8
1,2 ÷ 2
1,5 ÷ 3
3 ÷ 5
5 ÷ 12
≥12
≥20
1,6
2
2,5
3,25
4
≥5
Table 4
Ø electrode (mm) Current (A)
1,6
2
2,5
3,25
4
5
6
30 ÷ 60
40 ÷ 75
60 ÷ 110
95 ÷ 140
140 ÷ 190
190 ÷ 240
220 ÷ 330
The current to be used depends on the welding positions and
the type of joint, and it increases according to the thickness and
dimensions of the part.
The current intensity to be used for the different types of weld-
ing, within the field of regulation shown in table 4 is:
• High for plane, frontal plane and vertical upwards welding.
• Medium for overhead welding.
•
Low for vertical downwards welding and for joining small pre-
heated pieces.
Afairly approximate indication of the average current to use in
the welding of electrodes for ordinary steel is given by the fol-
lowing formula:
I = 50 × (Øe - 1)
Where:
I = intensity of the welding current
Øe = electrode diameter
Example:
For electrode diameter 4 mm
I = 50 × (4 - 1) = 50 × 3 = 150A
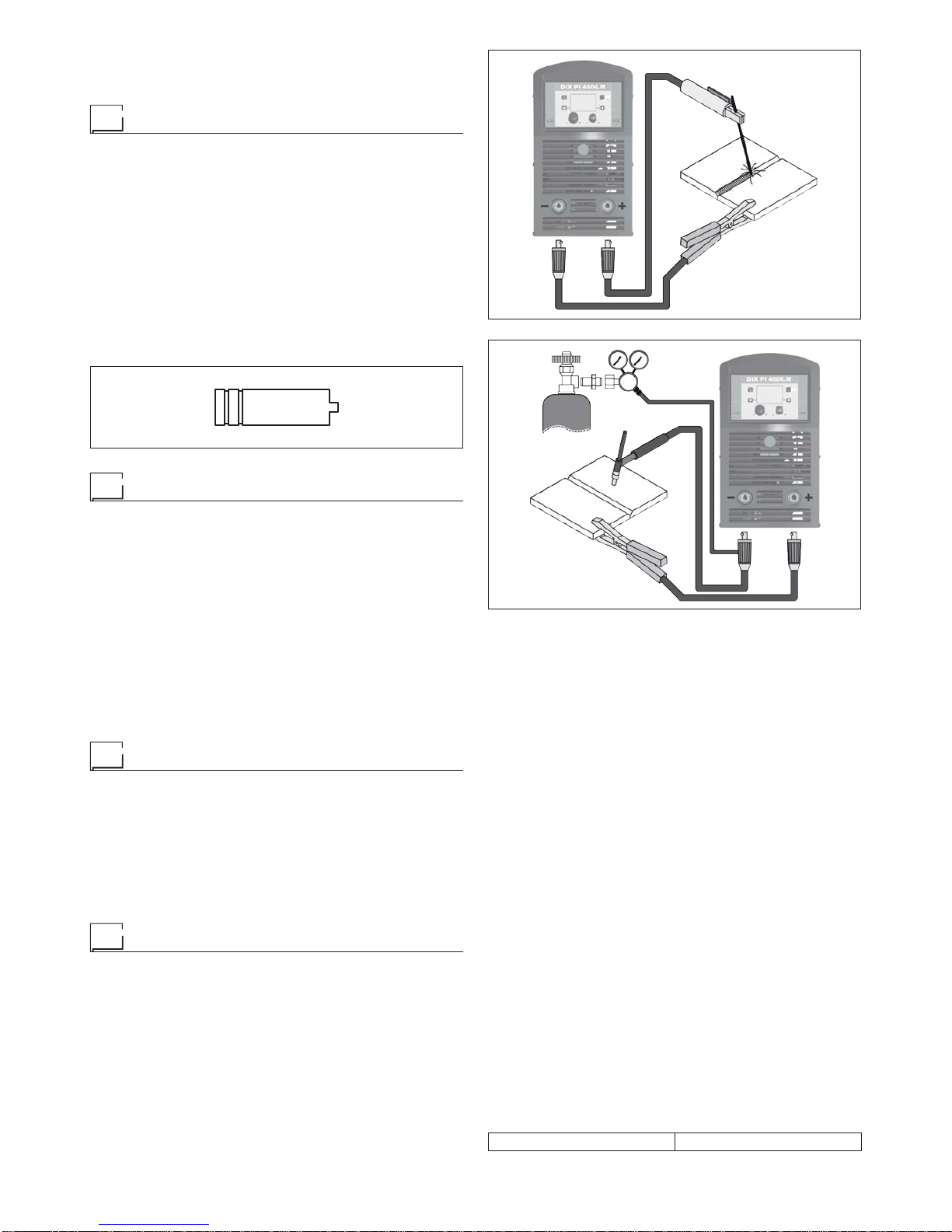
TIG welding with “Lift”
This type of ignition is commonly used where high frequency
igniters are not permitted, e.g. Hospitals and nuclear power
plants. The “Lift” type ignition makes it possible to reduce tung-
sten inclusions on ignition to a minimum. The molten bath and
the electrode are protected by and inert gas (for example, Ar-
gon). This type of welding is used to weld thin sheet metal or
when elevated quality is required.
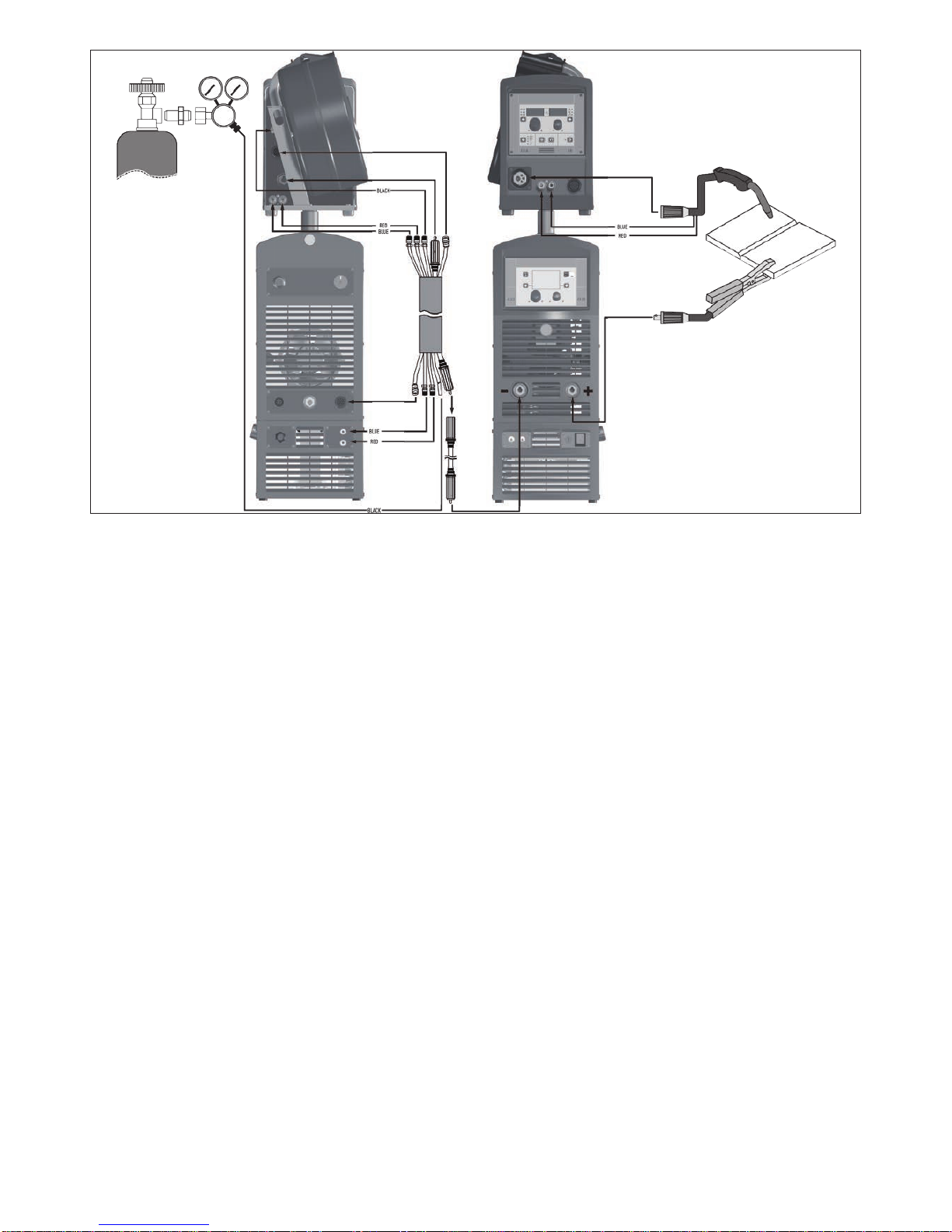
1) Connecting the welding cables (Fig. E):
•
Connect one end of the gas hose to the gas connecter on
the TIG torch and the other end to the pressure reducer
on the inert gas cylinder (Argon or similar).
• With the welding power source switched off:
-
Connect the ground cable to the snap-on connector
marked + (positive).
-
Connect the relative ground clamp to the workpiece or
to the workpiece support in an area free of rust, paint,
grease, etc..
-
Connect the TIG torch power cable to the snap-on con-
nector marked - (negative).
2) Switch the welding power source on by moving the power
supply switch to I(Pos. 3, Fig. A).
3) Make the adjustments and do the parameter settings on
the control panel.
4) Open the gas cylinder and regulate the flow by adjusting
the valve on the TIG torch by hand.
5) Ignite the electric arc by contact, using a decisive, quick
movement without dragging the tungsten electrode on the
piece to be welded (“Lift” type ignition).
6) The welder has a SWS “Smart Welding Stop” system for
the end of TIG welding. Lifting up the torch without switch-
ing off the arc will introduce a slope down and it will switch
off automatically.
7) When you have finished welding remember to shut the
valve on the gas cylinder.
Table 5 shows the currents to use with the respective elec-
trodes for TIG DC welding. This input is not absolute but is for
your guidance only; read the electrode manufacturers’instruc-
tions for a specific choice. The diameter of the electrode to use
is directly proportional to the current being used for welding.
Table 5
Ø ELECTRODE
(mm)
ELECTRODE TYPE
Current adjustment field (A)
TIG DC
Tungsten
Ce 1%
Grey
Tungsten
Rare ground 2%
Turchoise
110-50 10-50
1,6 50-80 50-80
2,4 80-150 80-150
3,2 150-250 150-250
4200-400 200-400
Maintenance
ATTENTION: Cut off the power supply to the equipment be-
fore effecting any internal inspection.
DIX PI 3006.M PULS, DIX PI 4006.M PULS and
DIX PI 4606.M PULS
IMPORTANT: For fully electronic welding power sources, re-
moving the dust by sucking it into the welding power source by
the fans, is of utmost importance.
In order to achieve correct functioning of the welding power
source, proceed as described:
•
Periodic removal of accumulations of dirt and dust inside the
equipment using compressed air. Do not point the jet of air
directly at the electrical parts as this could damage them.
•
Periodical inspection for worn cables or loose connections
that could cause overheating.
TORCH
The torch is subjected to high temperatures and is also stressed
by traction and torsion. We recommend not to twist the wire and
not to use the torch to pull the welder.As a result of the above
the torch will require frequent maintenance such as:
• Cleaning welding splashes from the gas diffuser so that the
gas flows freely.
• Substitution of the contact point when the hole is deformed.
•
Cleaning of the wire guide liner using trichloroethylene or
specific solvents.
• Check of the insulation and connections of the power cable;
the connections must be in good electrical and mechanical
condition.
SPARE PARTS
Original spares have been specifically designed for our equip-
ment. The use of spares that are not original may cause vari-
ations in the performance and reduce the safety level of the
equipment. We are not liable for damage due to use of spare
parts that are not original.
Optional
NOTE: The digital control unit of the welding power source is
fitted with a control recognition device which allows it to identify
which device is connected and take action accordingly.
REMOTE CONTROL ANALOGIC RC
This command (that must be plugged into the relevant connec-
tor on the front panel of the WF 793.M drawing unit):
•
Completely replaces the ENCODER - A knob on the WF
793.M feeder’s front panel.