Source Connections
(Boiler/Tower/Ground)
Control
Wiring
Load Connections (Hot
Water/Chilled Water) Automatic Flow
Regulator
Valve
with Pressure
Temperature Port
..............Ball Valve
,_ with Pressure
emperature Port
e Y Strainer with
Blow Down Valve
/' Power
Disconnect
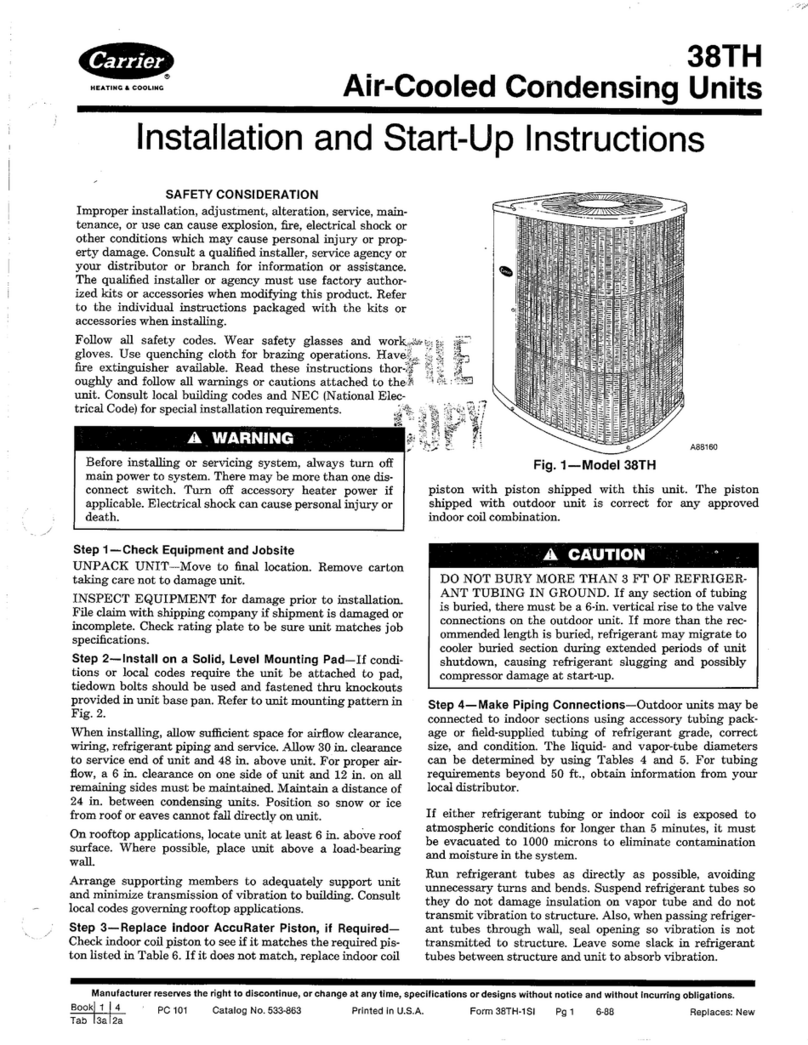
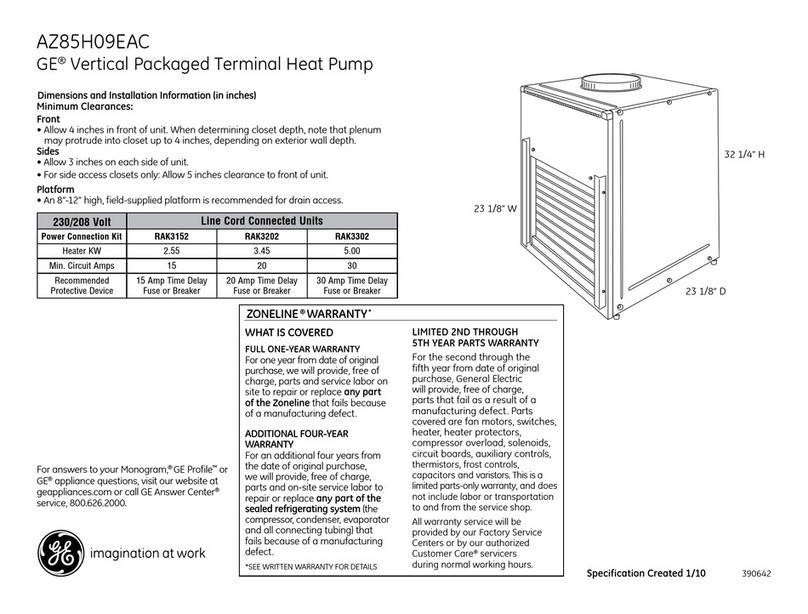
Fig. 3 -- Typical Water Loop System --
Boiler, Tower, or Ground (Sizes 180,360 Shown)
Step 5 EConnect Piping EDepending on the appli-
cation, there are 3 types of WSHP piping systems to choose
from: water loop, ground-water and ground loop. Refer to the
Carrier System Design Manual for additional information.
All WSHP units utilize low temperature soldered female
pipe thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing
and out-of-round leak problems which are typically associated
with high temperature brazed connections. When making pip-
ing connections, consider the following:
• A backup wrench must be used when making screw con-
nections to unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
• Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensa-
tion in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at
temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
• Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may
be subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may
be used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid
galvanic corrosion.
• Units may be manifolded together via top water connects
to get increased temperatures, when piped in series, or
greater capacity, when piped in parallel.
WATER SUPPLY AND QUALITY -- Check water supply.
Water supply should be plentiful and of good quality. See
Table 2 for water quality guidelines.
IMPORTANT: Failure to comply with the above required
water quality and quantity limitations and the closed-
system application design requirements may cause damage
to the robe-in-robe heat exchanger that is not the responsi-
bility of the manufacturer.
In all applications, the quality of the water circulated
through the heat exchanger must fall within the ranges listed in
the Water Quality Guidelines table. Consult a local water treat-
ment firm, independent testing facility, or local water authority
for specific recolranendations to maintain water quality within
the published lhnits.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS -- Water loop applica-
tions usually include a number of units plumbed to a colmnon
piping system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce
air into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination
equipment comprises a major portion of the mechanical room
plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.25 and 3 gpm per ton
of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing,
pressure-temperature (P/T) ports are necessary for temperature
and flow verification.
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consid-
er the following for system piping:
• Piping systems utilizing water temperatures below
50 F require 1/2-in. closed cell insulation on all piping
surfaces to eliminate condensation.
• All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided
due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Teflon* tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize
internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
• Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• The piping system should be flushed prior to operation to
remove dirt and foreign materials from the system.
GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS -- In addition to
complying with any applicable codes, consider the following
for system piping:
• Install shut-off valves for servicing.
• Install pressure-temperature plugs to measure flow and
temperature.
• Boiler drains and other valves should be connected using
a "T" connector to allow acid flushing for the heat
exchanger.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use PVC SCH80 or copper piping material.
NOTE: PVC SCH40 should not be used due to system high
pressure and temperature extremes.
GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS -- Temperatures be-
tween 25 and 110 F and a cooling capacity of 2.25 to 3 gpm of
flow per ton are recolmnended. In addition to complying with
any applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Piping materials should be limited to only polyethylene
fusion in the buried sections of the loop.
• Galvanized or steel fittings should not be used at any
time due to corrosion.
• All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided
due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Pressure-temperature (P/T) plugs should be used to mea-
sure flow of pressure drop.
UNIT LOAD PIPING -- For applications with wide temper-
amre variation such as heating/cooling coils:
• Use piping materials that are rated for the maximum tem-
perature and pressure combination. This excludes PVC
for most heating applications.
• Ensure load water flow in high temperature heating
applications is at least 3 gpm per ton to improve perfor-
mance and reduce nuisance high pressure faults.
• DO NOT employ plastic to metal threaded joints.
• Utilize a pressure tank and air separator vent system to
equalize pressure and remove air.
• Employ an 800-micron particulate strainer in both load
and source plumbing to protect the plate heat exchanger.
Swilmnin_ Pool Hot Tub Applications -- Load heat ex-
changer should be isolated with secondary heat exchanger
constructed of anti-corrosion material in all chlonne/bromine
fluid applications.
Potable Water Applications
• Load coax material should always be vented double
walled for use in potable water systems.
• Ensure load water flow in high temperature heating
applications is at least 3 gpm per ton to improve perfor-
mance and reduce nuisance high pressure faults.
*Teflon is a trademark of E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company.