GV48002a_e.doc / Mrz-11 Page 5 / 14
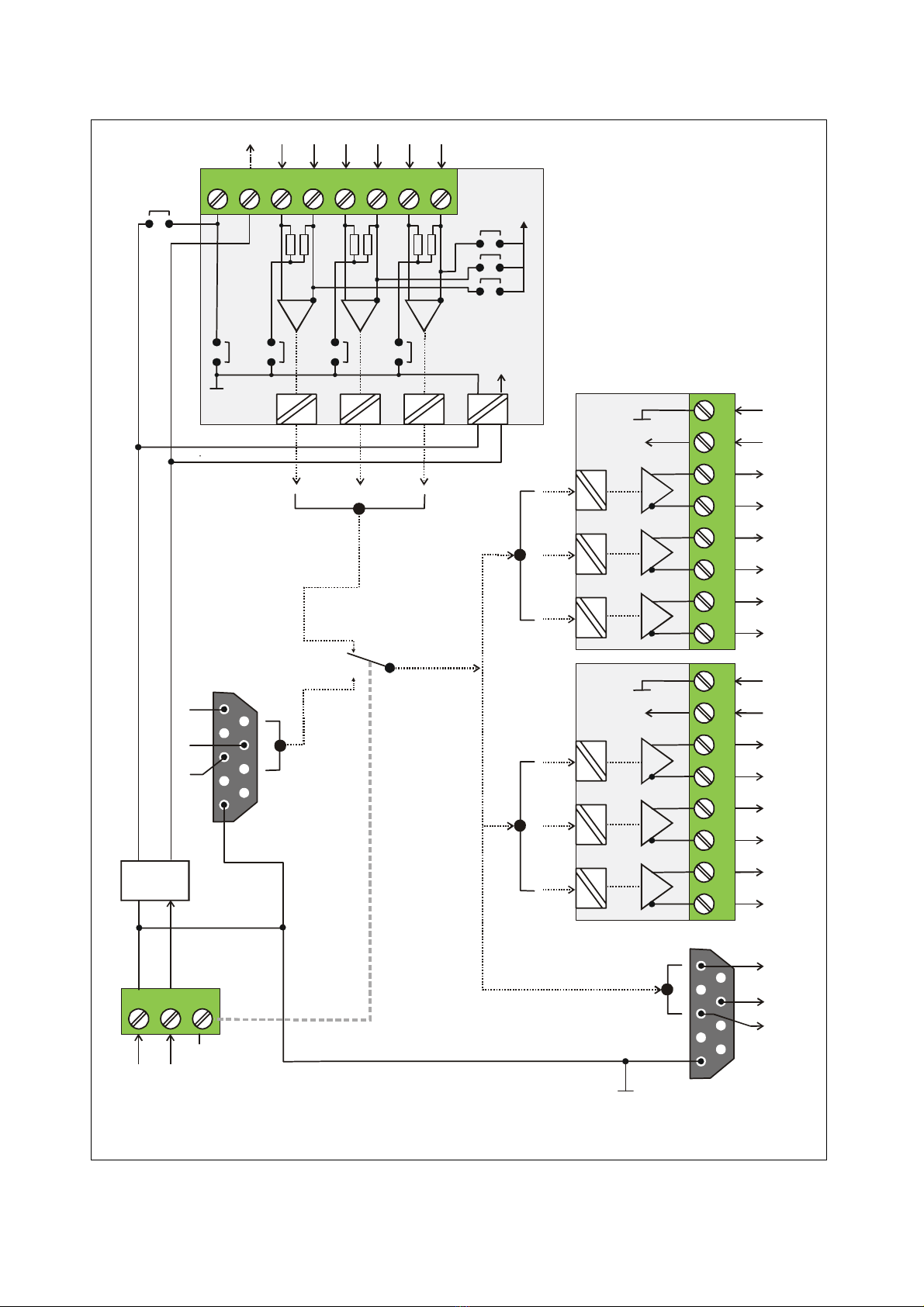
1. Introduction and Block Diagram
GV460, GV461, GV480 and GV481 represent a series of incremental encoder splitters with a
most compact, space-saving design and with most versatile technical features. All models are
fully identical except for the number of output channels (4 or 8 channels) and the system of
potential separation.
Models GV460 and GV461 are lower in price but provide only a 2-circuit potential separation
between the input on one side and the outputs with power supply on the other side.
Models GV480 and GV481 provide total galvanic separation between inputs, the power supply
and all outputs one against each other. This feature, in general, can be most advantageous
with impulse distribution among expanded production lines with adverse conditions of
EMC / grounding / potential shift etc.
The encoder input is switch-selectable for operation with either standard RS422 signals, with
differential TTL or HTL signals or with single-ended HTL encoder signals. All encoder outputs
provide fully isolated push-pull drivers with individual assignment of the output level for each
of the output channels.
Separate cascading ports provide easy cascading of multiple units without loss of regular
encoder outputs. Furthermore, cascaded units allow selection and commutation between
different encoder inputs.
The adjoining block diagrams clearly explain the principle of operation and the potential
conditions between all circuits. For simplification the illustrations show only two of the outputs,
since all other outputs are fully identical.
All units of this series provide an extended range of ambient temperatures for use under
difficult environmental conditions (see Technical Specifications)