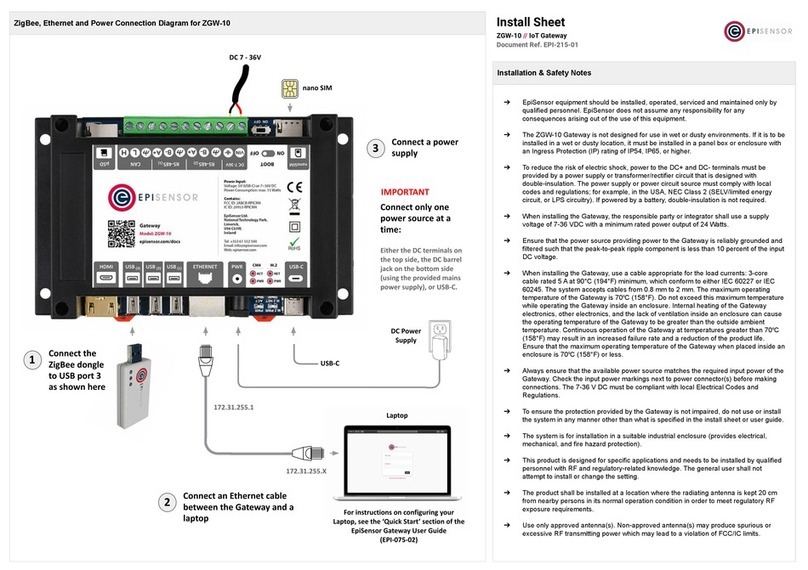
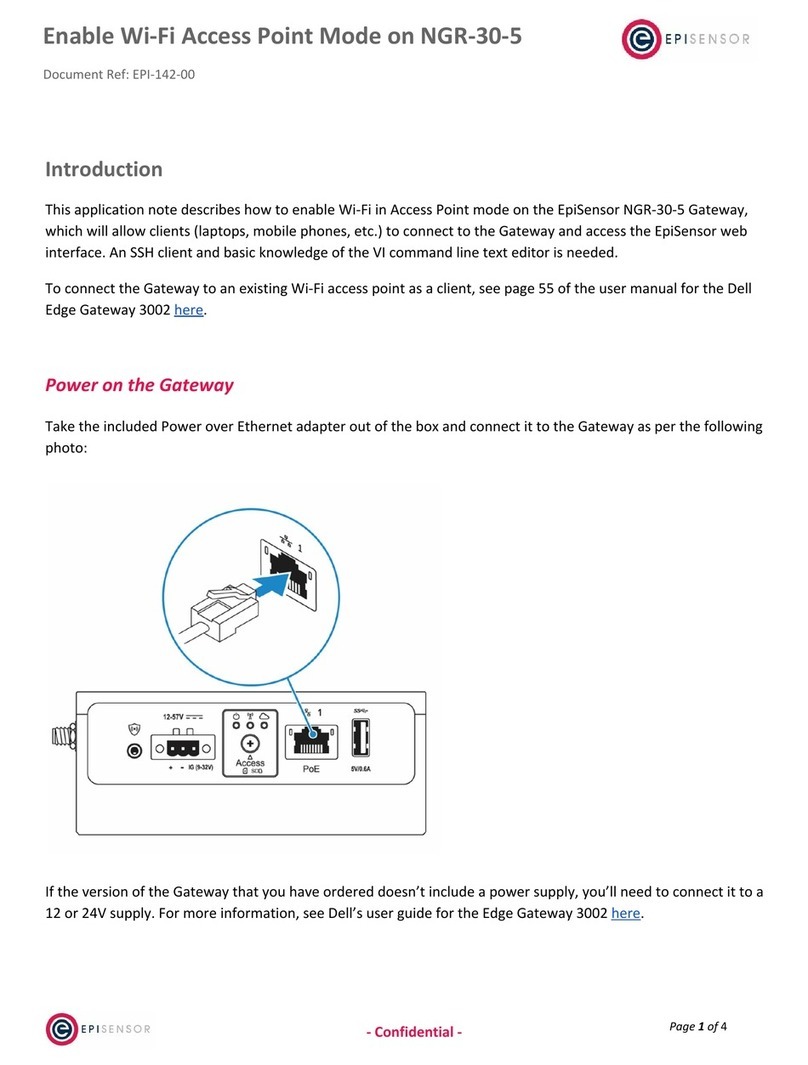
EpiSensor ZGW-10 User manual



















Other manuals for ZGW-10
1
Table of contents
Other EpiSensor Gateway manuals
Popular Gateway manuals by other brands

Fortinet
Fortinet FortiGate 400 Installation & configuration guide

RTA
RTA 460ECMS-N2E user guide

ADT Pulse
ADT Pulse PGZNG1 installation guide

Funkwerk
Funkwerk bintec R230a user guide

Ksenia
Ksenia Porta KSI4300000.300 Installation and programming manual

Cisco
Cisco Small Business Pro SA520 Quick start up guide

ThingsMatrix
ThingsMatrix TMX09 user manual

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications N4100 quick start guide

Avaya
Avaya Media Gateway G350 Quick start for hardware installation

Dension
Dension Lite BT user manual

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications P-660HW-D Series user guide

Fluke
Fluke 3561 FC Getting started manual

LETRIKA
LETRIKA COMMUNICATION GATEWAY user manual

Motorola
Motorola SURFboard SBG6580 Install Sheet

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications PRESTIGE 660 HW Series Quick setup guide

Actisense
Actisense NGT-1 user manual

RTA
RTA 460SCQT-NNA1 Product user guide

TopJet Alert
TopJet Alert Ethernet Gateway quick start guide