CommFront User Manual 1
Contents
1.0 INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Features ................................................................................................................................. 3
1.2 Factory Settings ................................................................................................................ 4
1.3 Hardware ............................................................................................................................... 4
1.3.1 Specifications ..............................................................................................................................................4
1.3.2 Connections ...........................................................................................................................................5
1.3.3 LED Indicators............................................................................................................................................5
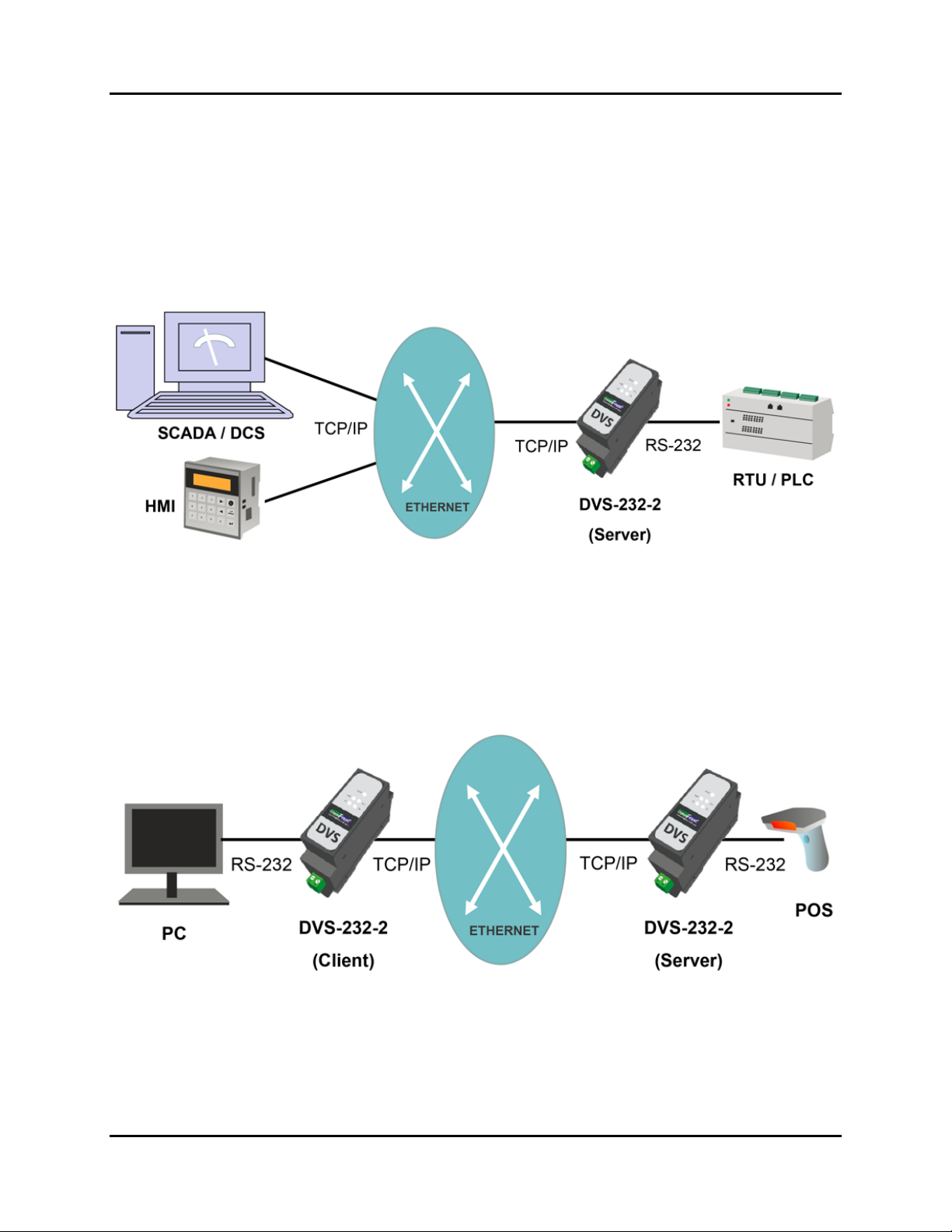
1.4 Typical Applications ........................................................................................................ 5
1.4.1 Device Server..............................................................................................................................................6
1.4.2 Serial over Ethernet.....................................................................................................................................6
1.4.3 Modbus Gateway ........................................................................................................................................7
1.4.4 Modbus Protocol Converter ........................................................................................................................7
1.4.5 Converting RS-232 Network into TCP/IP...................................................................................................8
1.4.6 Remote Control and Monitor ......................................................................................................................9
2.0 SETTING UP THE DEVICE SERVER ................................................................................. 10
2.1 AT Commands (optional) ........................................................................................... 10
2.2 Web Management........................................................................................................... 11
3.0 WEB MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................................ 12
3.1 Logging On.......................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Current Status .................................................................................................................. 12
3.3 Local IP Settings ............................................................................................................. 13
3.4 Serial Port Settings........................................................................................................ 14
3.4.1 COM Port Settings ....................................................................................................................................14
3.4.2 Operating Mode ........................................................................................................................................15
3.4.3 Reset..........................................................................................................................................................21
3.4.4 Link ...........................................................................................................................................................21
3.4.5 Index .........................................................................................................................................................21
3.4.6 RFC2217 ...................................................................................................................................................22
3.5 Advanced Settings ......................................................................................................... 24
3.5.1 Modbus RTU to Modbus TCP ..................................................................................................................24
3.5.2 Heartbeat Packet .......................................................................................................................................24
3.5.3 Registry Packet .........................................................................................................................................25
3.5.4 Short Connection.......................................................................................................................................26
3.5.5 Disable Old Connections (TCP Server) ....................................................................................................26
3.5.6 Clear Cached Serial Data upon TCP/IP Connection .................................................................................27
3.5.7 Allow Settings via Serial Port ...................................................................................................................27
3.6 Preferences............................................................................................................................. 27
3.6.1 Device Name and Web Server Port...........................................................................................................27
3.6.2 User Name and Password..........................................................................................................................28
3.6.3 Maximum Number of Client Connections ................................................................................................28
3.6.4 Auto-Restart Timeout................................................................................................................................29
4.0 TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................................................................... 30