Eburon 160 User manual

160 / 200
2
CONTENTS:
1 –Safety instructions ...................................................................................... page 3
2 –Control Panel..............................................................................................page 7
3 –Technical data ............................................................................................page 8
4 –Installation...................................................................................................page 8
5 - Functions.....................................................................................................page 9
6 –Errors descriptions......................................................................................page 10
6.1 - Connection to the network ....................................................................... page 10
6.2 - Earth connection ......................................................................................page 10
7 –Electrical diagram ....................................................................................... page 11
7.1 - MMA welding ...........................................................................................page 11
7.2 LIFTIG Wetting ..........................................................................................page 12
8 - Description of the error ...............................................................................page 12
9 - Electrical scheme .......................................................................................page 13
10 - Nomenclature ...........................................................................................page 14
11 - Maintenance .............................................................................................page 15
11.1 - Repairs ..................................................................................................page 15

160 / 200
3
1. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
In its conception, specification of parts and production, this machine complies with the regulation in
force, namely the European Standards (EN) and internationals (IEC).
There are applicable the European Directives “Electromagnetic compatibility”, “Low voltage” and
“RoHS”, as well as the standards IEC / EN 60974-1 and IEC / EN 60974-10.
Electric shocks can be deadly.
- This machine must be connected to earthed sockets. Do not touch the live parts of the machine.
- Before any intervention, disconnect the machine from the mains. Only qualified personnel should
intervene in these machines.
- Always check the state of the input power cable.
It is essential to protect the eyes against the radiations of the electric arc. Use a welding mask or
helmet with a suitable protective filter.
Use closed-in smoke extractor. Smoke and gases can damage the lungs and cause poisoning.
Welding can originate risks of fire or explosion.
- Remove flammable or explosive materials from welding area;
- Always have sufficient firefighting equipment;
- Fire can break out from sparks even several hours after the welding work has been finished.
Hot parts can cause burns. The work piece, the projections and the drops are hot. Use gloves,
aprons, safety shoes and other individual safety equipment.
Electromagnetic fields generated by welding machines can cause interference with other devices.
They can affect cardiac pacemakers.
Gas bottles can explode (MIG or TIG welding). It is essential to comply with all safety regulations
regarding gases.

160 / 200
4
1.1 ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
The user is responsible for installing and using the arc welding equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If
electromagnetic disturbances are detected, then it shall be the responsibility of the user of the arc welding equipment to
resolve the situation with the technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases, this action may be as simple as
connecting to earth the welding circuit. In other cases, it could involve constructing electromagnetic screens enclosing the
welding power source and the work complete with associated input filters. In all cases, electromagnetic disturbances shall
be reduced to the minimum to avoid troubles.
Before installing arc welding equipment, the user shall assess potential electromagnetic problems in the surrounding area.
The following shall be considered:
a) Supply cables, control cables, signalling and telephone cables, above, below and adjacent to the arc welding equipment;
b) Radio and television transmitters and receivers;
c) Computer and other control equipment;
d) Safety critical equipment, e.g. guarding of industrial equipment;
e) The health of the people around, e.g. the use of pacemakers and hearing aids;
f) Equipment used for calibration or measurement;
g) The immunity of other equipment in the environment. The user shall ensure that other equipment being used in the
environment is compatible. This may require additional protection measures;
h) The hour of day when welding or other activities are to be carried out.
1.1.1 Methods of reducing emissions
Connection to mains
Arc welding equipment should be connected to the input supply system according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
If interference occurs, it may be necessary to take additional precautions such as filtering of the supply system.
Consideration should be given to shielding the supply cable of permanently installed arc welding equipment, in metallic
conduit or equivalent. Shielding should be electrically continuous throughout its length. The shielding should be connected
to the welding power source so that good electrical contact is maintained between the conduit and the welding power
source enclosure.
Welding cables
The welding cables should be kept as short as possible and should be positioned close together, running at or close to the
floor level.
Equipotent bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the welding installation and adjacent to it should be considered. However, metallic
components bonded to the work piece will increase the risk that the operator could receive an electric shock by touching
these metallic components and the electrode at the same time. The operator should be insulated from all such bonded
metallic components.
Connexion to earth of the work piece
When the work piece is not bonded to earth for electrical safety, nor connected to earth because of its size and position,
e.g. ships hull or building steelwork, a connection bonding the work piece to earth may reduce emissions in some, but not
all instances. Care should be taken to prevent the earthling of the work piece increasing the risk of injury to users, or
damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary, the connection of the work piece to earth should be made by a
direct connection to the work piece, but in some countries where direct connection is not permitted, the bonding should be
achieved by suitable capacitance, selected according to national regulations.
Screening and shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate problems of
interference. Screening of the entire welding installation may be considered for special applications.

160 / 200
5
1.2 ELECTRICAL SECURITY
1.2.1 Connection to the network
Before connecting your equipment, you must check:
- The safety device against over-currents, and the electrical installation are compatible with the maximum power and the
supply voltage of the welding power source (refer to the instructions plates).
- The connection, either single-phase, or three-phase with earth can be effectuated on a socket compatible with the welding
power source cable plug.
- If the cable is connected to a fixed post, the safety device against electric shocks will never cut the earth.
- The ON/OFF switch located on the welding power source is turned off.
1.2.2 Working area
The use of arc welding implies a strict respect of safety conditions regarding electric currents. It is necessary to check that
no metal piece accessible by the operators and to their assistants can come into direct contact with a phase conductor and
the neutral of the network. In case of uncertainty, this metal part will be connected to the earth with a conductor of at least
equivalent section to the largest phase conductor.
Make sure that all metal pieces that the operator could touch with a non-insulated part of his body (head, hands without
gloves on, naked arms, etc) is properly grounded with a conductor of at least equivalent section to the biggest supply cable
of the ground clamp or welding torch. If more than one metal ground is concerned, they need to be all interlinked in one,
which must be grounded in the same conditions.
Unless very special care has been taken, do not proceed to any arc welding or cutting in conductive enclosures, whether it
is a confined space or the welding machine has to be left outside. Be even more prudent when welding in humid or not
ventilated areas, and if the power source is placed inside (Decree dated 14.12.1988, Art. 4).
1.2.3 Risks of fire and explosion
Welding can originate risks of fire or explosion. You must pay attention to fire safety regulation
- Remove flammable or explosive materials from welding area;
- Always have sufficient fire fighting equipment;
- Fire can break out from sparks even several hours after the welding work has been finished.
1.3 INDIVIDUAL PROTECTION
1.3.1 Risks of external injuries
Arc rays produce very bright ultra violet and infrared beams. They will damage eyes and burn skin if the operator is not
properly protected.
-The welder must be dressed and protected according to the constraints of his works impose to him.
-Operator must insulate himself from the work-pieces and the ground. Make sure that no metal piece, especially those
connected to the network, comes in electrical contact to the operator.
-The welder must always wear an individual insulating protection.
Protective equipment: gloves, aprons, safety shoes that offer the additional advantage to protect the operator against burns
caused by hot pieces, spatters, etc. Check the good state of this equipment and replace them before you are not protected
any more.
- It is absolutely necessary to protect eyes against arc rays.
- Protect hair and face against sparks. The welding shield, with or without headset, must be always equipped with a proper
filter according to the arc welding current. In order to protect shaded filter from impacts and sparks, it is recommended to
add a glass in front of the shield.
160 / 200
6
NOTE: A higher step must be used when welding with low ambient light.
1.3.2 Risk of internal injuries
Gases and fumes
- Gases and fumes produced during the welding process can be dangerous and hazardous to your health. Arc welding
works must be carried out in suitable ventilated areas.
- Ventilation must be adequate to remove gases and fumes during operation. All fumes produced during welding have to be
efficiently removed during its production, and as close as possible from the place they are produced.
- Vapours of chlorinated solvents can form toxic gas phosgene when exposed to ultraviolet radiation from an electric arc.
Safety in the use of gases (welding with TIG or MIG inert gases)
Compressed gas cylinders
Compressed gas cylinders are potentially dangerous. Refer to suppliers for proper handling procedures:
- No impact: secure the cylinders and keep them away from impacts.
- No excess heat (over 50°C)
Pressure relief valve
- Check that the pressure relief screw is slackened off before connecting to the cylinder.
- Check that the union is tight before opening the valve of the cylinder. Open it slowly a fraction of a turn.
- If there is a leak, NEVER tighten a union under pressure, but first close the valve on the cylinder.
- Always check that hoses are in good condition.

160 / 200
7
2. MMA WELDING (coated electrode)
To establish an electric arc, a potential difference is induced between the
electrode and the workpiece. The air between them is ionized and
conductive, so that the circuit is closed and the electric arc is made.
The high temperature of the arc melts the base material and electrode that
is deposited by creating a welding bath. Arc welding is still very common due
to the low purchase cost of equipment and consumables used in this
process.
The metal core of the electrode is covered with a flux material that upon
assembly creates a protective atmosphere that prevents the oxidation of the
molten metal and facilitates the welding operation.
On DC current sources (rectifiers), the polarity of the electrical current
influences the metal transfer mode.
Normally the electrode is connected to the positive (+), although it can be connected in very thin materials
with the negative (-).
Although the horizontal weld position is the most favorable, this process allows use at all positions.
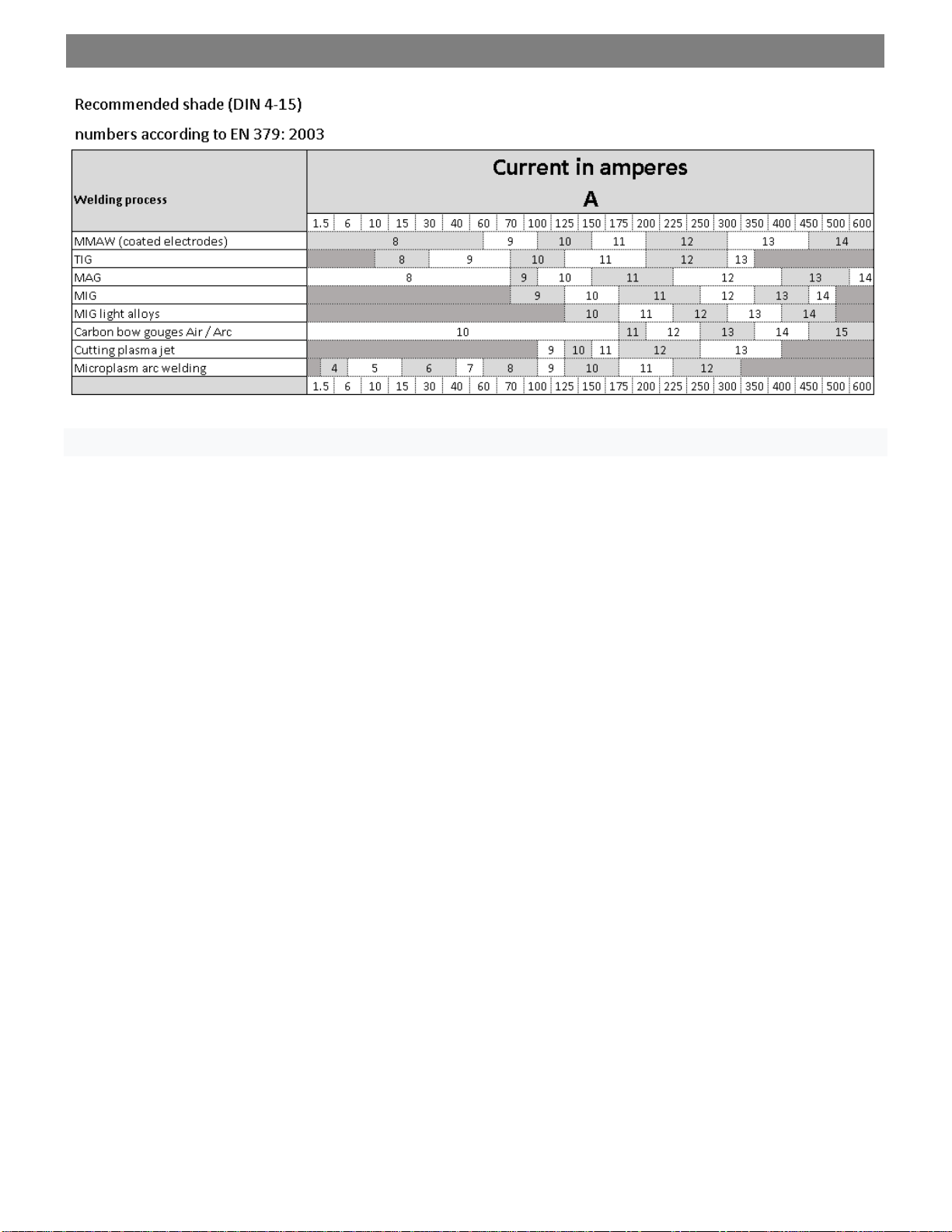
MMA welding parameter table:
Diameter electrode
Welding current
Thickness of sheet metal
2,5 mm
40 –125 A
> 2 mm
3,2 mm
105 –250 A
> 3 mm
4,0 mm
75 –185 A
> 6 mm
5,0 mm
140 –305 A
> 9 mm
6,0 mm
210 –430 A
> 9 mm
8,0 mm
275 –450 A
> 9 mm
3. TIG WELDING (Tungsten inert gas)
It is the process of arc welding under shield gas,
using a torch with a fusible tungsten electrode and
which can be used with or without filler metal in an
inert gas atmosphere such as argon and mixtures
thereof.
This process makes the arc more stable without
splashing, which guarantees a strong mechanical
resistance of the weld connection. This TIG process
replaces with many advantages the oxyacetylene on welding of steel, stainless steel, copper, brass DC, the aluminum
on AC welding and, in various cases, the MMA and Mig welding, especially when the weld seam remains visible.
160 / 200
8
Chemical composition of the electrodes
Code
Composition
Type
Color
Welding
WP
Pure tungstene
W
Green
AC –Aluminium, Magnesium
WT4
0,35-0,55% thorium
Th
Blue
DC
Mild steel, stainless steel, Titanium
Copper
WT10
0,80-1,20% thorium
Yellow
WT20
1,7-2,3% thorium
Red
WT30
2,7-3,3% thorium
Violet
WT40
3,8-4,3% thorium
Orange
WZ3
0,15-0,50% zirconium
Zr
Brown
Stainless steel, Nickel,
Non-ferrous metals
WZ8
0,70-0,10% zirconium
White
WL10
1,0-1,2% lanthanum
La
Black
All TIG applications
WC20
1,9-2,3% cerium
Ce
Grey
All TIG applications
Table of diameters and currents applicable to electrodes
electrode
(mm)
Amp. DC
Amp. AC
Negative (-)
Positive (+)
1,6 mm
40-130 A
10-20 A
45-90 A
2,0 mm
75-180 A
15-25 A
65-125 A
2,5 mm
130-230 A
17-30 A
80-140 A
3,2 mm
160-310 A
20-35 A
150-190 A
4,0 mm
275-450 A
35-50 A
180-260 A
5,0 mm
400-625 A
50-70 A
240-350 A
Shielding gases: The gases used in TIG welding contribute to:
- Wrap the electric arc in an ionizable atmosphere.
- Avoid contamination of the welding bath by oxygen existing in the atmosphere.
- Cool the electrode.
Argon (Ar)
- Is the most common gas and is used with a degree of purity of 99.9%. Helium (He)
- Pure helium is used in welding copper mixed with argon in percentages between 10% and 75%.
Hydrogenated (H) - is an inert gas at ambient temperature and is used especially in copper welding. It is not
recommended to weld in closed spaces because it combines with oxygen by turning the air unbreathable.
160 / 200
9
4. CONTROL PANEL
1
Welding process selector: MMA welding, LIFTIG (TIG welding with arc ignition without high frequency) and
PULSE (when lit with another mode also lit, indicates the pulse welding with the respective welding mode)
2
Machine LED connected and powered
3
Overload or overload alarm indicator - Turns off the machine in case of overheating
4
VRD option - MMA VRD - Reduction of secondary voltage for use in environments with increased risk of
electric shock.
5
Digital welding current display
6
Setting and Parameter Selection - Selects parameter / setting parameters by turning the knob
7
Welding parameters - see the description of these parameters in this user guide

160 / 200
10
5 TECHNICAL DATA
PRIMARY
160
200
Single phased power supply
V
1 x 230 V (-+10%)
1 x 230 V (-+10%)
Frequency
Hz
50/60
50/60
Maximum primary current (MMA)
A
34
43
Maximum primary current (TIG)
A
24
30
Maximum power consumption (MMA)
KVA
7,8
9,9
Maximum power consumption (TIG)
KVA
5,5
6,9
SECONDARY
No-load voltage
V
74
80
Welding current range
A
10 - 160
10 - 200
Welding current at 40 %
A
160
200
Welding current at 60 %
A
135
160
Welding current at 100%
A
105
125
Protection degree
IP 21S
IP 21S
Insulation class
H
H
Norms
IEC / EN 60974-1
IEC / EN 60974-1
Weight
Kg
5,1
5,7
Dimensions
cm
15 x 24 x 32
15 x 24 x 32
6. INSTALLATION
4.1 CONNECTION TO THE MAIN SUPPLY
This unit must be connected to a mono-phase 230V - 50 Hz/60 Hz + ground.
Main supply must be protected by fuses or circuit breaker according to the value I1eff written on the specifications of the
power source.
It is strongly suggested to use a differential protection for the operator’s safety.
4.2 CONNECTION TO EARTH
For the operator's protection, the power source must be correctly grounded (according to the International Protection
Norms).
It is necessary to set a good earth connection with the green/yellow wire of the power cable. This will avoid discharges
caused by accidental contacts with grounded pieces. If no earth connection has been set, a high risk of electric shock
through the chassis of the unit remains possible.

160 / 200
11
7. FUNCTIONS
7.1 MMA WELDING MODE (coated electrode)
- Make the necessary connections to mains and earth as described in “Installation”. Connect the earth and electrode holder
cables to welding plugs + (positive) and –(negative) according to electrode polarity. If necessary, pay attention to electrode
manufacturer instructions.
- Turn the main switch on rear panel to ON position.
- The Power ON indicator lights, indicating that machine is under voltage.
- Select MMA welding (coated electrode) or MMA PULSED welding (both indicators are lit).
- Adjust welding current (Fig.1 - 3), according to the following table:
Electrode diameter (mm)
2,0
2,5
3,2
4,0
5,0
6,0
Adjusting current scope (Amp)
50 - 70
60 - 100
80 - 150
130 - 200
150 - 260
200 - 360
- Hot Start (Fig.1 - 1) - To force arc ignition, adjust hot start percentage of main current and/or time (seconds).
- Arc Force (Fig.1 - 2) - To avoid electrode sticking during welding, adjust arc force current percentage of main current.
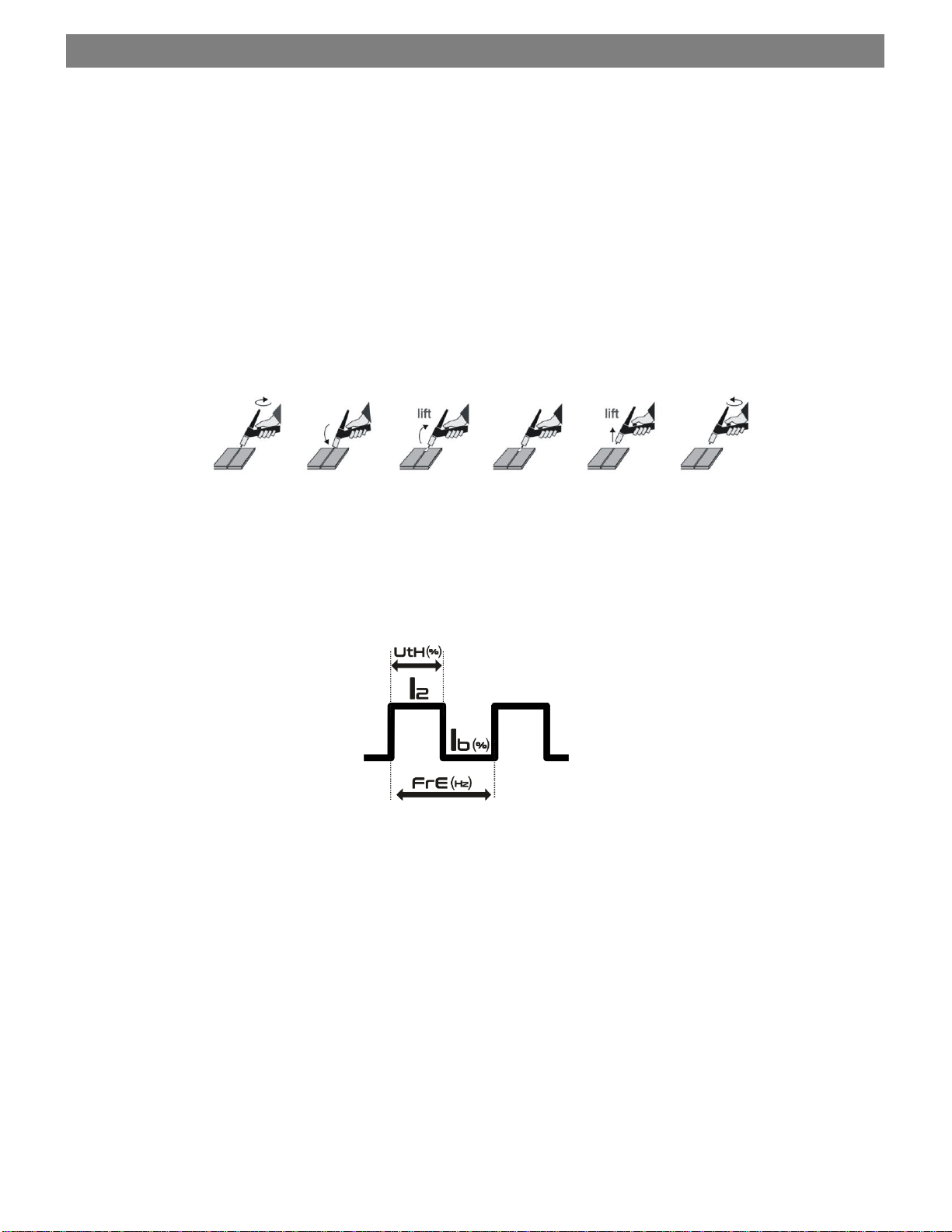
Pulsed MMA welding –the welding current oscillates between a high and a low current value allowing less thermal input in thinner
plates and greater arc control in the most demanding positions (vertical ascending).
- Ib - adjust welding base current in percentage of main current (the digital display shows Ib).
- UtH - WIDTH - adjust the time of the peak current (main current) from 10% to 90% (the digital display shows UtH).
- FrE - PULSE FREQUENCY - adjust pulsed current frequency in Hertz (the digital display shows FrE).
- Start welding.
Fig. 1 –MMA parameters
160 / 200
12
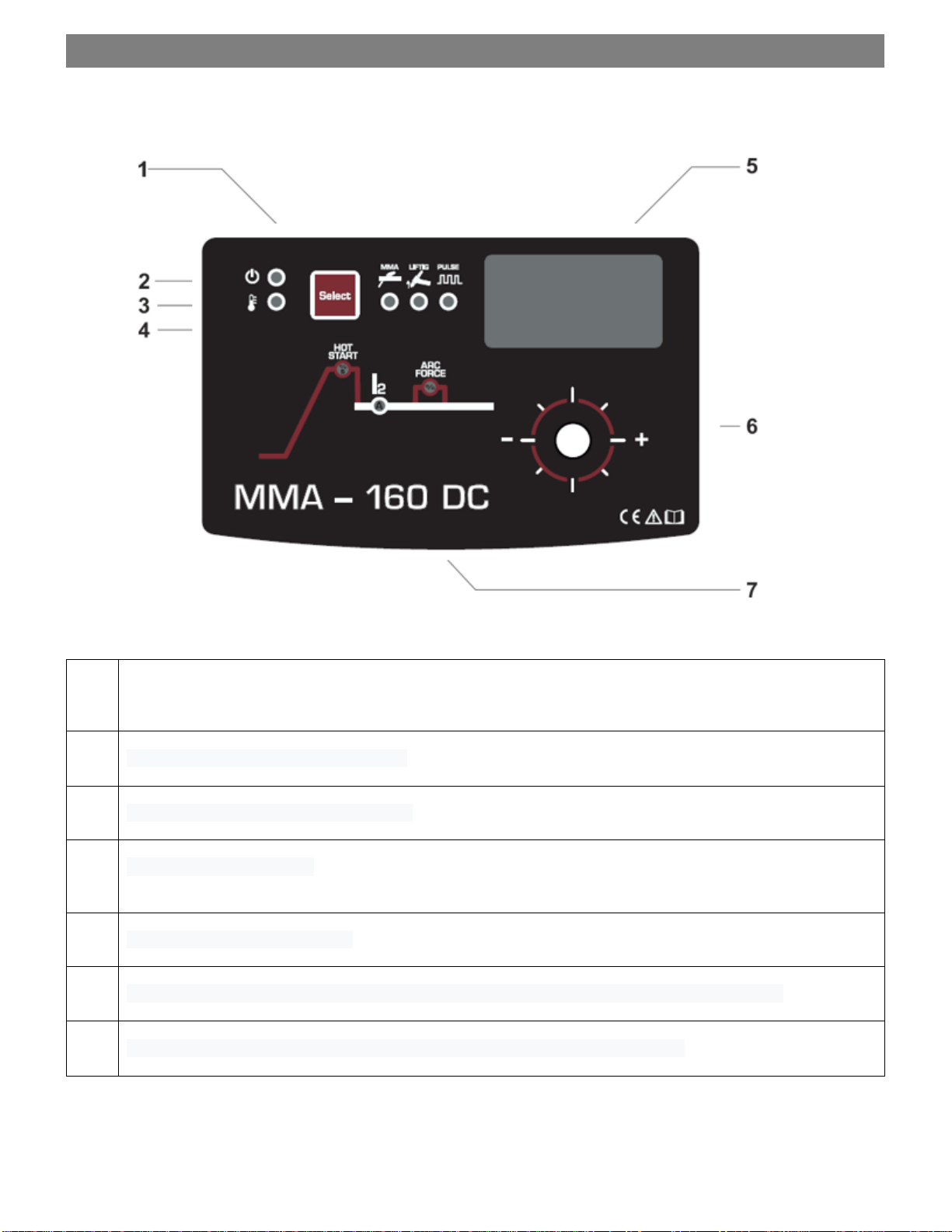
1-opengas 2-contact 3-arcignition 4-welding 5-stop 6-closegas
7.2 TIG WELDING MODE
- Make the necessary connections to mains and earth as described in “Installation”.
- Connect earth cable to positive plug by turning it firmly to right to assure a perfect electric contact.
- Connect TIG torch power cable to negative plug by turning it to right to assure a perfect electric contact.
- Connect gas tube to gas bottle. Check the content of gas bottle, and replace it, if necessary.
- Adjust gas flow 6 l/min and 12 l/min according to the value of the current.
- Apply a tungsten electrode on TIG torch. The electrode must be sharpening according the welding method: TIG DC (tip sharpen).
- Turn the main switch on rear panel to ON position.
- The Power ON indicator lights, indicating that machine is under voltage.
- Select LIFTIG* (TIG welding with contact ignition). There is the PULSED welding mode available (both indicators are lit
respectively).
* LIFTIG:
LIFTIG ignition (by contact) should be used when the high frequency radiations could disturb the functioning of electronic devices
near the welding zone (computers, pace-makers, medical tools, etc).
- Adjust welding current (Fig.1 - 3).
Pulsed LIFTIG welding –the welding current oscillates between a high and a low current value allowing less thermal input in
thinner plates and greater arc control.
- Ib - adjust welding base current in percentage of main current (the digital display shows Ib).
- UtH - WIDTH - adjust the time of the peak current (main current) from 10% to 90% (the digital display shows UtH).
- FrE - PULSE FREQUENCY - adjust pulsed current frequency in Hertz (the digital display shows FrE).
- Start welding.
8. ERRORS DESCRIPTION
Er1 - Overheating - Cuts off machine in case of over temperature
160 / 200
13
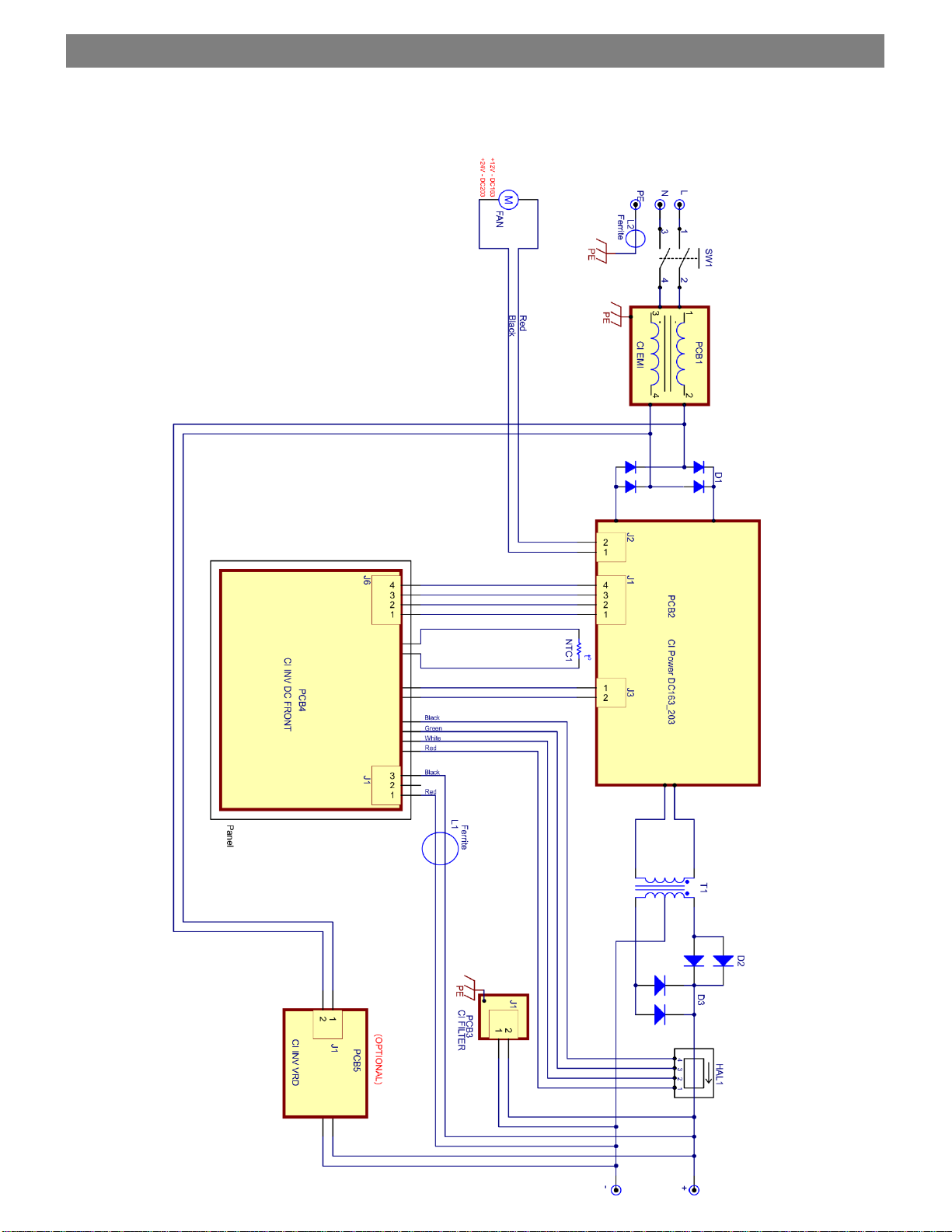
9. ELECTRICAL DIAGRAM
160 / 200
14
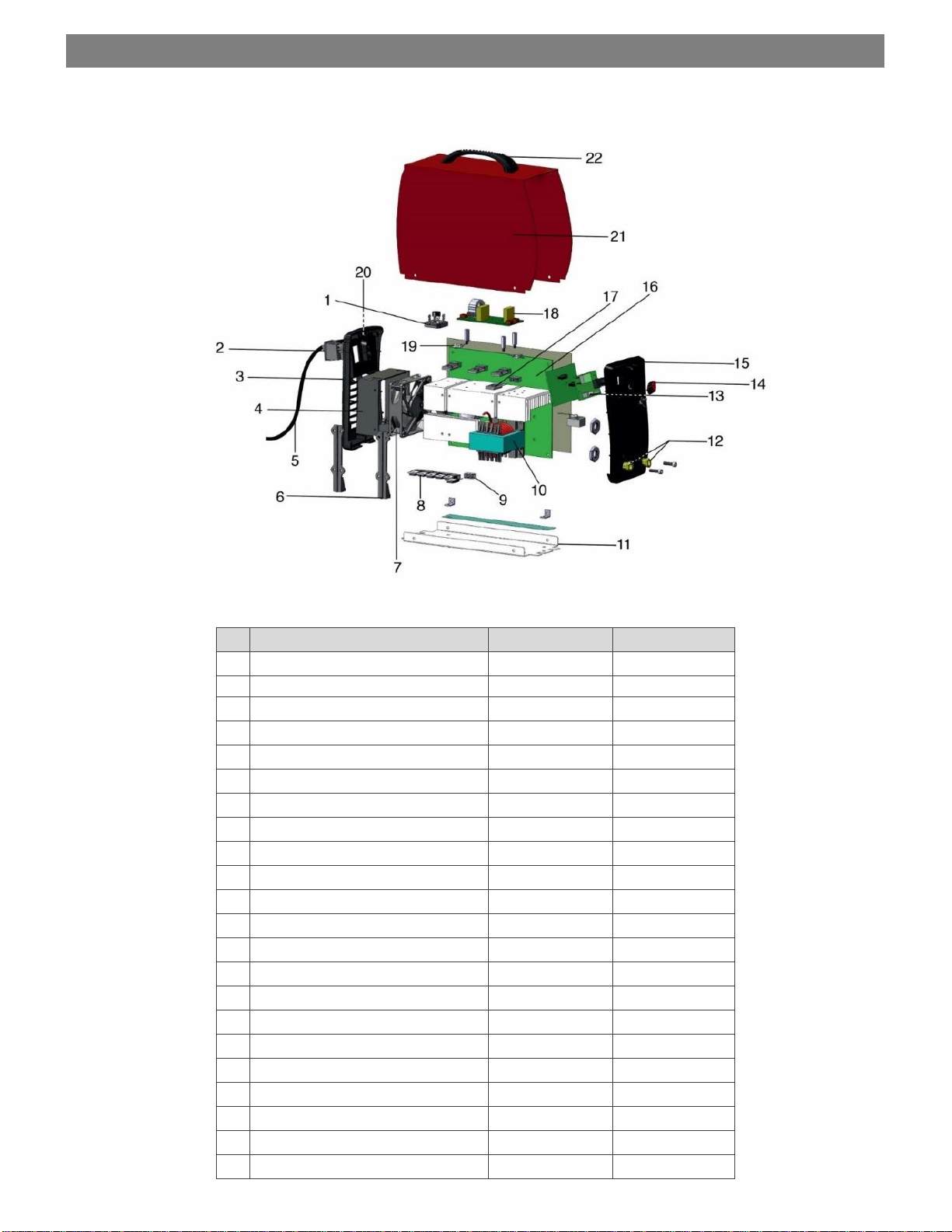
10. SPARE PARTS LIST
Nr.
Description
160
200
1
Rectifier
CO108279
CO108289
2
Main switch
CO109401
CO109401
3
Rear panel
CO9R302G06
CO9R302G06
4
Fan holder
PF109262
PF109262
5
Primary cable
CO2C0252T025B
CO2C0252T025B
6
Support bracket
CO108285
CO108293
7
Fan
CO108284
CO108292
8
Diodes
CO108286
CO108294
9
Diodes isolator
CO98713180
CO98713180
10
Main transformer
CO108276
CO108288
11
Base plate
PF109254
PF109254
12
Quick connections
CO109403
CO109403
13
PCB - Control
PF109645
PF109646
14
Knob
CO109679
CO109679
15
Front panel
CO106610
CO106610
16
PCB - Main control
CO107835
CO107836
17
IGBT module
CO108280
CO108290
18
PCB - EMC
CO108277
CO108277
19
Thermal sensor
CO109397
CO109397
20
Cable clamp connector
CO101584
CO101584
21
Cover
PF109257
PF109257
22
Handle
CO101893
CO101893
160 / 200
15
11. MAINTENANCE
This arc welding equipment should be routinely maintained according to the manufacturers’ recommendations. All access
and service doors and covers should be closed and properly fastened when the arc welding equipment is in operation. The
arc welding equipment should not be modified in any way, except for those changes and adjustments covered in the
manufacturer’s instructions. In particular, the spark gaps of arc striking and stabilising devices should be adjusted and
maintained according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Before carrying out any internal checking or repair work, check that the power source has been disconnected from the
electrical installation by locking and guard devices. Ensure and avoid accidental connection of the plug to a socket. Voltages
are high and dangerous inside the machine.
Despite their robustness, ours power sources require some regular maintenance. Each 6 months (more often in dusty
surroundings):
- The machine must be blown through with dry, oil free compressed air.
- Check for continuity all electrical connections.
- Check the connection of cables and flat top.
Check the good state, insulation and connection of all the equipment and electrical accessories: plugs and flexible supply
cables, conduits, connectors, extension cables, sockets on the power source, ground clamp and electrode holder. These
connections and mobile accessories are marked according to standards, if consistent with the safety rules. They can either
be controlled by you or by accredited firms.
- Repair or replace all defective accessories
- Check periodically that the electrical connections are tightened and do not heat.
Maintenance works of electrical equipment must be entrusted by qualified people (Section VI, Art. 46).
11.1 TROUBLESHOOTING
POSSIBLE CAUSES
CHECK
DISPLAY OFF = NO SUPPLY
ON/OFF main switch is OFF
Switch it ON
Power supply cable is cut
Check cable and connections
No main supply
Check circuit breaker and fuses
Defective ON/OFF main switch
Replace the switch
THERMAL INDICATOR ON = INPUT VOLTAGE OVER RATED LIMIT
Duty cycle over rated (if ambient > 25°C)
Let the machine cool, it will automatically start again
Insufficient cooling air
Clean the air inlets
Very dusty machine
Open the generator and blow it through
Fan doesn’t start
Replace the fan
IMPROPER WELDING
Wrong electrode polarity
Use the right polarity according to the indications of
electrode’s manufacturer
Dirtiness in the weld parts
Clean and eventually degrease the weld parts

160 / 200
16

160 / 200
17

160 / 200
18
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Popular Inverter manuals by other brands

PSC
PSC XANTRA VV ADVANCED Installation and operating instructions

Cotek
Cotek SK120 Series user manual

Kaco
Kaco Powador 30.0 TL3 M/X operating instructions

Sunny Boy
Sunny Boy 700 Technical description

Huawei
Huawei SUN2000-4.6KTL-L1 quick guide

Turbo Energy
Turbo Energy HYBRID 48V 5.0 Series instruction manual











