4
II – KF700 Series Array Philosophy
Since we set o t to develop the KF700 Series for ease of se, we insisted that arrays designed to cover any ven e
co ld be flown q ickly, easily, and safely as a dead h ng cl ster. S ch a system wo ld save the ser both time and
money while providing his/her client with an aco stically consistent and aesthetically pleasing cl ster.
To f rther enhance tility, the KF700 Series ses a m lti-axial approach that creates compact mod les that provide
the high “Q” pattern control associated with m ch larger devices. Combined with the tightly packed, dead-h ng
nat re of the cl ster, this allows for maxim m co pling of array elements, providing tremendo s o tp t capability
thro gh the low and mid freq ency s bsections of the array.
Finally, KF700 Series arrays will provide niform coverage with relatively simplistic processing. We have developed
AS3D array shading to enhance array control and coverage witho t req iring additional DSP nits.
THE GOLDEN RULES
Both o r experience and ser feedback has led s to develop two Golden R les for KF700 Series sage. Following
these r les will not g arantee s ccess. However, not following them will definitely compromise array performance.
1
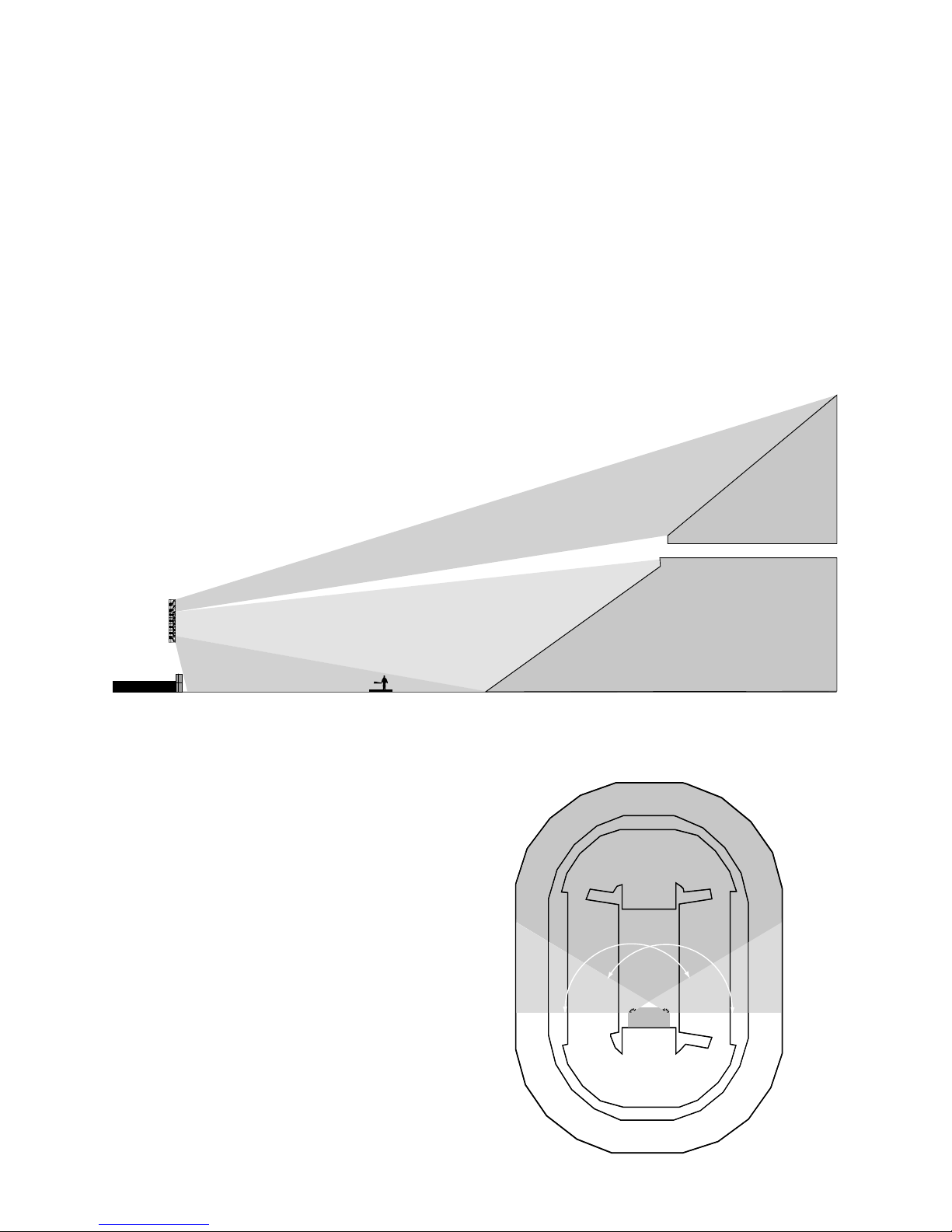
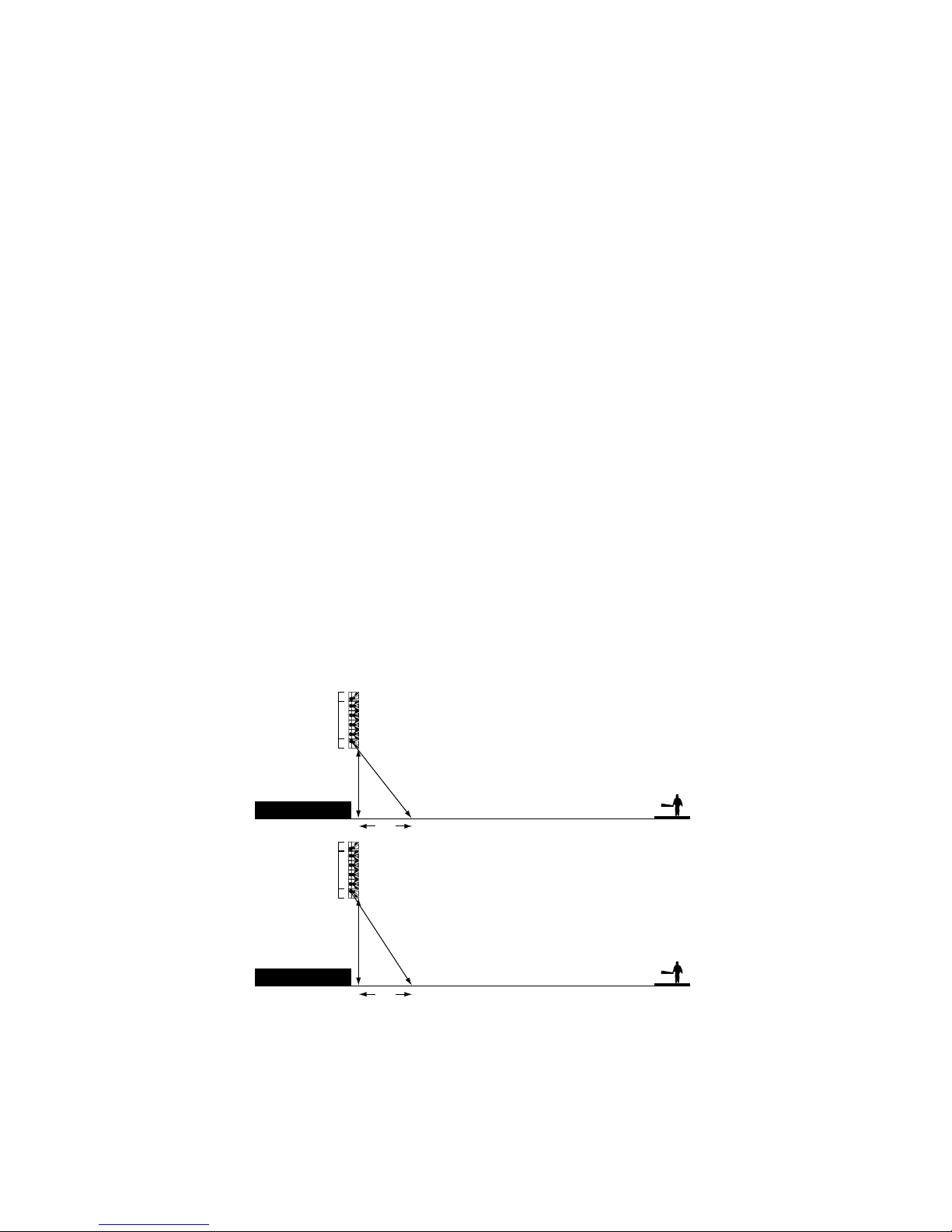
Never let an a dience member see a handle on a mod le in their primary cl ster. (It is alright if someone seated
ho se-right sees a handle on the ho se-left cl ster). The KF700 Series lo dspeakers provide a 30∞horizontal pat-
tern that drops off very rapidly o tside of this nominal angle. Since the physical angle of the enclos re is also 30∞,
if yo can see the handle, yo are o t of the pattern. The difference in performance will be a dible.
Provide separate processing for each row of KF755’s. Using m ltiple rows of KF755’s allows KF700 Series arrays to
work in a n mber of challenging ven es, b t each row of KF755's m st be processed independently in order to
achieve proper integration. (N. B. This req ires only two channels of o tp t per row in large arrays in which the
KF750's alone prod ce s fficient LF response.)
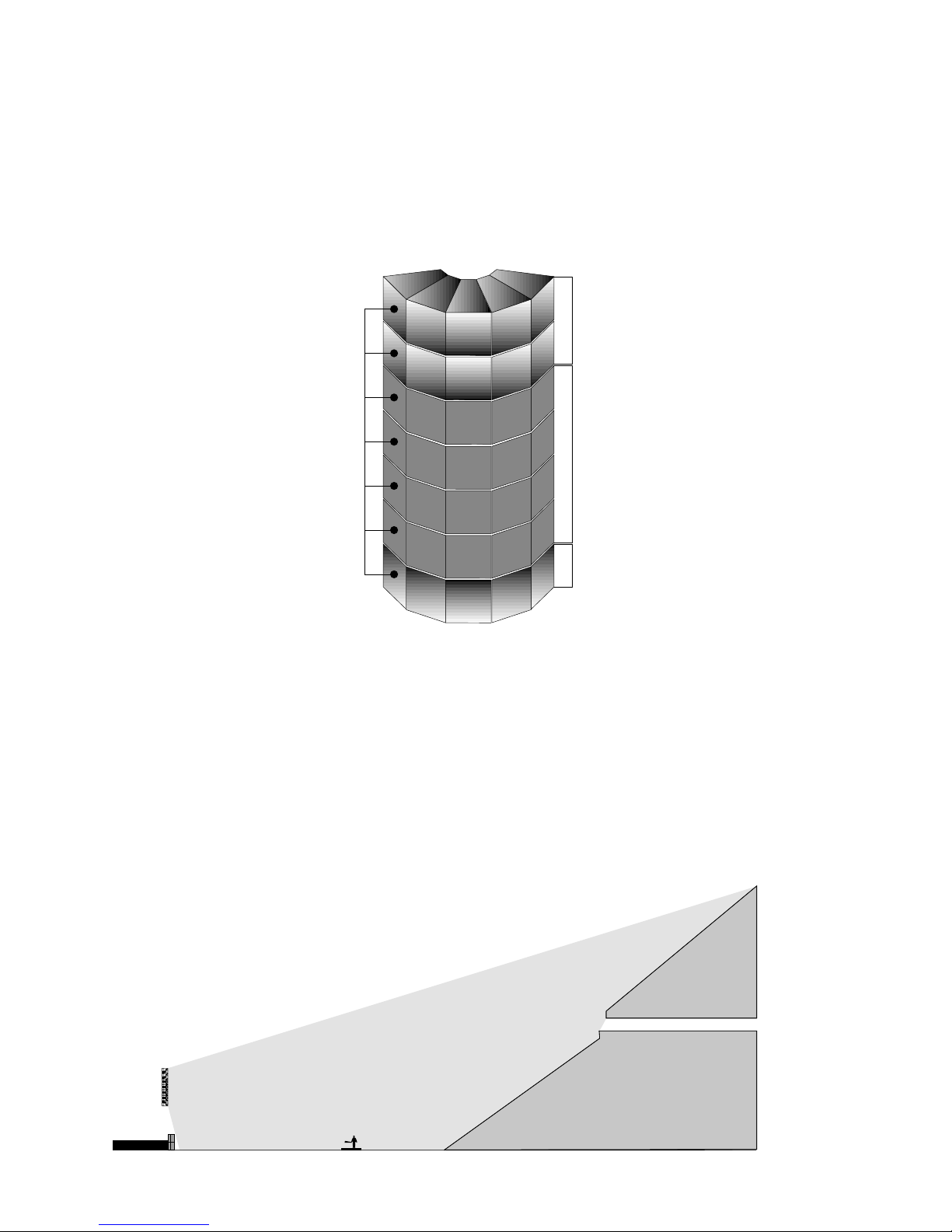
III – Building Arrays:Bandwidth by Bandwidth
The soon-to-be-released KF700 Series Owner’s
Man al provides information regarding the f nda-
mental design attrib tes of the mod les within the
series. These systems are designed to exhibit pre-
dictable behavior when arrayed, b t it is important to
realize that array behavior is not the same as mod le
behavior. In fact, when arrayed, the individ al
devices within a mod le combine with their co nter-
parts in adjacent mod les to achieve a different level
of performance that m st be addressed as a system. It
is vital to nderstand the nat re of this device cooper-
ation in order to consistently b ild and ltimately
t ne these high performance cl sters.
Distributed HF Horns MF Line Source LF Line Array