circuit must have as few bends and horizontal
sections at different levels as possible.
-Install shut-off valves near the water inlets and outlets in order
to isolate the exchangers.
-Install manual or automatic air bleed valves at the high points
of the circuit(s).
-The manual or automatic air bleed valves tted on the
machine are not intended to be used to bleed the rest of the
hydraulic circuit.
-A static pressure of 1 bar must be maintained at all times
(machine and pump off or on) on the pump intake.
-Install drain connections at all circuit low point(s).
-Install the accessories that are essential for any hydraulic
circuit (balancing valves, expansion vessel, safety valve,
thermometer pockets, etc.).
-Insulate the pipes and tubes (after performing leak tests) in
order to reduce heat losses and prevent damage from frost.
-Install heating elements on all pipes that could be exposed
to frost.
-The installer must provide the necessary systems for lling
and draining the energy transfer uid.
-To keep the pressure in the coolant circuit below the intended
operating pressure, avoid introducing static or dynamic
pressure into the circuit.
IMPORTANT:
-To prevent any risk of fouling or damage to the plate heat
exchangers (evaporator and condenser), it is essential to t
a strainer to the water inlets as close as possible to the
exchangers and in a place which is easily accessible for
disassembly and cleaning. The maximum mesh size of this
lter should be 800 μm.
-Flexible couplings must be used on the hydraulic pipework
(evaporator and condenser).
The system pipework must be secured to the wall of the building
and must not place any additional load on the unit.
-Using untreated or incorrectly treated water may cause
corrosion or erosion or the formation of scale, algae or sludge
deposits. CARRIER shall not be held liable for damage
resulting from the use of untreated or incorrectly treated water,
or of saline or brackish water.
When the unit is used as a heat pump, the maximum water
return temperature of the installation will be 55°C. Never
series-connect the condenser with a high-temperature water
network (boiler). Doing so will result in damage.
NOTE: The maximum operating pressure on the water side should
be 10 bar (evaporator and condenser). The water ow sensor is
supplied tted to the unit. Stopping the pumps will automatically
cause the unit to stop to avoid any risk of freezing. The pump
or pumps must be slaved to the refrigeration unit (auxiliary
operation switch of the pump to be wired).If the hydraulic circuit
is drained for a period of more than one month, ll the entire
circuit with nitrogen to prevent any risk of corrosion.
IMPORTANT :
If antifreeze is not added to the circuit and the unit is not operated
during periods of freezing weather, drain the evaporator and the
outside pipes.
10