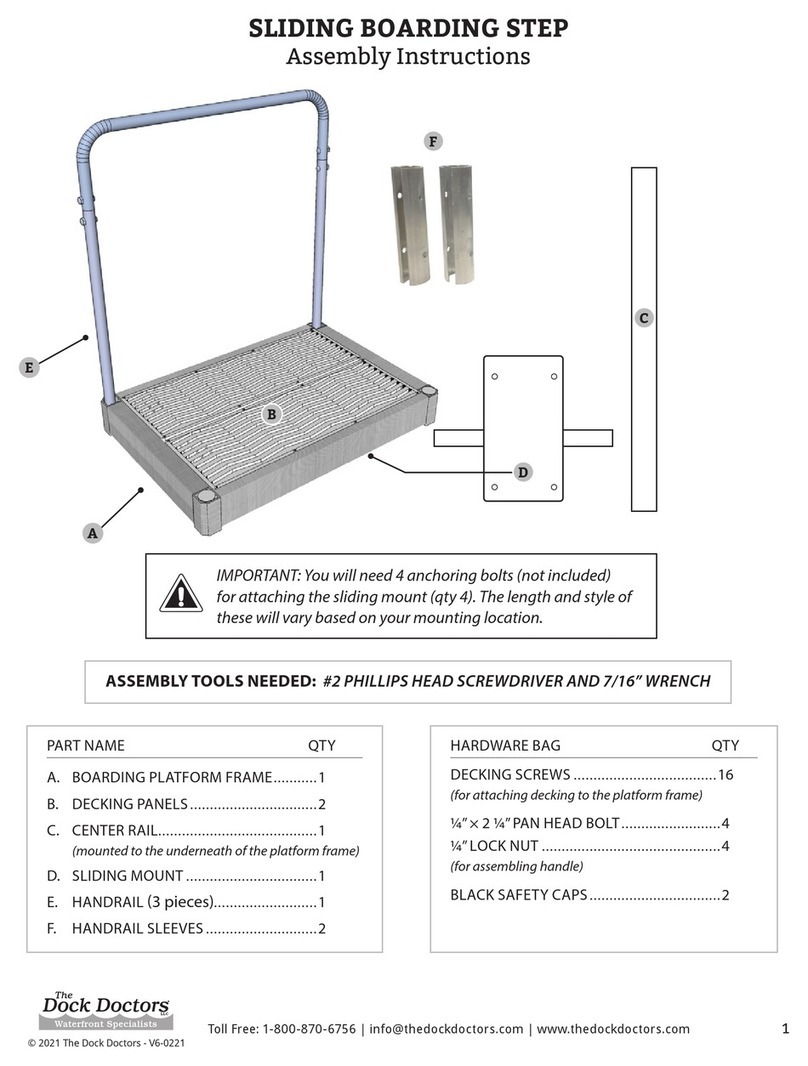
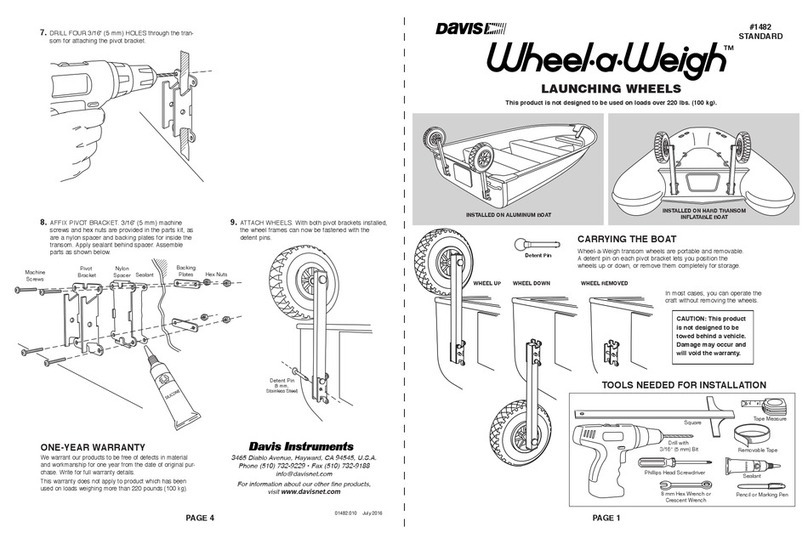
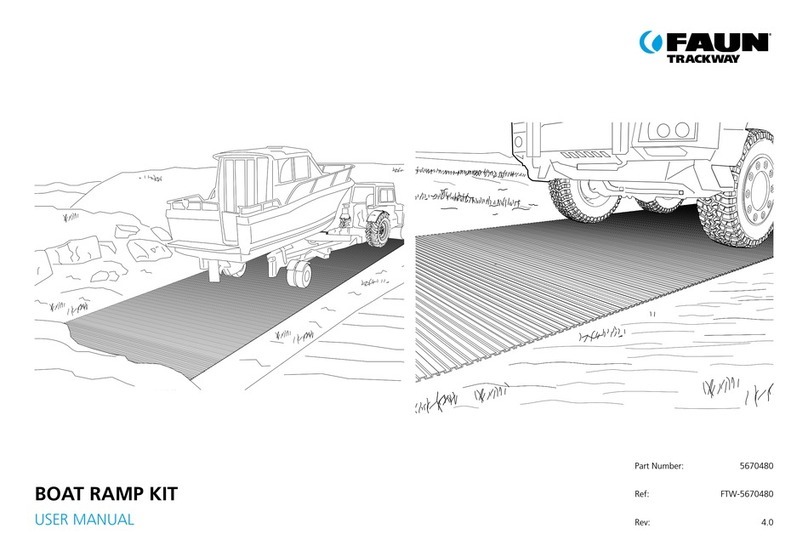
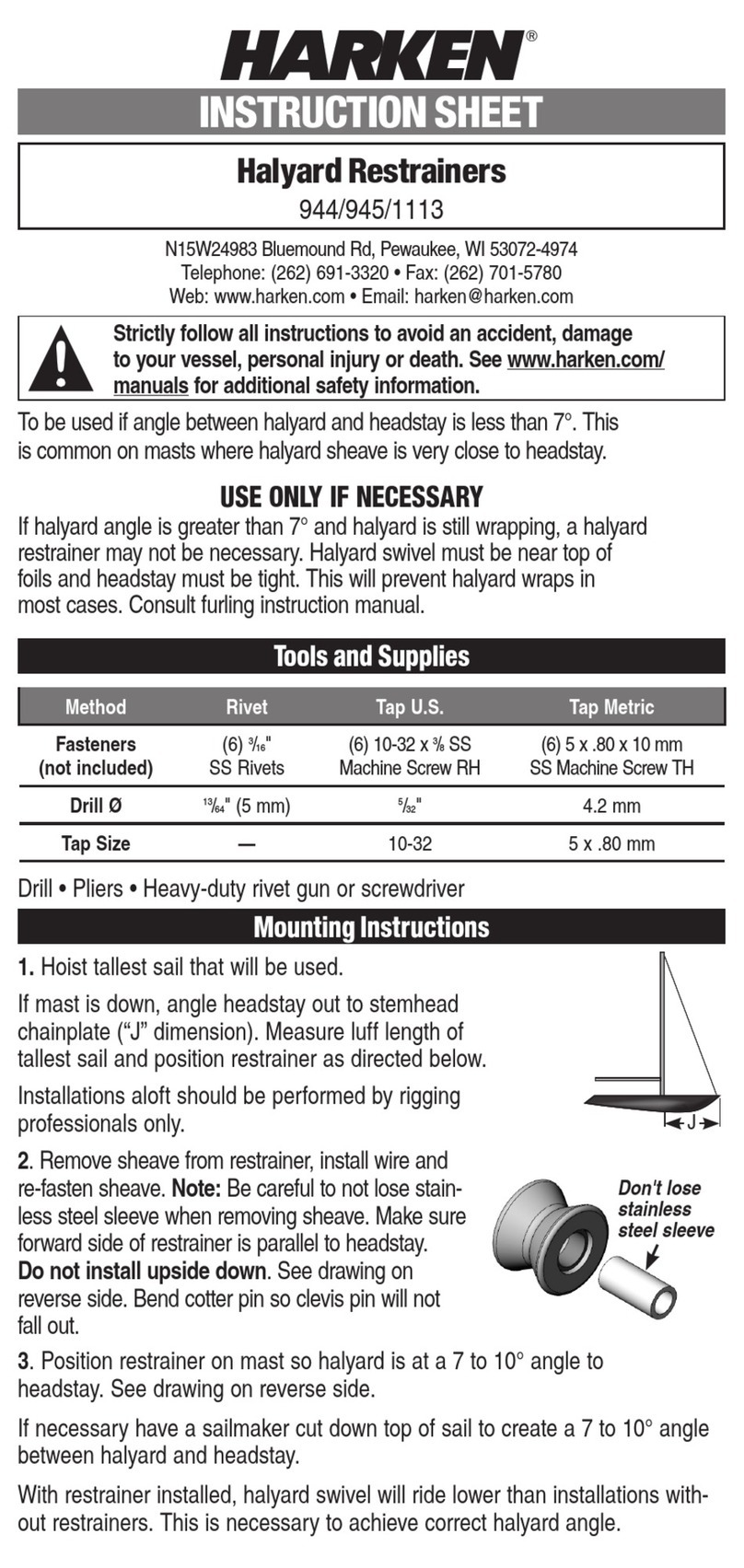
Page 7
FINDING LOCAL NOON & THE SUN’S ALTITUDE
AT MERIDIAN PASSAGE
A meridian is an imaginary line drawn on the earth’s surface from pole to pole; a
local meridian is one which passes through the position of an observer. When the
sun crosses the local meridian, it is at its highest point. It is said to be in meridian
passage and the time is local noon. Local noon may vary a half an hour (and in
daylight savings time, one and one-half hours) from the noon shown on the clock,
due to both the equation of time (to be discussed later) and the fact that our
clocks are set to zone time. All clocks in a zone 15° wide show the same time.
To find local noon, follow the sun up with a series of sights, starting about half an
hour before estimated local noon. Note the time and the sextant reading carefully.
Take a sight about every three minutes until the sun’s altitude is no longer
increasing. During meridian passage, the sun will seem to “hang” in the sky for a
short period at its highest point, going neither up nor down. Carefully note the
sextant reading. This is the sun’s altitude at meridian passage. To determine
the exact time of local noon, set your sextant at the same altitude as your first
sight. Wait for the sun to drop to this altitude, and note the time again. The time of
local noon is exactly half way between the times of the two sights.
Record the local time and the sextant reading when the sun was at the highest
point. These two readings will serve to locate your position. The time is used to
determine longitude and the sextant reading to determine latitude.
AN EXAMPLE OF A COMPLETE SIGHT
Let us assume for this example that your ship is sailing from San Francisco to
Hawaii and you have been using the sun to find your position each day. To allow
plenty of time to follow the sun up to its highest point, you make sure that you
have completed all your preparations by 10:00 a.m. local time. Your chart shows
yesterday’s position. From this position, you draw a line in the direction you are
traveling equal in length to the estimated number of miles to be traveled by noon
today. This is your “dead reckoning position” (D.R.), which will be compared with
your “noon sight.”
You note that you are standing on deck with your eye ten feet above the water (for
Dip correction) and that the index error of your sextant is +5'.
At about 11:20 a.m., you begin taking sights. At 11:23:30, your first sextant read-
ing is 82° 56'. You continue recording the sun’s altitude approximately every three
minutes until the sun seems to “hang” in the sky, dropping to a lower altitude at
your next sight. The maximum altitude of the sun, 84° 56', is the altitude of the
sun at meridian passage. You continue taking sights until 12:03:30, when the sun
has dropped to your original reading of 82° 56'. You know that the sun reached its