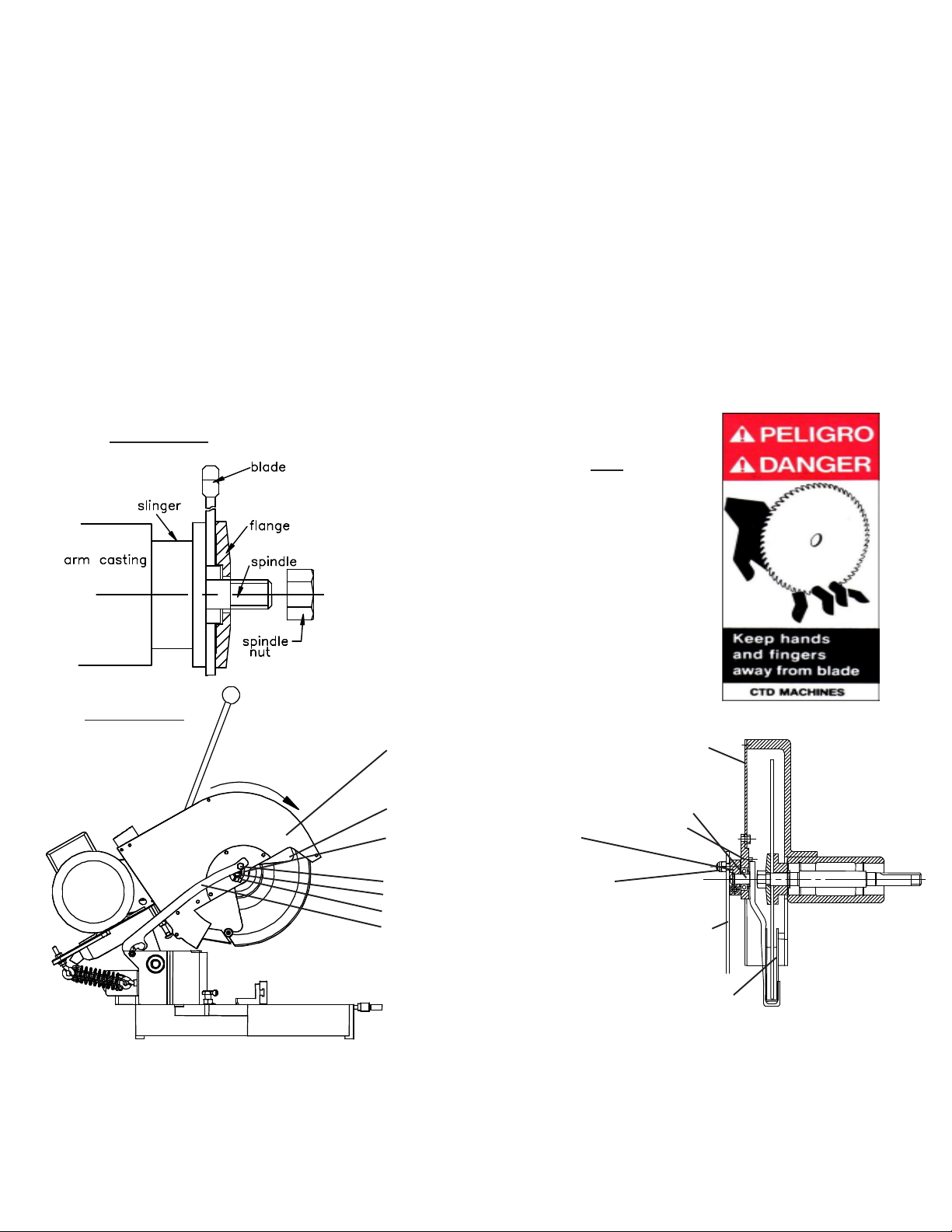
Blade Installation (continued):
1. Remove Spindle Nut, P/N 2B1P36 or 2B1P37 and Outer Flange, P/N 200BM03. If necessary, hold blade
in hand with rag or lower blade into a piece of wood, and loosen spindle nut by pushing down on a 15/16”
wrench.
2. Place blade on spindle with tips pointing down. Make sure Slinger (inner flange), P/N 200BM04, and
blade surface are clean before putting blade on spindle. This is a critical surface and is ground within
.0005 flatness. Any debris or dust will wear this surface. Wipe both surfaces (blade and slinger) with
a clean rag.
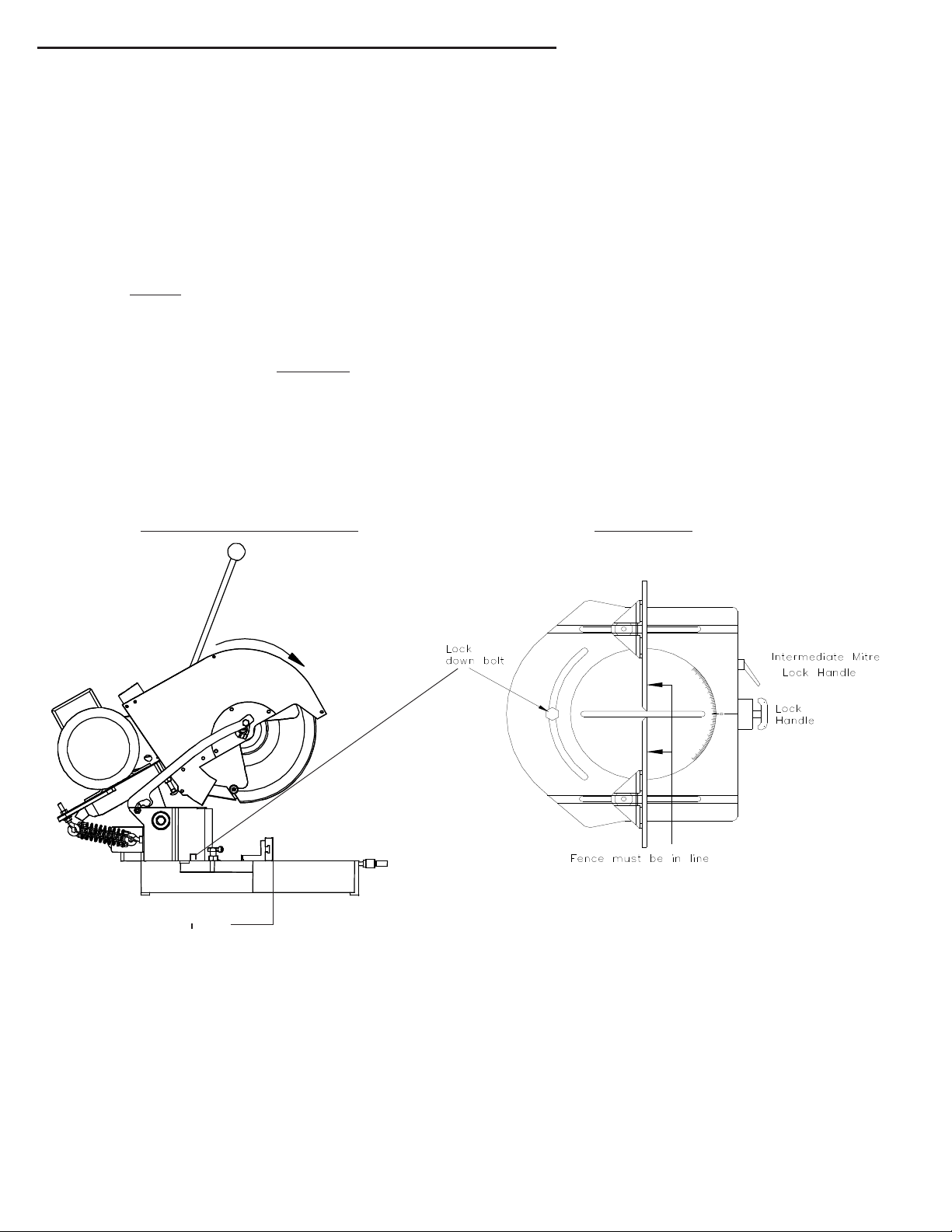
A. The blade must ALWAYS rotate to the rear of the machine on the underside of the blade
(see Diagram “D”). Always check rotation before cutting a piece of material.
3. Replace Outer Flange, P/N 200BM03 and nut as before and tighten (refer to Diagram “C”). Pull up with
15/16” wrench. Do not over-tighten. Snugging the blade is all that is necessary.
4. Replace Blade Guard Cover Assembly as before making sure Lower Blade Guard covers blade.
If blades were purchased from CTD, your machine has been set with your blades. If not, blade diameters may
vary. Check to see if the blade contacts the base or disc in the down position. If repositioning is necessary,
adjust down stop bolt located under Arm casting, P/N 200BC01L or R.
These machines are general purpose in
their design, therefore the user should
attach any additional guarding to the
blade guard or table base if the cutting
application causes unsafe blade exposure.
This label is attached to the blade guard.
Never put hand or fingers near or
under the moving blade.Use a piece
of wood to remove short pieces from saw.
Blade Guard:
The blade and belt drive are enclosed. When the saw arm is lowered, the lower blade guard rotates up into the
main blade guard. The blade continues through the work as the lower blade guard rotates up.
NEVER remove any blade guard part, exposing the blade.
-5-
Diagram “C”
1. 200F250R/L 12" N.S. Blade Guard Cover-200 Series
300F250R/L 12" Cover- CM325R
2. 200A26R/L 12" Main Blade Guard, Rt. Or Lt. – 200Series
300A26R/L Main Blade Guard – CM325R
3. 200A270 Lower Rotating Blade Guard- ½” pin
4. 200M265R/L Bearing Housing Blade Guard Assy.
5. 200M261 Rotating Pawl
6. 2B2P09 Rotation Bearing for Housing
7. 2BM13 Spacer Washers (3) for Pin
8. 200B1P267 Shoulder Bolt Pawl
9. 200B1P268 External Tooth Lock Washer
10. 200B1P269 Teflon Spacer Washer (outside)
11. 200M320 N.S. Blade Guard Link/Puller-200 Series
300M32 Link Puller- CM325R
12. 200B7P35 Rear Bushing for Link/Puller
13. 200B7P36 Front Bushing for Link/Puller
13. 200B2P30 Roller Bearing Lower Blade Guard
15. 200M36R/L Rear Blade Guard Channel Rt. or Lt.-200 Series
300M36R/L Rear Channel Rt. or Lt.- CM325R
16. 200M35 Top Dust Tube Main Blade Guard- 200 Series & CM325R
300M35 Rear Dust Tube Connector – CM325R
300A12 Rear Dust Outlet 4" CM325R
Parts for Blade Guard Assembly-See exploded views on pages 20 & 21
Diagram “D”
Blade rotation