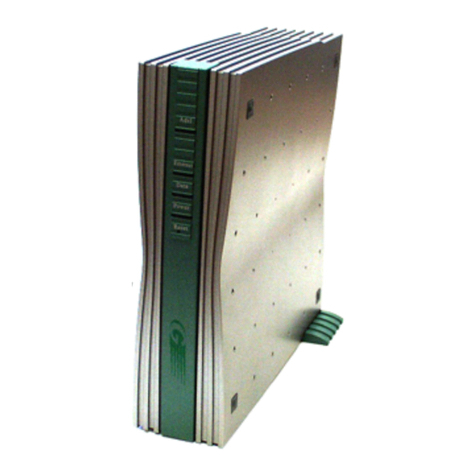
Datum Systems PSM-500 Technical document

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-1
Appendix G5 G.703/E1 Interface
PSM-500 Series G.703/E1 Interface Addendum
Revision History
Rev 0.10 2-1-2012 Initial Release.
Rev 0.11 5-2-2012 Corrected E1 transport stream descriptions. Corrected front
panel menu entries.
1.0 Optional G.703/E1 Interface Overview
G.703/E1 is a legacy interface standard that is used in Telephony and Cellular Backhaul
applications. The installation of the optional G5 (G.703/E1) interface provides the M500 Class
modems (PSM-500/500L/500LT) with an economical access solution for E1 and Fractional E1
network services over satellite. The G5 fully meet all of the E1 rate 2048 kbit/s specifications
including ITU recommendations:
G.703 - Physical/electrical characteristics of hierarchical digital interfaces.
G.704 - Synchronous frame structures used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8448 and 44 736
kbit/s hierarchical levels.
G.706 - Frame alignment and cyclic redundancy check (CRC) procedures relating to
basic frame structures defined in Recommendation G.704.
G.732- Characteristics of primary PCM multiplex equipment operating at 2048 kbit/s.
G.823 - The control of jitter and wander within digital networks which are based on the
2048 kbit/s hierarchy.
NOTE: If the G5 interface card is not already installed in the modem refer to Section 4 for
installation information.
Typical use of the G5 interface is in a duplex point to point link with a similarly configured PSM-
500 series modem at the other end of the link. The setup of the satellite link is very simple
because the modems at both ends of the link are connected to DTE equipment with this same
G.703/E1 interface type. Each port of the G5 interface can be configured independently for
either Full E1 or Fractional E1 operation.
The Full E1 mode allows for transmission of an the 2.048Mbps input data stream without
synchronizing to the imbedded framing of the E1 signal. In this case the port data rate though the
satellite link is the full 2.048Mbps of the E1 transport stream. Note in Unframed E1 there is no
requirement for G.704 framing.
The Fractional E1 mode allows for data rates of Nx64kbps to be transmitted over the satellite.
The G5 interface has flexible selection the number of timeslots to be transmitted and for selection
of standard signaling formats.
PCM30-CAS (Channel Associated Signaling) (Nx64Kbps, N = 1 to 15, 17 to 31 TS).
PCM31-CCS (Common Channel Signaling) (Nx64Kbps, N = 1 to 31 TS).
The FullE1 or Fractional E1 modes are controlled via the G.703 Frame parameter. Any
combination of Full E1 or Fractional E1 can be used independently on each port, and can be
used independently on the transmit or receive side of each port.

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-2
Key Features
Single or Dual port G.703/E1
Unframed & Fractional E1 operation
Data rate: User selectable N x 64Kbps in PCM30-CAS or PCM31-CCS modes
Fully transparent signal conversion under unframed mode
Clock Regeneration from incoming HDB3 or AMI formatted data
CRC4 ON/OFF modes.
Diagnostic Loopbacks for both Terrestrial and Satellite side
E1 alarm monitoring for all common E1 transport stream alarms:
LOS - Loss Of Signal. (All Modes)
AIS - All 1's at input port. (All Modes).
LFA - Loss of Framing Alignment. (PCM30-CAS and PCM31-CCS).
LMFA - Loss of Multi-Frame Alignment. (PCM30-CAS only).
RAI - Remote Alarm Indication. (PCM30-CAS and PCM31-CCS).
TS16AIS - All 1's in TS 16. (PCM30-CAS only).
The G5 G.703/E1 interface is only available for PSM-500 Series of modems, either new or as an
upgrade to existing customer modems. This optional Interface card is designed to be installed in
the option interface position inside the main modem assembly.
2.0 Technical Specifications:
2.1. E1 Signal Structure
The G.703/E1 interface operates at a nominal rate of 2.048Mbps. The data transferred over the
E1 transport stream is organized in frames. Each E1 frame contains 256 bits which are
comprised of 32 timeslots, each containing eight bits. The data rate of each timeslot is 64Kbps.
For 8-bit PCM encoded voice audio, each timeslot provides for an 8 kHz sampling rate.
Timeslot 0 is used for frame synchronization and alarms. Timeslot 16 is used for signaling,
alarms, or data. Timeslot 1 to 15 and 17 to 31 are used for carrying data or PCM encoded voice
audio.
There are two E1 frame formats,
Normal frame (PCM31-CCS)
Multi-frame (PCM30-CAS)
Framing is necessary in order for equipment receiving the E1 signal to identify timeslot alignment
and extract or insert the proper data. E1 signals configured with the PCM31-CCS format use the
frame alignment signal (FAS) for synchronization. When the PCM30-CAS format is used the
multi-frame alignment signal (MFAS) is used along with the FAS. The multi-frame structure also
provides channel associated signaling (CAS) for PCM30. There is also an optional a cyclic
redundancy check (CRC) in both PCM30-CAS and PCM31-CCS modes that is used to detect
errors in the data stream.Frame Alignment Signal (FAS)

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-3
Timeslot 0 of every other frame is reserved for the FAS. Alternate frames contain the FAS Distant
Alarm indication bit and others bits reserved for national and international use.
2.1.1. Multi-Frame Alignment Signal (MFAS)
MFAS framing provides Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) that transmist A/B/C/D bit signaling
information for each of 30 channels in timeslot 16. This method uses the 32 timeslot frame format
with timeslot 0 for the FAS and timeslot 16 for the MFAS and the CAS.
2.1.2. Channel Associated Signaling (CAS)
When timeslot 16 of the E1 frame is used for Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) purposes,
frame 0 contains the MFAS and timeslot 16 of frames 1-15 is used to convey the state of the
A,B,C and D signaling bits.
NOTE: The ABCD state of 0000 is not allowed. If all bits in timeslot 16 are 0, a loss of the MFAS
can be assumed. When A-Bit only signaling is used (No BCD bits), the BCD bits should be fixed
at: B=1, C=0, D=1 (101). A detection of all 1's in timeslot 16 declares a TS16AIS alarm, which
indicates a remote alarm with the upstream E1 equipment.
2.1.3. Common Channel Signaling (CCS)
When Common Channel Signaling (CCS) is employed, G.704 allows for various types of
signaling information to be carried in any timeslot, therefore timeslot 16 is available for user or
bearer data.
Common channel signaling (CCS) is signaling in which a group of voice-and-data channels share
a separate channel that is used only for control signals. This signaling protocol can be SS7,
ISDN, or PBX/Switch Proprietary protocols. The channel used for common-channel signaling
does not carry user information.
2.1.4. E1 Line Coding
The basic E1 signal is coded using the Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) or High-Density Bipolar 3
(HDB3). In AMI coding, “ones” are alternately transmitted as positive and negative pulses,
whereas “zeros” are transmitted as a zero voltage level. AMI is not used in most E1 transmissions
because synchronization loss will occur during long strings of data zeros. In HDB3 coding, a
string of four consecutive zeros is replaced with a substitute string of pulses containing an
intentional bipolar violation. The HDB3 code substitutions provide high pulse density so that the
receiving equipment is able to maintain synchronization with the received signal.
The G5 supports two E1 link line codes:
AMI coding
HDB3 coding.
2.1.5. E1 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
The ITU standard describes an optional implementation where a 4-bit Cyclic Redundancy Check
(CRC4) can be used to provide error detection for Frames 0 through 7, and Frames 8 through 15.
When this CRC4 format is used, the even frame’s International Bit is replaced with a CRC-4 bit.
The National Bits are relabeled as spare bits.
The G5 interface allows for the CRC4 function to be Enabled or Disabled.
2.1.6. Other Interface Specifications
Balanced: 120 ohm impedance on a RJ48c
Unbalanced: 75 ohm impedance using an external 120 ohm to 75 ohm converter (i.e. Balun-B2S)

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-4
Jitter performance is in according to ITU G.823
2.1.7. Alarm Indication Signal (AIS)
The AIS signal is an unframed “all-ones” signal, and is used to maintain line signal
synchronization in case of loss of input signal. The G5 interface will provide an AIS on the
receive data line if there is a fault condition in the demodulator. There will also be an indication
on the G5 interface if there is an AIS condition received on the transmit data line.
3.0 G5 Setup and Operation
The addition of a the G5 interface card provides G.703/E1 physical and electrical interfaces
designed to operate at 2.048 Mbps. When installed, the G5 interface card is automatically
recognized by the PSM-500 modem controller and the user interface menus are populated with
the appropriate G5 interface selection menu’s. Refer to Section 3 in the PSM-500 Installation and
Operation Manual for instructions on how to navigate the front panel menus.
Selection of G.703 as the currently active interface is accomplished by using the front panel or
the remote control protocols. Refer to Section 2.2 below for operation via the front panel and
Appendix B (Rev-0.96 or higher) for the remote protocol that is used to select and control the G5
interface.
2.2. Configuring the G5 G.703/E1 Interface from the front panel.
From the front panel you would select <Intf: I/O –Mode> for the G.703 option. This is
accomplished by pressing the Int’f button to the right of the LCD display, then scroll right to
display “I/O” in the upper left of the display, and down if necessary to display “Mode” in the upper
right of the display. To select G.703 you can then either press “?” and “Enter”, or press the “Edit”
key and scroll up or down until “G.703” is displayed in the LCD lower line, pressing “Enter” to
select that option.
The G5 has the ability to perform local loopback from either the terrestrial data side or the
satellite. When used with a BERT, the terrestrial loopback function allows testing of the E1
interface cables and connectors. IF Loopback allows for compete modem testing by connecting
the modulator output to the demodulator input. Section 3.2 describes these tests in more detail.
Table 1 G5 Interface Front Panel Parameter Details
Interface Parameter Detail (when G.703 is Active)
Representation
Type
Entry
Description
Status I/O
Online
Read Only
N/A
Interface Status **
Status RTS
Off
Read Only
N/A
Interface RTS line status
Status CTS
On
Read Only
N/A
Interface CTS line status
Status DCD
On
Read Only
N/A
Interface DCD line status
Status DTR
Off
Read Only
N/A
Interface DTR line status
Status DSR
Off
Read Only
N/A
Interface DSR line status
Status Test
Mod BER
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status BER
0.0 E-7
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-5
Interface Parameter Detail (when G.703 is Active)
Representation
Type
Entry
Description
Status SyncLoss
3
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status Errors
7
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status Bits
1.45 E7
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status EFS
99.95%
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status ErredSec
1
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
Status TotalSec
2135
Read Only
N/A
Interface Test status
I/O Mode
G.703
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = RS-232
2 = RS-449
3 = RS-449/Unterm
4 = V.35
5 = V.36
6 = EIA-530
7 = EIA-530A
8 = Ethernet IP (Option)
9 = G.703(Option)
10 = (Reserved)
11 = HSSI (Option)
Interface electrical mode.
Some option interfaces may
replace the SnIP, HSSI or
Ethernet IP, and Dual G.703
interface.
Other options may be added
in the future.
I/O RTS
Ignore
Selection
0 = Normal
1 = Control CXR
2 = Ignore
Interface RTS line control
I/O CTS
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Force Active
Interface CTS line control
I/O DCD
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Force Active
Interface DCD line control
I/O DTR
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Ignore
Interface DTR line control
I/O DSR
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Force Active
Interface DSR line control
I/O XmtData
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Inverted
Transmit Data Inversion
I/O XmtClock
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Inverted,
2 = Auto
Transmit Clock Phase. Auto is
now default standard.
I/O RcvData
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Inverted
Receive Data Inversion
I/O RcvClock
Normal
Selection
0 = Normal,
1 = Inverted
Receive Clock Phase
I/O RTSMonitor
Normal
Selection
0 = Disabled,
1 = to Alarm A,
2 = to Alarm B
Allows using Alarm relay
contacts to show RTS Status,
overriding other alarms.

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-6
Interface Parameter Detail (when G.703 is Active)
Representation
Type
Entry
Description
For Advanced I5 Option Only
IIP Mode
Type
Selection
Read Only
Displays type of IP interface
present (I5, SnIP, etc.)
IIP IPAddr
192.168.100.1
Numeric
IP Address for Ethernet IP
Interface.
IIP NetwrkMask
255.255.255.0
Numeric
IP Mask Address for Ethernet
IP Interface.
IIP MACAddr
0080A800256C
Read Only
Read Only
Allows read of fixed Interface
MAC Address..
IIP Options
00007f
Read Only
Read Only
Displays Ethernet IP Options
enabled
IIP Version
021771-001-50
Read Only
Read Only
Displays Ethernet IP Software
Version Number
IIP Serial#
1000047
Read Only
Read Only
Displays Ethernet IP Serial
Number
G703P1 TxMode
E1
Selection
1=E1
G.703/E1 interface Port 1
always active if G.703 IO
Mode selected.
G703P1 TxCode
HDB3
Selection
0=AMI
1=HDB3
Line Coding selection.
G703P1 TxFrame
PCM31-CCS
Selection
0=Full E1
1=PCM30-CAS
2=PCM31-CCS
Input Framing selection;
Full E1 = Unframed Mode.
G703P1 TxCRC4
Enable
Selection
0=Disable
1=Enable
Cyclic Redundancy Check for
error reporting.
G703P1 TxNx64k
512 kbps
Read Only
Nx64kbps fractional E1 rate
for Port 1 transmitter.
G703P1 DropMap
TS08-On
Selection
TSxx –0=Off, 1=On.
xx = 01 to 31.
Press Up/Down key to toggle
between Off and On. Press
Left/Right keys to change
Timeslot number. Press
enter to program all timeslots.
Used for FractionalE1 mode to
select which timeslots (1-31)
that are to be dropped from
the input E1 framed signal and
transmitted over the satellite.
Timeslot 16 not available in
PCM30-CAS framing.
G703P1 RxMode
E1
Selection
1=E1
G.703/E1 interface Port 1
always active if G.703 IO
Mode selected.
G703P1 RxCode
HDB3
Selection
0=AMI
1=HDB3
Line Coding selection.
G703P1 RxFrame
PCM31-CCS
Selection
0=Full E1
1=PCM30-CAS
2=PCM31-CCS
Output Framing selection
G703P1 RxCRC4
Enable
Selection
0=Disable
1=Enable
Cyclic Redundancy Check for
error reporting
G703P1 RxNx64k
512 kbps
Read Only
Nx64kbps fractional E1 rate
for Port 1 receiver.

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-7
Interface Parameter Detail (when G.703 is Active)
Representation
Type
Entry
Description
G703P1 InsMap
TS08-On
Selection
TSxx –0=Off, 1=On.
xx = 01 to 31.
Press Up/Down key to toggle
between Off and On. Press
Left/Right keys to change
Timeslot number. Press
enter to program all timeslots.
Used for FractionalE1 mode to
select which timeslots (1-31)
that are to be inserted to the
output E1 framed signal
received over the satellite.
Timeslot 16 not available in
PCM30-CAS framing.
Port 2
G703P2 TxMode
E1
Selection
0=Disable
1=E1
Activate the G.703/E1
interface Port 1
G703P2 TxCode
HDB3
Selection
0=AMI
1=HDB3
Line Coding
G703P2 TxFrame
PCM-31-CCS
Selection
0=Full E1
1=PCM30-CAS
2=PCM31-CCS
Input Framing selection
G703P2 TxCRC4
PCM-31
Selection
0=Disable
1=Enable
Cyclic Redundancy Check for
error reporting
G703P2 TxNx64k
512 kbps
Read Only
Display the Nx64kbps satellite
rate
G703P2 DropMap
TS08-On
Selection
TSxx –0=Off, 1=On.
xx = 01 to 31.
Press Up/Down key to toggle
between Off and On. Press
Left/Right keys to change
Timeslot number. Press
enter to program all timeslots.
Used for FractionalE1 mode to
select which timeslots (1-31)
that are to be dropped from
the input E1 framed signal and
transmitted over the satellite.
Timeslot 16 not available in
PCM30-CAS framing.
Port 2
G703P2 RxMode
E1
Selection
0=Disable
1=E1
Activate the G.703/E1
interface Port 1
G703P2 RxCode
HDB3
Selection
0=AMI
1=HDB3
Line Coding
G703P2 RxFrame
PCM-31
Selection
0=Full E1
1=PCM30-CAS
2=PCM31-CCS
Input Framing selection
G703P2 RxCRC4
PCM-31-CCS
Selection
0=Disable
1=Enable
Cyclic Redundancy Check for
error reporting
G703P2 RxNx64k
512 kbps
Read Only
Display the Nx64kbps satellite
rate
G703P2 InsMap
TS08-On
Selection
TSxx –0=Off, 1=On.
xx = 01 to 31.
Press Up/Down key to toggle
between Off and On. Press
Left/Right keys to change
Timeslot number. Press
enter to program all timeslots.
Used for FractionalE1 mode to
select which timeslots (1-31)
that are to be inserted to the
output E1 framed signal
received over the satellite.
Timeslot 16 not available in
PCM30-CAS framing.
Alarm TstActive
to Alarm A
Selection
0=None, 1=A, 2=B, 3=A & B
Selects destination of alarm
Alarm BERLoss
to Alarm B
Selection
0=None, 1=A, 2=B, 3=A & B
Selects destination of alarm

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-8
Interface Parameter Detail (when G.703 is Active)
Representation
Type
Entry
Description
Alarm Enet
to Alarm A
Selection
0=None, 1=A, 2=B, 3=A & B
Selects destination of alarm
Alarm E1-Port1
to Alarm
Selection
0=None, 1=A, 2=B, 3=A & B
Selects destination of alarm
Alarm E1-Port2
to Alarm A
Selection
0=None, 1=A, 2=B, 3=A & B
Selects destination of alarm
Test TerLoopbck
Disabled
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Interface terrestrial loop-back
Send Data input to Receive
Data output.
Test SatLoopbck
Disabled
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
Interface satellite loop-back
demodulator output to
modulator input.
Test BERI/O
Satellite
Selection
0 = Satellite
1 = Terrestrial
BERT Function. See Main
User Manual for Description
Test ModBER
Disabled
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = 2047
2 = 2^23-1
3 = Insert 1 Error (if enabled)
BERT enable to modem
transmit input.
Test DemodBER
Disabled
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = 2047
2 = 2^23-1
BERT enable from modem
receive output.
2.3. Making Connections to the G5 Interface
Figure 1 shows the rear interface panel of the PSM-500 series modem with the G5 optional
interface installed.
Figure 1 - PSM-500 rear panel G5 Interface Location
2.3.1. G5 Connections
The G5 interface has five (5) user interface connectors on the rear panel of the optional card.
Refer to Table 2 through Table 4 for the connector type, signal names, and connector pinouts.
J3 Data Interface
AC
Line XMT IF OUT
EXT. REF IN RCV IF IN
S1
J1
J2
J8J7 J9
90 - 260 VAC, 50 W. MADE IN U.S.A.
J5
Alarm
J6
Control
AUX
J4
G5 Option Interface
P1 and P2
GbE - IP
Console Control
P1
P2
GI-5
Interface
G.703 E1/T1
No Connection with
G5 Only Option

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-9
Figure 2 –G5 Option Rear Interface View
2.3.1.1. G.703/E1 120 ohm Balanced Interface
The G5 interface offers dual G.703/E1 balanced interface presented on 2
RJ48c connectors –(Port 1) and (Port 2). The pinouts for the two
connectors are shown in Table 2 and
Figure shows picture of the interface connectors using a balanced (120ohm) to unbalanced
(75ohm) converter on Port 1.
Table 2 Port 1 & Port 2 Connector –120 ohm Balanced Pinouts (RJ48c)
Signal Name
Description
Direction
Pins
SD-T
Send Data Tip
To Modem
1
SD-R
Send Data Ring
To Modem
2
RD-T
Receive Data Tip
From Modem
4
RD-R
Receive Data Ring
From Modem
5
GND
Ground
n/a
3,6
2.3.1.2. G.703/E1 75 ohm Unbalanced
The G5 interface offers dual G.703/E1 120 ohm balanced interface presented on 2 RJ-48c
connectors –(Port 1) and (Port 2). For 75 ohm unbalanced connections, a balanced (120ohm) to
unbalanced (75ohm, BNC) converter must be used, like shown in Figure 3. This Balun adapter
is available from Datum Systems.

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-10
Figure 3 - Balanced to unbalanced converter (Balun)
2.3.1.3. 10/100 Ethernet (via the GbE- IP Connection)
The 10/100 Ethernet interface connector is used for SNMP control and monitor of the PSM-500
modem. Please refer to SnIP SNMP Guide for support information.
Table 3 GbE-IP Connector Pinouts (RJ45)
Name
Description
Pin
TX D1+
Transmit Data+
1
TX D1-
Transmit Data-
2
RX D2+
Receive Data+
3
BI D3+
Bi-directional pair C +
4
BI D3-
Bi-directional pair C -
5
RX D2-
Receive Data-
6
BI D4+
Bi-directional pair D +
7
BI D4-
Bi-directional pair D -
8
Figure 4 - Ethernet SNMP interface
2.3.1.4. Console Connector
The console connector is available for command line control and monitor of the Optional G5
processor card.
Table 4 Console Connector Pinouts (9 pin D female)
Signal Name
Description
Direction
Pins
Notes
RXD
Console RX
From Modem
2
EIA 232
TXD
Console TX
To Modem
3
EIA232
GND
Ground
5
2.3.1.5. USB2.0
The USB2.0 interface is reserved for future use.
3.0 G5 Interface Installation
The G5 interface is normally factory installed, but can be field installed by technical personnel.
The option card itself is an approximate 3.5-inch by 7.25 inch printed circuit board designed to be
mounted in the interface option position inside the PSM-500 series modem chassis.
Remove the modem unit from service before installation of the G5 Interface option. Unplug the
modem unit and remove the power cord from the rear for safety.
75 Ohm, BNC
Unbalanced I/O
120 Ohm, RJ-48
Balanced I/O

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-11
Place the unit on a flat surface and remove the 8 flathead screws holding the cover to the main
chassis using a number 2 Philips screwdriver. The location for the option card installation is
shown in Figure below.
WARNING: Failure to remove power from the modem unit before removal of the cover
can expose the operator to hazardous voltages and result in harm to personnel and
equipment.
3.1. Installing the G5 Interface
Position the rear option plate supplied into the chassis and align the mounting plate holes with the
holes in the chassis rear panel. Just start inserting the two #4 pan head screws without lock
washers to hold the plate in place. Slide the G5 interface assembly into the chassis and line up
the connectors with its opening on the rear plate. Slide the interface back and align the card’s
standoffs with the 4 standoffs in the chassis.
Figure 5 - G5 Interface Installation

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-12
Mount the G5 card to the chassis using the 4 #6 mounting screws with lock washers. An
additional flat washer may be required to keep the PCB mounting screws from extending beyond
the chassis bottom. Tighten the rear plate mounting screws and then the PCB mounting screws.
Connect the upper 40 pin ribbon cable connector to the main PCB header and press down to
close the latches. Care must be taken to avoid bending the installed FEC card which is very close
to one latch.
Re-install the cover and plug the unit in. Using the front panel arrow keys scroll down to the
interface parameter and verify that the modem recognizes the newly installed card. The modem is
now ready to be put into service.
3.2. Physical Connectivity Tests
The following tests will verify the proper installation and performance of the G5 card within the
PSM-500 modem. Connectivity and performance will require the use of a Bit Error Rate Tester
(Fireberd or similar) with an E1 and/or Fractional E1 interface.
3.2.1. Local Loopback
This first test checks the local interfaces and cable and does not require a satellite link or other
earth station equipment.
The G5 interface will loopback the transmit input data back out on the receive data port by using
the Local Loopback settings on the front panel <Intf:Test> menu. Refer to the front panel
configuration menus in the PSM-500 I&O Manual and
Table 1 above for setup information of all the modem functions. Table 5 shows the menu
selection for enabling the local terrestrial loopback function.
Table 5 Front Panel Terrestrial Loopback menu
Function
Type
Entry
Description
Test TerLoopbck
Enable
Selection
0 = Disable1 = Enable
Interface terrestrial
loop-back Send Data
input to Receive Data
output.
Verify that the BER tester is able to achieve data synchronization and there are no errors. Once
the test is finished, remove the test mode by setting the TerLoopbck to Disable.
3.2.2. Modem IF Loopback
If the Local Loopback test passed, then test the performance of the G5 interface within the PSM-
500 modem. The test setup for this test is shown in Error! Reference source not found..
The PSM-500 modem will loopback the Modulator TX IF Output back to the Demodulator RX IF
input by using the Local Loopback settings on the front panel <Dem:Test> menu. Refer to the
front panel configuration menus in the PSM-500 I&O Manual and
Table 1 above for setup information of all the modem functions. Table 6 shows the menu
selection for enabling the IF Loopback function.
Table 6 Front Panel IF Loopback menu
Function
Type
Entry
Description
Test IFLoopbck
Enable
Selection
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
IF Loop-back control.

Rev 0.11 Page G.703-13
Verify that the BER tester is able to achieve data synchronization and there are no errors. Once
the test is finished, remove the test mode by setting the IF Loopbck to Disable. The unit is now
ready for normal operation.
Other manuals for PSM-500
1
Table of contents
Other Datum Systems Modem manuals