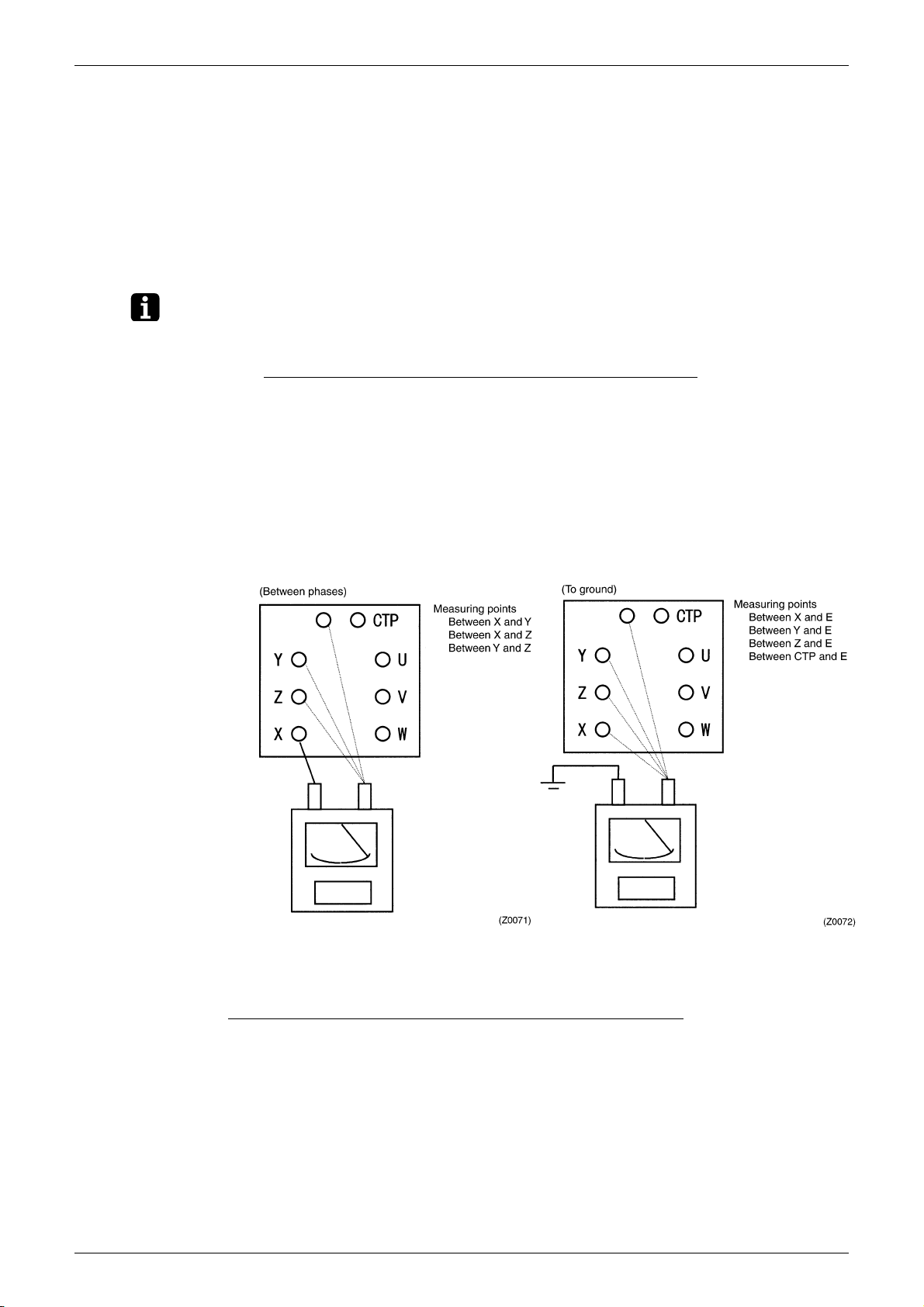
Si50-203 Periodic Inspection
Semi-Hermetic Single Screw Compressor Version III 7
(4) Charging oil
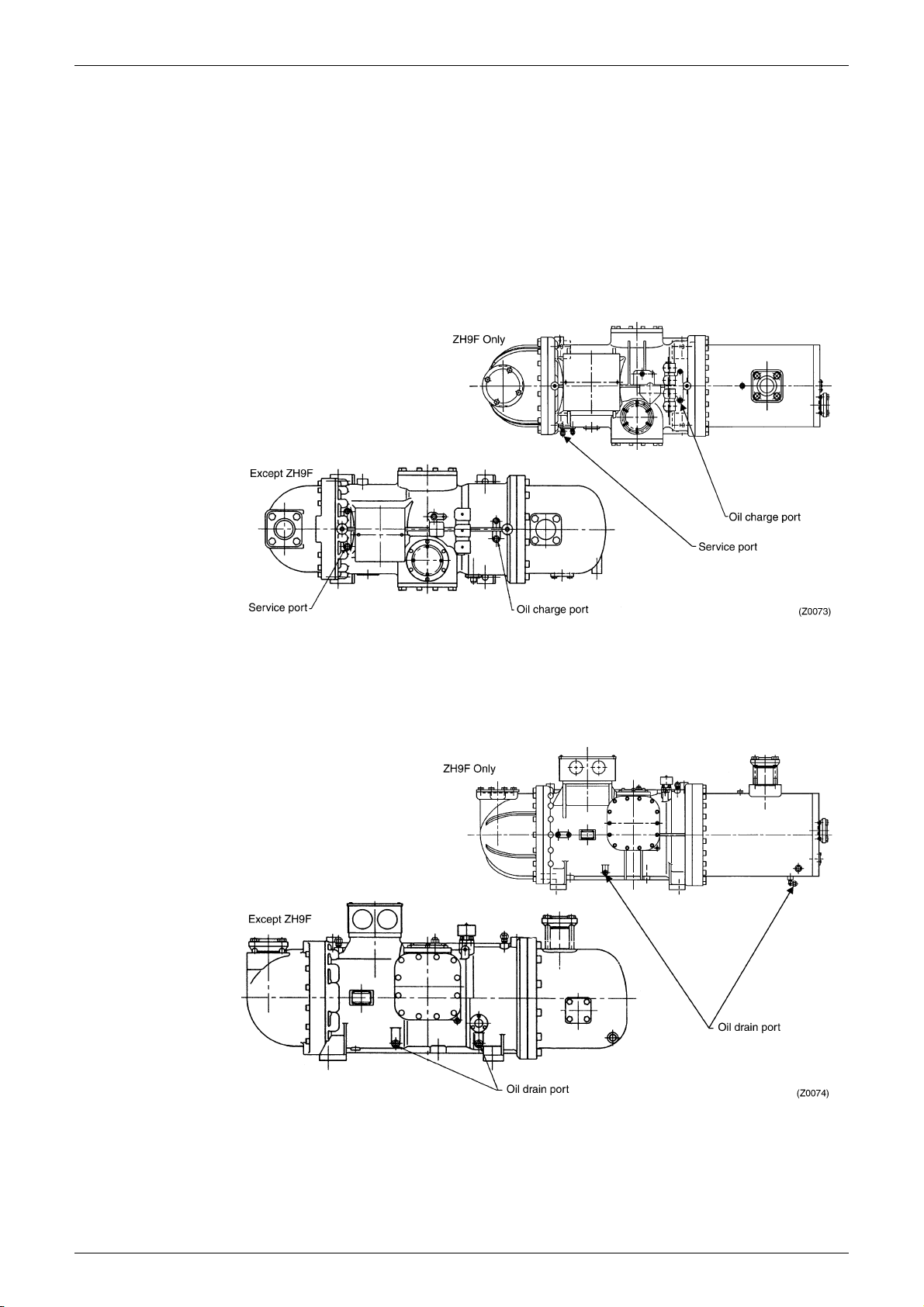
Connect a vacuum pump to the suction service port (1/4" DCut) on the casing. While
evacuating the compressor, add oil from the discharge service port (3/8" DCut).
Use SUNISO 4GSD refrigeration oil (possible for use equal product) for refrigerant R22
and DAPHNE FVC68D refrigerant oil for refrigerant R407C and R134a.
Add the same amount of new oil as drained because some remains in the refrigerant and
on various parts inside. Drained oil contains refrigerant and appears to be more in
volume than actual oil amount. Stir the oil to evaporate the dissolved refrigerant before
measuring. Do not add more oil than necessary, since an excessive amount of oil
reduces oil separation efficiency and causes system problems. (Oil surface should be
visible on the level gauge during equipment operation.)
Take care not to let in air, or dust and other foreign particles remaining on the bottom of
the oil container.
When charging oil from a previously opened container, conduct vacuuming of the
compressor to remove moisture and air.
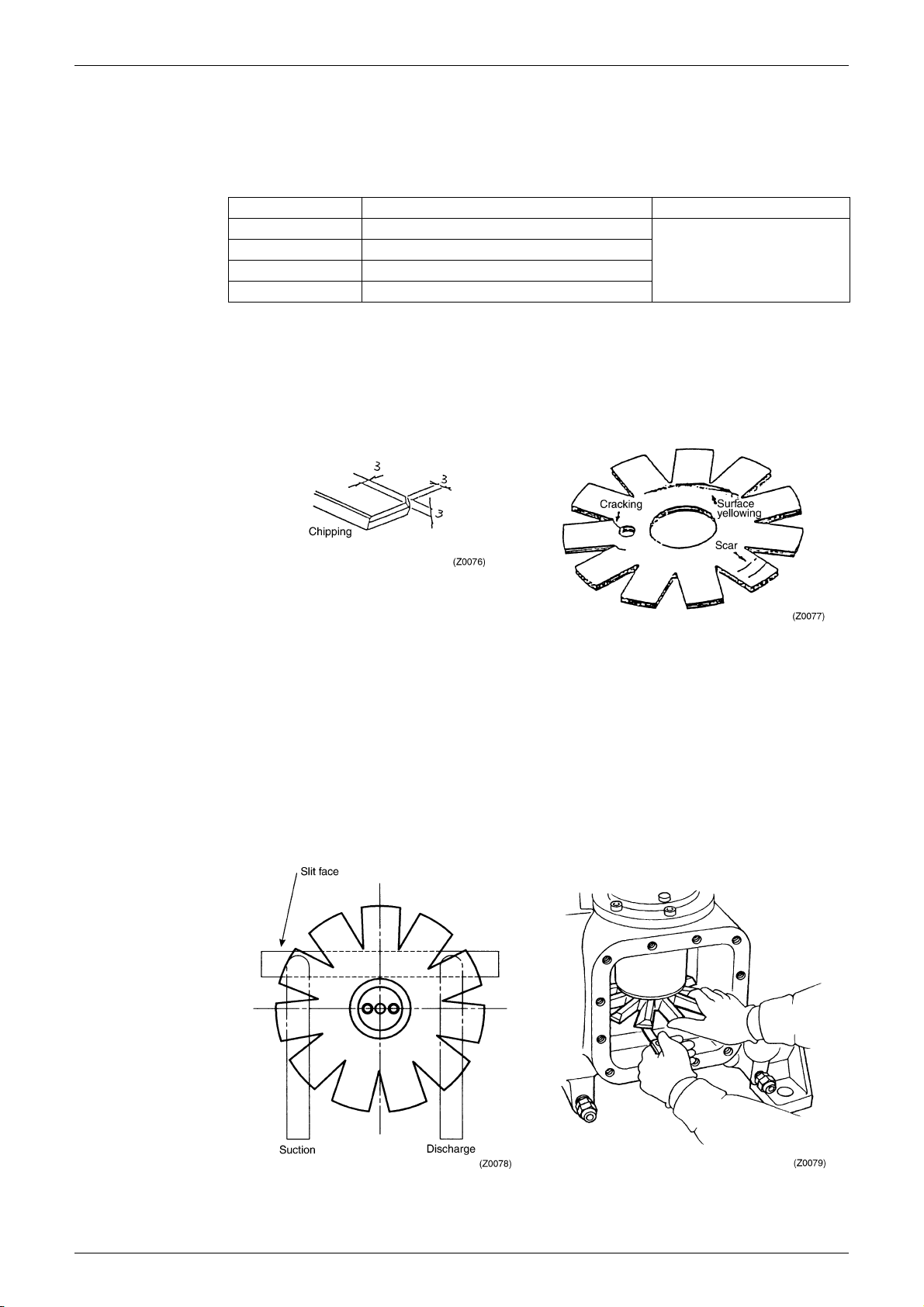
3. Inspecting The Gate Rotor
This inspection is done to check that no abnormal condition is present due to dust and other
foreign particles inside or harsh operating conditions of liquid compression, etc..
(1) Perform a pump down operation to reduce pressure inside the compressor.
(2) Release the internal pressure of the compressor.
Loosen the flare nut of the service port (with check valve) of the compressor (see Fig. 3-2).
Remove the partition lid, then tighten the flare nut to discharge refrigerant from the
compressor.
(3) Remove the side caps from both sides of the compressor. (Fig. 3-4)
Since a small amount of oil is still in the compressor, place drain pans under the side caps to
receive oil before opening the side caps.
Fig. 3-4 Side cap locations