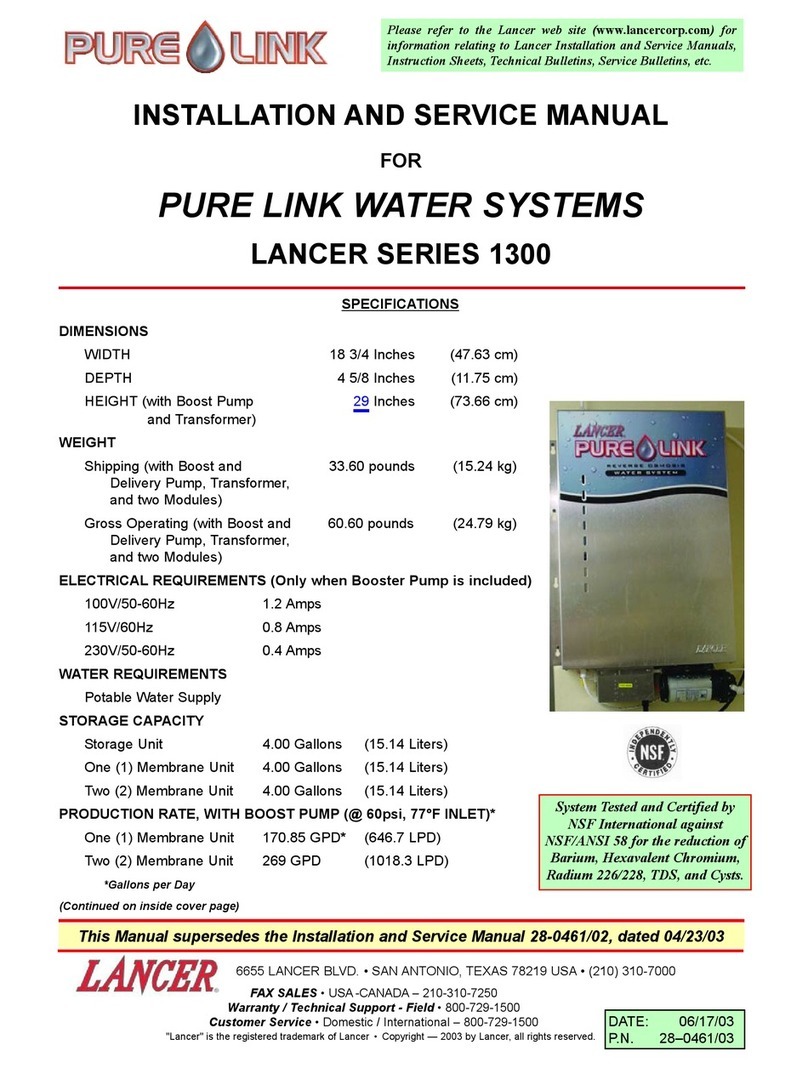
ERL Aquamist HFS3-v3.2 User manual

Page 1
Page 2
HFS3
-
v
3.2
F-IDC tracking PWM water injection system
User manual -v3.2
N:104004on
Whats new on Aquamist HF 3-v3.2 pwm system (August 2022)
The latest v3.2 systems are now shipped with the all new DD 4-v2 dash gauge. It com-
prises the following technical enhancements.
1. Captures and holds peak flow rate
2. hows clear failsafe window settings automatically
3. uper smooth gauge dimming adjustment
4. IDC pre-scaler extended to x6 for E85 integration
5. Accepts inline 5V adaptor for powering external MAP sensor *
6. Decoder for new tank fluid level and temperature with the new multi-level sensor **
* Inline Adaptor is sold separately (available 3rd qtr of 2022)
** Multi-level tank sensor sold separately (designed for 5/10L aquamist tanks, available
3rd qtr of 2022)
Aquamist has been pioneering the IDC (injector duty cycle) tracking water injection system
with constant pressure/PWM inline valve for the last 20 years with great effect. This offers
precise engine load mirroring, resulting in seamless integration with the factory fuel
delivery system. Little or no tuning is required. Very high quality components are part of
the package.
PWM

Page 4
Page 3
Contents:
ystem Check Page
4 Checking the contents of the box
5 Getting started on the installation
Installation
6 Installation for long-term reliability
7 Generic wiring diagram for HF -3
8-9 Choosing jet sizes
ystem testing
10 HF -3 function directory
11-12 Quick tart & manual testing
Gauge
13 Flow management and other trimmers
14 Preparation for test run of the system
Dash gauge
15-16 DD 4-V2 Dash Gauge functions
Fail-safe
17-19 etting up the fail-safe
Advanced
20-21
HF 3-v3.2 extended flow options
22 Trouble shooting guides
Appendix
23 Appendix, Guarantee and Warranty
Checking the contents of the box carefully
This is a “must do” immediately
after unpacking ....
Water pump
Water pumpWater pump
Water pump
Unpack the corrugated sheet carefully. The pump
should be labelled with the original custom
Aquatec/Aquamist logo.
The white box
The white boxThe white box
The white box
♦ 6 of 6mm OD nylon hose (806-261)
♦ 2 of 4mm OD nylon hose (806-266)
♦ HFS-3 Flow Control odule
♦ 0.8 mm water jet (806-323) in plastic bag
♦ 0.9 mm water jet (806-324) in plastic bag
♦ 1.0 mm water jet (806-325) in plastic bag
♦ 1x 4mm Tee compression fitting (806-395) in
plastic bag (new for v3.1 on kit)
♦ 2x 8 x 1/8 NPT jet adapter with plug (806-
357N)l
♦ x water tank adapter 1/8 BSP (806-270), 6mm
compression fitting and in-tank filter (806-258)
♦ 4x 5x40mm bolt, washers and fasteners for pump
♦ 1x 6 grounding stud with washer and nuts and
6mm eyelet for pump ground.
♦ 2x 6mm to 1/8 BSP compression fitting for pump..
♦ 2x 3/8BSP- to 1/8BSP-F reducer for pump.
♦ 1x 4mm to 1/8 BSP compression fitting for FAV.
♦ 1x 6mm to 1/8 BSP compression fitting for FAV.
♦ Water pump harness. 6 of #12 AWG cable and
6 of multi-core cable with blue harness.
♦ 1x Fast acting valve with red harness
♦ 1x flow sensor with yellow harness (HFS-3 only)
♦ 1x water level switch with connector (806-281c)
♦ 1x DDS3v12 Gauge & 1.5 x 8-way cable (HFS-3
only)
♦ 1x Dash button with 6-way cable (HFS-2 only)
♦
1.5 of multi-core with grey capped RJ48 for
. ECU interface, fail-safe and map switching.
♦ olex type 4-way power in harness
♦ Green harness for Direct injection engines (v3).
♦ User manual (on request only for D-I engines)
Note: Please contact your supplier immediately should you discover any missing parts.

Page 5
Getting started on installation
Before installation guidelines
Before installation guidelinesBefore installation guidelines
Before installation guidelines
♦ The pump and water tank are designed to be
fitted in the trunk. Install the water pump below
the water tank if possible.
♦ Ensure all fittings are tightened and leak proof
before filling up with methanol, test it with water
test it with water test it with water
test it with water
first
firstfirst
first.
..
. If a high concentration of methanol mix is
used, please vent the tank’s breather hole exter-
nally. ethanol is poisonous when inhaled.
Assembling the pump in steps
Assembling the pump in steps Assembling the pump in steps
Assembling the pump in steps
♦ Gently assemble the two 3/8 BSP adapters into
the pump without crossing the threads. Ensure
the o-ring is properly seated between the fitting
and the I/O port. Do not over-tighten.
Water tank components
Water tank componentsWater tank components
Water tank components
♦ Ensure the outlet is facing the rear or the side of
the tank. Drill/bore a burr-free 23mm hole. Clear
up all the burred edges and wash the tank thor-
oughly. No debris or plastic shavings should re-
main in the delivery system. 1-2 inches from the
bottom of the tank is ideal.
♦ Screw fit the in-tank filter on the inlet side of the
tank adaptor, insert the assembly into the tank
and tighten the 16 plastic nut. Stop the assem-
bly from rotating with a 6mm allen key into the
centre of the assembly. Do not over tighten to
avoid splitting the rubber gasket seal.
♦
Drill the same hole size for the water level sensor.
IF using a washer tank for supply, do not locate
the Aquamist float sensor near the stock washer
pump. The float arm should swing upwards.
♦
A tall and slim water tank is ideal for this type of
application. This minimises delivery surge prob-
lems at low water level.
Page 6
Installation for long-term reliability
This is the most important section of the HFS-2/3
This is the most important section of the HFS-2/3 This is the most important section of the HFS-2/3
This is the most important section of the HFS-2/3
chapter. Please do not skip reading this part.
chapter. Please do not skip reading this part. chapter. Please do not skip reading this part.
chapter. Please do not skip reading this part.
52mm Dash Gauge (HFS-3 only):
52mm Dash Gauge (HFS-3 only): 52mm Dash Gauge (HFS-3 only):
52mm Dash Gauge (HFS-3 only):
Location is not too critical as long as it is in view of
the driver. There aren’t too many pitfalls on this.
HFS-3 controller box:
HFS-3 controller box:HFS-3 controller box:
HFS-3 controller box:
Please locate the box in a dry location in the passen-
ger compartment. The glove box is a good place.
Please allow plenty of slack to ease accessibility
during tuning and diagnostic work.
Fast acting valve and flow sensor assembly (FAV):
Fast acting valve and flow sensor assembly (FAV):Fast acting valve and flow sensor assembly (FAV):
Fast acting valve and flow sensor assembly (FAV):
The location of this module is most critical to overall
system reliability. It is designed to be installed in the
engine compartment.
This module must be installed in a cool, dry and well
ventilated area away from any heat source. The
bulkhead/fire wall is not always a good location as
most heat is flowing towards it during driving. Avoid
locations near any electromagnetic components
such as the ignition coil, solenoid valves and elec-
tronic motors. It is very important that the hose is
cut cleanly with a razor blade to retain the “round-
ness”. The use of side cutters produces a semi-
round hose end, resulting in a major leak sooner or
later. It is also vital that the hose must be cut
perpendicular/square relative to its length. This is
because the compression fitting has a short hose-
tail. An accurate cut will allow maximum grip on the
walls of the hose.
Ensure the thin rubber gasket is placed between the
FAV coil and electrical plug (red harness) before
tightening. Press the clip of the yellow harness into
the centre section of the flow sensor body, Orienta-
tion is not important. Ensure the electrical plug’s
cable outlet is facing downwards. All cables leading
away from the assembly must be looped downwards
to avoid condensed water trickling into the clip and
plug.
The tank level sensor:
The tank level sensor: The tank level sensor:
The tank level sensor:
Drill/bore the same hole size for the water level
sensor. A 23mm burr-free hole must be used to
ensure a good seal.
The float arm should swing
upwards.
Check that there is ample room for the
sensor arm to swing before drilling.
A tall and slim
water tank is ideal for this type of
application. This
minimises delivery surge problems at low water
levels.
If the stock washer tank is going to be used, do not
mount the float near the stock washer pump. The
motor magnet
will affect the sensor reading properly.
The sensor can be installed 3/4 way down the tank,
preferably at the rear facing w
all of the tank. Never
over tighten or the seal will split; just tighten enough
to prevent leakage, no more.
.
WATER TANK
IN TRUNK BATTERY+
30A
RELAY
DDP5800
160 PSI BYPASS PUMP
MADE IN USA
BY
AQUATEC
THIS PUMP IS FACTORY SET TO 160PS. DO NOT
ATTEMPT TO INCREASE THE BY-PASS VALVE
PRESSURE OR THE LIFE E PECTANCYWILLBE
GREATLY REDUCED. IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED
TO RUN BEYOND 50% METHANOL BECAUSE OF
FLAMMABILITY AND VAPOUR INHALATION CAN
BE HAZARDOUS TO YOUR HEALTH.
TO FAV ASSEMBLY
TO CONTROLLER
(BLUE HARNESS)
15A FUSE

Page 7
Generic wiring diagram for HF -2/3
Page 8
Choosing jet sizes
This is a general guide only:
- 100% water ................................1cc/hp.
- 50:50 methanol/water ............... 1.5cc/hp.
- 100% methanol ............................2cc/hp
Choosing the jet by calculation:
First determine the target HP and multiply the
result by the preferred ratio recommended above.
Pick the nearest jet/jets size to match the flow.
Don’t forget to subtract the boost pressure from
the line pressure of 160psi. For example, if you are
boosting 25psi, you should select the jet flow at
135 psi. Allow 10-15% drop due to system loss.
Alternatively, pump pressure can be increased to
offset the boost pressure with a 1/16“ allen key in
the front of the pump head. 1/2T = ~25psi
Pressure vs Flow
(compensated)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
550
600
6
7
5
00
0
0
760 0 80 90 100 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200
Flow (cc/min)
Pressure (psi)
1.2mm (M7.5)
1.0mm (M6.0)
0.9mm (M5.3)
0.8mm (M4.5)
0.7mm (M3.9)
0.6mm (M3.2)
0.5mm (M2.6)
0.4mm C (M1.9)
0.4mm (M1.5)
0.4mm A (M0.8)
11.4.15
WATER TANK
IN TRUNK
GND
FLOW
ml/m100 20 0 300 4 00
Aquamist
WL W HSC
WATER LEVEL
M
a
d
e
in
E
n
g
la
n
d
W. IN ECTIO N
12V
+
HEAD LAMP
SWITCH
PUMP RELAY & LEVEL SENSOR
FAV & FLOW SENSOR
(ENGINE BAY)
FUEL
INJECTOR(-)
FUEL INJECTOR(+) or
IGN. SW+ (pre-crank)
MAP SENSOR (optional)
DDP5800
160 PSI BYPASS PUMP
MADE IN USA
BY
AQUATEC
THIS PUMP IS FACTORY SET TO 160PS. DO NOT
ATTEMPT TO INCREASE THE BY-PASS VALVE
PRESSURE OR THE LIFE E PECTANCYWILLBE
GREATLY REDUCED. IT I S N OT RECOMMENDED
TO RUN BEYOND 50% METHANOL BECAUSE OF
FLAMMABILITY AND VAPOUR INHALATION CAN
BE HAZARDOUS TO YOUR HEALTH.
FLOW
806-239
FAST
ACTING
VALVE
FAST ACTING VALVE
AND TURBINE FLOW
SENSOR ASSEMBLY
+12V 15A
(fused and
switched)
30A
RELAY
15A FUSE
DASH GAUGE
(DDS4v2)
33OHM 7W
K1C12H
COIL 12VDC
3A 30VDC/125VAC
K1C12H
COIL 12VDC
3A 30VDC/125VAC
5A FUSE
POWER
FAV USER
v3.2

Page 9
Page 10
HF 3-v3.2
1. DASH GAUGE (P.15)
2. 12V, HEAD LIGHT SWITCH and GROUND (P.11)
3. FAST ACTING VALVE in ENGINE AY (P.6)
4. WATER FLOW SENSOR (FAV CLUSTER) (P.6)
5. ECU INTERFACE AND FAILSAFE (P.11/18)
6. WATER TANK and PUMP in TRUNK AREA (P.5)
7. DIRECT INJECTED ENGINES (instructions in bag)
8. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION Y USER (P.12)
9. FLOW & SYSTEM MANAGEMENT TRIMMERS (P.13)
10. IDC PRE-SCALER (P.20)
Since the introdution of the Aquatec 5800 se-
ries pump in 2011, we have received no re-
port on any related issues on running high
ratio of methanol.
Great care and attention must be taken to
ensure the fluid tank is capable of handling
methanol and is designed for this type of appli-
cation. These tanks are normally termed as a
Fuel Cell and are available from most reputable
racing parts suppliers. Follow the maker’s
guidelines carefully.
The breather hole on the tank must be vented
externally with a suitable hose. All fluid deliv-
ery hoses and fittings must be free of all leaks.
Ensure the area is well ventilated and isolated
from the driver’s compartment. Take whatever
measures to avoid any methanol fumes build-
ing up in trunk area.
Using a engineered tank cap with an inbuilt
checkvalve capsule will not alleviate the fume
from escaping out of the tank and into the
cabin area. This is because pure methanol has
a saturated vapour pressure of 2psi+ at 22C
(70F) and over 4psi @35C (95F). It is most likely the cabin
will reach those temperatures
on a hot day or parked on an
open air car park under the sun.
Higher crack pressure caps will
only allow several psi of pres-
sure trapped in the tank and
may causing leaks or cracking...
For this reasons, please vent
the tank to the outside of the
cabin. ethanol fume is odour-
less and extremely toxic when inhaled.
ethanol is highly flammabl
ethanol is highly flammablethanol is highly flammabl
ethanol is highly flammable
ee
e
. The main delivery hose to
the engine bay should be routed underneath the car. En-
sure it is securely clipped and fastened. Avoid kinks and
close proximity of moving parts and heat producing compo-
nents. Please treat this recommendation seriously. If in
doubt, ask advice from a professional person familiar with
this kind of application. DO NOT take any undue risks. It is
recommended that a suitable fire extinguisher is placed
within easy reach of the driver. All electrical connections
must be properly tightened to avoid spark production.
Managing Methanol usage on the system
33OHM 7W
K1C12H
COIL 12VDC
3A 30VDC/125VAC
K1C12H
COIL 12VDC
3A 30VDC/125VAC
5A FUSE
POWER
FAV
USER
2 3 4 5 6 7
v3.2
8
9
10

Quick tart
Page 11
Mechanical work (checklist :
Only after testing with distilled water should
methanol be used. BEFORE hooking up line to
the jet the system should be manually activated
to flush any possibly dirt/debris from the lines.
Wiring work (checklist :
The HFS-3 is pre-configured from the factory.
Plug in the following harness for testing the
power supply into the controller.
1. 4-way Power-in connector:
1. 4-way Power-in connector: 1. 4-way Power-in connector:
1. 4-way Power-in connector:
- Red ................ Switched 12V (IGN SW#2)
- Black ............... Chassis ground
- White .............. Chassis ground
- Purple .............. Head lamp switch (optional)
2. Signal to the grey RJ48 connector:
2. Signal to the grey RJ48 connector:2. Signal to the grey RJ48 connector:
2. Signal to the grey RJ48 connector:
- Red ................. Ignition switched 12V
- Green ............. Fuel injector (-) pin
- Blue .................. AP sensor (optional)
3. grey flat cable to the Dash Gauge
3. grey flat cable to the Dash Gauge 3. grey flat cable to the Dash Gauge
3. grey flat cable to the Dash Gauge
Power-up procedure:
Please follow this procedure “strictly” or per-
manent damage to the system may result. Do
not SKIP
SKIPSKIP
SKIP any steps please....
1. Ignition key on the “OFF” or “0” position:
1. Ignition key on the “OFF” or “0” position:1. Ignition key on the “OFF” or “0” position:
1. Ignition key on the “OFF” or “0” position:
- Dash Gauge button is depressed (system on)
- No leds should be lit anywhere.
2. Ignition key on the “ACC” or “#1” position:
2. Ignition key on the “ACC” or “#1” position:2. Ignition key on the “ACC” or “#1” position:
2. Ignition key on the “ACC” or “#1” position:
Absolutely no change, same as the above conditions.
3. Ignition key on the “pre-cranking” or “#2” position:
3. Ignition key on the “pre-cranking” or “#2” position:3. Ignition key on the “pre-cranking” or “#2” position:
3. Ignition key on the “pre-cranking” or “#2” position:
- Do not crank. Observe the gauge and controller leds
- Yellow led on the gauge will stay lit for 5-10s before
the rest of the gauge lights up.
4. Start the engine and let it idle for a minute or so:
4. Start the engine and let it idle for a minute or so: 4. Start the engine and let it idle for a minute or so:
4. Start the engine and let it idle for a minute or so:
- The green led on the controller should flicker
- The flicker should speed up with engine speed.
- If the system behaves as stated above, you have
successfully wired up the HFS-3!
Now plug in the rest of the harnesses:
Now plug in the rest of the harnesses:Now plug in the rest of the harnesses:
Now plug in the rest of the harnesses:
- The “S” led should confirm the presence of the flow
sensor.
- The yellow led will activate if the tank level is low.
This completes the basic system test. The next stage
will be testing the system manually by using the
jumper links on the controller board. You will need a
small 3/32“slotted screw driver. .
Page 12
Quick tart - ystem setting and manual testing.
Knowing the default controller functions:
(function explained from left to right)
(function explained from left to right) (function explained from left to right)
(function explained from left to right)
1.TRIG:
The system is set to be triggered by IDC (fuel injec-
tor duty cycle) % from factory. The alternative trigger
mode is PS ( anifold Pressure Sensor). Flow will
be progressive depends on “ ODE” setting.
2. MODE:
- PW mode (factory default):
PW mode (factory default): PW mode (factory default):
PW mode (factory default): Flow can be progres-
sive with IDC, Boost or Both (P20.4).
-
--
- SSG (single stage) mode:
SSG (single stage) mode:SSG (single stage) mode:
SSG (single stage) mode: “all on” or “all off”
3. ON: Enabled FAV (default) or disable FAV.
4. PRK: Parking for unused jumper link.
5. M. TEST:
- FDC:
- FDC:- FDC:
- FDC: Link to display F-IDC on gauge (testing only)
- BAR
- BAR- BAR
- BAR: Link to test bargraph with the “SC” trimmer.
- SYS:
- SYS:- SYS:
- SYS: This link can be used to activate the pump only
for the purpose of priming the system. Unlink the #3
(FAV) to disable FAV to avoid hydro-lock.
6. CEL:
Boost cut without CEL (check engine light) activa-
tion. This is only used in conjunction with internal
relay fail-safe output. DR1 = No CEL.
7. SET FAIL SAFE:
- CLP (factory default):
- CLP (factory default):- CLP (factory default):
- CLP (factory default):
Output voltage is clipped
from 8V to 5V.
- FS0 (factory default):
- FS0 (factory default):- FS0 (factory default):
- FS0 (factory default):
Fail-safe output to ground
upon activation.
- FS1
- FS1- FS1
- FS1
: Fail-safe output switches from 0 to 5V or 8V
upon activation.
(this fail-safe output option is on the orange wire of
the grey harness.
-
DHB (defaut=linked)
DHB (defaut=linked)DHB (defaut=linked)
DHB (defaut=linked)
:“Disable High Boost“. When
the gauge is switched off, all fail-safe outputs be-
come activated. This safe guards any engine dam-
age. If the DHB is ”unlinked“, the yellow LED
(water level) will be lit when the gauge is switched
off, giving the user a reminder that the engine is not
protected againist ”High Boost“.
- DFS (defaut=unlinked)
DFS (defaut=unlinked)DFS (defaut=unlinked)
DFS (defaut=unlinked)
:“Disable Fail-Safe“. Link to
stop all fail-safe activation during test or preliminary
test run prior to finalizing fail-safe window. .
8. DEFAULT:
Factory default setting (gold dots)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8

Page 13
Flow management and other trimmers
Setting the onboard trimmers:
(default=12 o’clock
The system
The system The system
The system requires no trimming from
the factory. If the user wants to alter the
flow and other parameters, just use a
small screw driver to complete the task.
Below are the working details of each
trimmer. (left to right).
1. LED panel:
Three leds monitor the real time opera-
tion of the system,
- Green (F-IDC):
- Green (F-IDC): - Green (F-IDC):
- Green (F-IDC): Blinks upon successful
detection of fuel injector duty cycle sig-
nal. The blink rate and brightness in-
crease with engine speed and duty
cycle respectively.
- Amber (THRES):
- Amber (THRES): - Amber (THRES):
- Amber (THRES): At 42% F-IDC (de-
fault), this led will activate, confirming
the system is triggered and delivery
commences.
- Red (95% DC):
- Red (95% DC):- Red (95% DC):
- Red (95% DC):
When the water/methanol duty cycle is
approaching 95%, The red led begins to turn on, indicating that
you have almost reached the maximum flow of your system.
ore flow requires additional jets.
2. Trimmers for fine tuning:
- THRES:
- THRES: - THRES:
- THRES: Factory set to 42%, User adjustment range is be-
tween 12-72%.
- GAIN:
- GAIN:- GAIN:
- GAIN: User can define the slope of water/
methanol relative to F-IDC from -25 to
300%. The factory slope is set to 1:1 ratio
of fuel duty cycle. Useful tool to compen-
sate low F-IDC when large fuel injector is
used. It can also be used to trim flow at
high F-IDC.
- FS-DL:
- FS-DL: - FS-DL:
- FS-DL:
Fail-safe delay
to undue fail-safe activation due to
spike and noise signal from the flow sensor. The factory
default setting (12-o’clock) is 400mS (milli-second). User ad-
justable between 200mS to 600mS.
- DI :
- DI :- DI :
- DI :
This trimmer works in conjunction with the head lamp
switch. When it sees a 12V signal, the trimmer becomes
active. This coincides with night drive conditions. The high-
intensity led used on the dash gauge is too bright for night
motoring. so wiring in the “purple wire” from the 4-way power
plug to the head lamp switch is essential. Do not wire it to the
car’s interior dimming circuit or unexpected results may occur.
Page 14
Preparation for a test run of the system
1. First step - system check list:
a.
a.a.
a. Tank and pump is fully secured and leak free.
b.
b.b.
b. The FAV assembly is securely located in a cool
and dry spot of the engine bay.
c.
c.c.
c. The controller is accessible and can be secured
down with minimum movement during motoring,
d.
d.d.
d. The jets are securely installed in the inlet tract.
e.
e.e.
e. Dash gauge installed.
2. Priming and purging of the system:
a.
a.a.
a. Fill up the tank with water half way.
b.
b.b.
b. Disconnect the 6mm hose from the FAV assem-
bly and put the hose into a container securely.
c.
c. c.
c. Ignition switch in pre-crank position and gauge is
switched on.
Uncover the controller and pull out the
“FAV” jumper (disabling the FAV) and put it to the
link marked “SYS”. The pump should power up and
water should come out of the 6mm hose within a
few seconds, Let it run for a 10-20 seconds so that
trapped air and debris are purged.
d.
d.d.
d. Listen to the pump during the priming period; it
should go very quiet after completion of purging
procedure. If not, repeat step “c”.
e.
e. e.
e. Upon successful completion of the above, rein-
state the 6mm hose into FAV assembly.
3. Testing the spray pattern of the jets:
a.
a.a.
a.
Secure an unused jet onto the windscreen and
connect it to the outlet port of the FAV assembly.
b.
b.b.
b.
Activate the system by linking up “ FAV” (default)
and “SYS” on the controller. You should see an instant
full-cone spray at the jet. Do it for a few seconds only.
You can repeat the test with the remaining jets. At the
same time the gauge should register a few bars.
Remove the “SYS” test link.
4. Activate the system by F-IDC:
a.
a.a.
a.
Set the far left trimmer to fully counter-clockwise.
Crank the engine and leave it to idle, you should see
the blinking green led on the controller board.
b.
b.b.
b.
Blip the accelerator paddle sharply to induce an
artificial load. The amber led should respond. A faint
but noticeable spray should develop at the jet.
5. Road test the system:
Still with jet on windscreen, make a short drive and
confirm the spray is progressive with load. After a
successful road test, reconnect the hose to the inter-
nal spray jets. This concludes the system test,
The system is ready for the next stage - fail-safe
setting. At anytime if there is a problem, please con-
tact us.
W AT E R F L O W
FUEL FLOW
+200%
-25%
IDC GAIN
trip point
95%
MAX

Dash Gauge Functions cont.
9. Under-range setting potentiometer (WL
This setting can indicate partial blockage and trapped
air inside a delivery hose. Again a 20-stepped poten-
tiometer is used. Each click represents a fixed por-
tion of the window width of 8-bars. Gauge will show
setting status in real time during adjustment.
10. Over-range setting potentiometer (WH
It is just as important to monitor over-range condi-
tions as well as under-range flow conditions. If a leak
develops close to the water jet and starves the
engine of the water, the user must know this condi-
tion. A 20-stepped potentiometer allows accurate
and repeatable adjustment range. Gauge will display
the setting status during adjustment.
WL covers the lower 4 bars of the display and the
WH covers the upper 4 bars. Figure on the right
illustrates the span of the coverage. Setting is very
simple once SC is calibrated.
NOTE:
NOTE:NOTE:
NOTE:
In order to make the
fail-safe adjustment
easier, it is recom-
mended to set the bar-
graph to display 5-6
bars at maximum
flow. This way, the
fail-safe window can
span from the centre
outwards.
If the WL and WH is set at 12 O’clock, the fail-safe
window width is approximately spanned between
3-7 bars. This is a good starting point.
inor trimming for the WL is necessary if the water
injection trigger point is set to commence earlier.
Recap:
1. “B” led
1. “B” led1. “B” led
1. “B” led
(right of the bargraph) will only stay
activated if the flow is inside the fail-safe window
during injection period, unless the DFS (Disable
Failsafe jumper is linked reminder)
2. The two “yellow” leds
2. The two “yellow” leds2. The two “yellow” leds
2. The two “yellow” leds
Both leds will activate
when fail-safe is triggered. Only the lower led illumi-
nates during low tank level.
As soon as the “fail-safe” is tripped, there will be a
3 second reset period before it reset while the
fail-safe drops boost.
When gauge is switched off, expect low boost and
safe map unless the DHB jumper is unlinked.
Please use the failsafe option offered as even your
application is not water/methanol critical.
WL WH
failsafe window width
coverage (20-clicks)
page16
Knowing DD 4-v2 Dash Gauge
1. 8-element Bargraph (0-100% Fullscale
Each segment is equivalent to a fixed percentage of
the total flow of the sensor scaled by the SC poten-
tiometer.
2. “S” indicates flow sensor connected.
The letter “S” (sensor) must be lit after power up
and stay on to show the flow sensor cable is con-
nected and on-standby.
3 Fail-safe activation LED (normally off
This LED turns on at approximately the same time
as the lower LED (water level) when failsafe is
triggered. Otherwise stays off at all time. This helps
to identify between low tank level and true failsafe
activation.
4. Water level LED (normally off
This LED will only activate when tank level is at its
lowest. Remains on until tank is refilled (even system
is turned off). It also prevents the system from turning
on If it stays on if tank level is high, it merely reminds
the users the DHB jumper is unlinked
5. SC (Sensor Calibration - default table
Scaling the flow sensor to display 5-6 bar during nor-
mal motoring. Treat this as an indictor similar to a n
engine temperature gauge. Hi-res output can be read
from yellow wire on the ‘USER’ port.
6. Backlit legend
Legend displays % of full scale of 8-bars
7. “B” High Boost Enabled LED
Stays on at when system is operating normally after
triggering. It also stays on if the DFS jumper is linked
at all time, reminding failsafe is disabled.
8. System on/off button (monentary
This multi-function button will access future upgrades
1.
1.1.
1.
Hold 3-4s to switch on the system, subsequent
short press will turn off the system immediately.
2.
2.2.
2.
Once system is turned on, this button can access
the multi-level tank sensor**. Press and hold to initi-
ate count down sequence from full 8 bars to 1.
a)
a)a)
a)
release at 7th bar displays fluid levels in the tank on
gauge (8-levels).
b)
b)b)
b) release at 6th bar displays water temperature be-
tween -30C to +40C on gauge “0”C on 4th bar.
** Sold separatelty.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Page 15

Page 17
etting up the fail-safe
etting up the alternative Fail-safe Channels
Page 18
1. The MAP Switching Channel:
The orange wire from the grey RJ48 connector is
a voltage based AP Switching for an ECU
equipped with this input. This wire is factory config-
ured to send out a voltage of 4.7V DC under a “no
fault ” condition, from idle to full boost. This volt-
age will switch to 0v upon a fail-safe activation or
the gauge is switched off.
Other voltages such as 0, 5V or 8V can be user
configured. This is by far the most effective
method to save your engine from lack of water
injection. A jumper link can invert the AP switch
output if necessary.
Although it is simple and convenient to use a
single wire to communicate a fail-safe activation, this can
only be achieved “as long as” the system is powered up
properly. The alternative way is to use the on-board relay
to convey a fail-safe activation since the relay will guaran-
tee a “make or break” circuit when system’s power is
lost or a blown system fuse.
2. Change-over relay: (HFS-3
The HFS-3 has an onboard relay to supply a set of
voltage-free, change-over contacts for the sole use of
fail-safe activation. It can be used to perform various
tasks to save your engine. Contact rated up to 1 amp.
Please
Please Please
Please refer to page 19 for full switching se-
quence under various conditions.
Example1: OE boost control valve (BCV):
Example1: OE boost control valve (BCV): Example1: OE boost control valve (BCV):
Example1: OE boost control valve (BCV):
Disabling the OE boost control valve.
“Cut and splice” the boost control cir-
cuit. White to “ECU side”. Brown to
“BCV side”. You will need to link the
“Anti-CEL” option on page 12.6 to avoid
the onset of CEL during fail-safe activa-
tion. Dummy resistor replaces the BCV.
Example 2: (third party boost controllers)
Example 2: (third party boost controllers) Example 2: (third party boost controllers)
Example 2: (third party boost controllers)
Disabling the third party electronic boost
control system. “Cut and splice” the
pulsed wire to the BCV. White to the
“Controller” and Brown to the “BCV”
side.
This option will not work with EBC (Elec-
tronic Boost controller) utilizing a stepper
motor to control boost. HKS-EVC is such an ex-
ample. Use the AC valve option on page 17.
Note: During the initial testing period soon after
Note: During the initial testing period soon after Note: During the initial testing period soon after
Note: During the initial testing period soon after
the installation, you can disable the fail-safe from
the installation, you can disable the fail-safe from the installation, you can disable the fail-safe from
the installation, you can disable the fail-safe from
activation by connecting the “DFS” (Disable Fail
activation by connecting the “DFS” (Disable Fail activation by connecting the “DFS” (Disable Fail
activation by connecting the “DFS” (Disable Fail
Safe) jumper link.
Safe) jumper link.Safe) jumper link.
Safe) jumper link.
orange
LACK
ROWN
WHITE
This final stage should be quick, simple and
effective. Please read it before proceeding.
It will save you time in the long run.
If fluid flow falls inside the fail-safe detection window
after triggering, no action will be taken. Setting up
the width of the window to accommodate the full
fluid flow is vital.
Setting up the fail-safe should only be done after the
Setting up the fail-safe should only be done after the Setting up the fail-safe should only be done after the
Setting up the fail-safe should only be done after the
car has been tuned or the jet/jets sizes are finalized
car has been tuned or the jet/jets sizes are finalizedcar has been tuned or the jet/jets sizes are finalized
car has been tuned or the jet/jets sizes are finalized.
Recommended steps to set up the fail-safe:
Recommended steps to set up the fail-safe:Recommended steps to set up the fail-safe:
Recommended steps to set up the fail-safe:
1. Adjust the “SC” to display 6 bars at manual test.
jJets are placed outside the engine to avoid hydrolock.
2. Rinstate jet/s into the engine. ental note the
number of bars displayed on the at spool up & WOT.
3. Set the WL to match the number of spool-up bars.
It is recommended to allow 2-3 clicks below that
point to avoid false triggering. Full span of WL is
20 clicks, covering from 0 bar to 4 bars.
4. Same procedure is used to set up the WH, allow-
ing 2-3 clicks above 6 bars. Full span of WH is 20
clicks covering 4-8 bars.
This completes the fail-safe set-up ...
Options after the fail-safe is triggered:
The most common way to minimize engine damage
in the absence of injection is to reduce the boost
pressure.
1.
For engines with an electronic boost control
For engines with an electronic boost control For engines with an electronic boost control
For engines with an electronic boost control
valve
valvevalve
valve:
The grey harness contains a set of relay
contacts that goes open circuit when the fail-safe is
triggered. See page 18 and 19 for more details.
2. For engines with BC (manual boost controller):
For engines with BC (manual boost controller):For engines with BC (manual boost controller):
For engines with BC (manual boost controller):
The onboard fail-safe relay can be used to control a
3-port solenoid valve to by-pass the BC or a step-
per motor type of boost controller. Essentially, this
directs full boost to the wastegate.
3.
3.3.
3.
For an engine with AP switching capabilities:
For an engine with AP switching capabilities:For an engine with AP switching capabilities:
For an engine with AP switching capabilities:
The orange wire on the grey connector has a dedi-
cated output to perform such a task. This pin can be
user configured to match the signal requirement of
the “third party” ECU to switch AP. See page
18-1 for more details. This pin is factory configured
to give a 5V for “OK” and “0v” is “flow fault”
aximum current of this output is 5mA.

Page 19
Page 20
Relay Fail-safe output switching tables
Fail-safe relay output truth table:
Fail-safe relay output truth table:Fail-safe relay output truth table:
Fail-safe relay output truth table:
The above table is created to simplify the fail-safe
relay switching status under all circumstances.
White, Brown and Black wires are located in the
grey harness. The relay contacts are capable of
switching 1A@30V continuous and 3A pulsed due
to the 24awg wires used.
Based on the table above, you can use these con-
tacts to either connect or disconnect electro-
mechanical components such as a wastegate con-
trol valve or third party fail-safe devices. The con-
tacts are gold flashed so it can be used for low
current signal switching.
GAUGE ON
IGNITION @ PRE-CRANK/RUN
GAUGE ON (NOT TRIGGERED)
IGNITION @ PRE-CRANK/RUN
GAUGE ON (TRIGGERED)
FLOW INSIDE FAILSAFE WINDOW
GAUGE ON (TRIGGERED)
FLOW OUTSIDE FAILSAFE WINDOW
GAUGE ON (FAILSAFE TRIGGERED)
RESET AFTER ~3 SECONDS
GAUGE OFF
IGN.SW @ PRE-CRANK/RUN
IGN.SW - ACCESSORY
IGNITION SW. KEY - OUT
NORMAL SYSTEM OPERATION
FAIL SAFE ACTIVATED
DH LINKED
(DEFAULT)
DH UNLINKED DFS LINKED
DFS UN-LINKED
(DEFAULT)
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
WHITE
ROWN
LACK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LACK
ROWN
WHITE
Advanced system configurations (optional)
1. System configuration (factory use
1. System configuration (factory use1. System configuration (factory use
1. System configuration (factory use
Reserved
ReservedReserved
Reserved
2. Rescale flow signal output:
Solder link this a reduce the flow signal by 50%
Solder link this a reduce the flow signal by 50%Solder link this a reduce the flow signal by 50%
Solder link this a reduce the flow signal by 50%
3. IDC signal detection polarity:
3. IDC signal detection polarity:3. IDC signal detection polarity:
3. IDC signal detection polarity:
Solder link to change edge detection to positive.
Solder link to change edge detection to positive. Solder link to change edge detection to positive.
Solder link to change edge detection to positive.
4. Configuring 70% IDC & 30% MPS:
(a) 100% IDC:
(a) 100% IDC:(a) 100% IDC:
(a) 100% IDC: system default from factory
(b) 70% IDC / 30% PS:
(b) 70% IDC / 30% PS:(b) 70% IDC / 30% PS:
(b) 70% IDC / 30% PS: If AP sensor signal is
available. Solder link PS.
(c) 100% PS:
(c) 100% PS:(c) 100% PS:
(c) 100% PS: Cut IDC link and solder link PS link.
5.
IDC pre-scaler (topside :
The option allows the
system to match the
incoming IDC signal.
Can be used for oversized
injectors with low duty
cycle. Select x2.5 for all
direct injection engines.
6. Select MAP sensor range:
(a) Absolute:
(a) Absolute: (a) Absolute:
(a) Absolute: This can be used for any
sensors with 0-5V output, such as throttle posi-
tion, mass air flow sensors etc.
(b) 2.5 bar AP sensor:
(b) 2.5 bar AP sensor: (b) 2.5 bar AP sensor:
(b) 2.5 bar AP sensor: Select this link to con-
vert a 2.5 bar AP sensor to read from atmos-
pheric to 22psi full scale 0-5V output.
(c) 3 - 3.5 bar AP sensor (default):
(c) 3 - 3.5 bar AP sensor (default): (c) 3 - 3.5 bar AP sensor (default):
(c) 3 - 3.5 bar AP sensor (default):
Select this link to convert a 3.5 bar AP sensor
to read from atmospheric to 36psi full scale 0-5V
output.
7 Flow map table:
(a)
(a)(a)
(a) Unlinked: two large jets (default).
(b)
(b)(b)
(b). Solder link 1&2 for single jet.
(c)
(c)(c)
(c) Solder link 2&3 for three very large jets .
IN
1 2 3 4 765
x1.00
x4.00
x1.75
x4.75
x2.50
x5.50
x3.25
x6.25

Page 21
Page 22
Trouble shooting
New installation power up issues
(failsafe disabled)
(failsafe disabled)(failsafe disabled)
(failsafe disabled)
1. System does not power up at “pre-crank”:
1. System does not power up at “pre-crank”:1. System does not power up at “pre-crank”:
1. System does not power up at “pre-crank”:
- Check gauge button is depressed
- Check the red wire of the grey harness is con-
nected to a 12V source.
.2. System does not power up at “pre-crank” but
.2. System does not power up at “pre-crank” but .2. System does not power up at “pre-crank” but
.2. System does not power up at “pre-crank” but
water led is lit:
water led is lit:water led is lit:
water led is lit:
- Check water tank level.
- Check level sensor is installed the right way up.
3. System powers up but green led does not blink
3. System powers up but green led does not blink 3. System powers up but green led does not blink
3. System powers up but green led does not blink
with RP :
with RP : with RP :
with RP :
- Check the green wire of the grey harness is spliced
Into the fuel injector’s “pulsed” wire (PI)
- Check the green and red wire of the green harness
is spliced Into the fuel injector’s wires (DI).
.4. THRES led lit on throttle blip but no spray:
.4. THRES led lit on throttle blip but no spray: .4. THRES led lit on throttle blip but no spray:
.4. THRES led lit on throttle blip but no spray:
- “THRES” should be set to fully counterclockwise.
- IDC pre-scaler is set to match PI’s IDC max.
- IDC prescaler is set to x2.5 for DI engines.
.5. Failsafe triggers during acceleration:
.5. Failsafe triggers during acceleration: .5. Failsafe triggers during acceleration:
.5. Failsafe triggers during acceleration:
- Disable failsafe by moving “PRK” jumper to “DFS”
Failsafe should only be set after system is setup and
tuned,
System running issues
(failsafe activated)
(failsafe activated)(failsafe activated)
(failsafe activated)
6. Flow bar display surges and drops:
6. Flow bar display surges and drops:6. Flow bar display surges and drops:
6. Flow bar display surges and drops:
- Reduce hose length to the jet/jets.
7. Failsafe trips at the WOT:
7. Failsafe trips at the WOT:7. Failsafe trips at the WOT:
7. Failsafe trips at the WOT:
- Set gauge’s S/C to only display 5-6 bars at WOT.
- If still trips, set WH clockwise until it settles.
Advance two more clicks.
8. Failsafe trips at the start of acceleration:
8. Failsafe trips at the start of acceleration:8. Failsafe trips at the start of acceleration:
8. Failsafe trips at the start of acceleration:
- IDC prescaler is not set correctly. See #4
You can check the incoming IDC% on the gauge by
linking “FDC” (fuel duty cycle) %
- If it still trips, set gauge’s WL counter-clocwise
until it settles. Advance two more clicks.
- If it still clicks, “THRES” on the controller is set too
low, set it to 10am. Then recal “WL” on the gauge
9. System blanks out during activation:
9. System blanks out during activation: 9. System blanks out during activation:
9. System blanks out during activation:
- Water tank level is dropped below permitted level
for ~20 seconds. System will trigger failsafe. The
system will not reset until the tank is refilled.
The water level led should flash long before this.
HF 3-v3.2 extended flow options
The HFS flow options:
Extensive developments have been made over the last few
years to extend the flow range HFS systems.
We are offering the following options:
We are offering the following options:We are offering the following options:
We are offering the following options:
1. For flowrates up to 1300cc/min there is no need to up-
grade the standard system. It is possible to increase the
160psi pump pressure to 200+ psi by clockwising the set
screw with 1/16“ allen key located at the front of the pump
head. When an audible click is heard, the maximum is
reached. This can be around 220psi depending on flow. It will
increase the standard flow rate to approximately 1500cc/min
2. Beyond 1500cc/min a 1600cc Tee (806-557D) is available.
But must accompany with Hi-flow sensor tube (806-555D.
As above, you can squeeze a bit more, some 50-100cc from
the standard pump. (free at initial purchase)
3. 1 & 2 can further upgraded by acquiring the 3000cc pump
(806-582D). Can maintain 200psi of line pressure, allowing
1800-1900cc of flow. (options with initial system purchase)
4. For those engines run high concentration of methanol and
requires flow rate beyond 1800cc to 3000cc, A large pump
accompanies the twin-FAV module (806-
401) is essential.
This drastically changes the charge-pipe
set up to a multi-port delivery where
charge pipe with large jets can no longer
guarantee even distribution of fluid into
the cylinders evenly.
However you can retain no more than two
small jets at the charge pipe for post-
intercooler charge cooling purposes. Size
of the charge pipe jet should can be the
same as the direct port jet.
Conclusions:
The standard system will support engine
power up to 800hp running 50/W50,
(based on 1.5cc/hp).
Power beyond 800 running 100% metha-
nol (2cc/min) should consider #1-#4 option.
But when making a new order, please
specify your target power goal, we will
supply you with a 1600cc FAV and a Hi-
Flow sensor at no extra cost.

Page 23
GUARANTEE
ERL guarantees, at our option, to replace faulty goods sup-
plied or repair the same, subject to the claim made in writing
to us within 12 months after the sale by us, or for such other
period as may be indicated by us for specific products in lieu
of any warranty or condition implied by law as to the quality
or fitness for any particular purpose of the goods.
Any claim against us must be made to us in writing within
the period of 12 months after the sale by us , or our agents,
or our distributors of goods in question (or such other period
as may be indicated by us) and any goods to which the claim
relates must be returned to us within that period suitably
packaged and cleaned and, with any particular instructions
which we may have notified to you at the time of supply.
Original invoice, the nature of any claimed defect must ac-
company the goods in question prior to despatch to us.
If these requirements are not complied with our Guarantee
shall not apply and we shall be discharged from all liability
arising from the supply of defective goods.
LIABILITY
We shall not be under any liability whether in contract, or
tort or otherwise and whether or not resulting from our neg-
ligence or that of our employees, in respect of defects in
goods supplied or for any damage or loss resulting from
such defects.
We shall not be under any liability for damage, loss of ex-
pense resulting from failures to give advice or information
or giving the incorrect advice or information whether or not
due to our negligence or that of our employees.
In no event shall any breach of contract on our part or tort
(including negligence) or failure of any time on our part that
of our employee give rise to liability for loss of revenue or
consequential loss or damages arising from any cause what-
soever.
Note: ERL reserves the right to make changes to our prod-
ucts without notice in order to improve design performance
and reliability.
ERL ltd Iroko House Bolney Ave Peacehaven East ussex BN10 8HF England
Useful Aquamist technical links
Aquamist owners have been pretty good in supporting each other. ost experienced users will
help new users with questions, not necessary to email or make long distance phone calls and
wait on hold to get help. Here are a list of forum links where users can seek help and advice from
others:
- http://www.waterinjection.info (general)
Page 24
END
ENDEND
END
Appendix
Pin Colour Size Description Electrical parameter
Molex Microfit power harness (1.5 M): Main Power supply and Dimmer control
1 red 20awg +12V Power supply (switched) 250mA max@12v
2 purple 20awg Gauge dimming input to head lamp switch+ 0-5 VDC @10mA
3 white 20awg 0V Ground (signal ground) 250mA max@12v
4 black 20awg 0V Ground (Power ground) -1A @12V max.
Red Harness to Engine bay (2.5M): To Flow Control assembly
1 red 24awg +12V PSU to Fast acting valve 1A max @12v
2 yellow 24awg +12V PSU to Fast acting valve 1A max @12v
3 blue 24awg PWM ground switch to Fast acting valve 1A max @0v
4 black 24awg PWM ground switch to Fast acting valve 1A max @0v
Yellow Harness to Engine bay (2.5M): To Flow Control assembly
1 red 24awg +5V Power supply to Turbine flow sensor 5mA max @5v
2 yellow 24awg Turbine fow sensor signal output 1mA max @5v
3 blue 24awg Feedback signal (return ground) 1mA max @0v
4 black 24awg 0V/ground power supply 1mA max @0v
Grey Harness to EMS (2.5M): IDC/ oost detection and Fail-Safe / Map-Switching interface
1 === 24awg Future extension I/O channel1 ----------------
2 red 24awg Ignition Switching detection 30mA max@12v
3 green 24awg Fuel injection IDC detection 10mA max@12v
4 pink 24awg Map switching interfacing 0, 5V, 7.5V @1mA
5 white 24awg Failsafe Relay contact (COM, Wiper) 1A @24V max.
6 yellow 24awg Reserved for internal communication Signal level
7 blue 24awg Map Sensor Signal input 0-5 VDC @1mA
8 black 24awg Failsafe Relay contact (N/C contact) or DR 1A @24V max.
9 brown 24awg Failsafe Relay contact (N/O contact) 1A @24V max.
10 === 24awg Future extension I/O channel 2 ----------------
lue Harness to Trunk Area (6M):
1 red 24awg +12V Power supply to 40A relay 0.5A max @12v
2 yellow 24awg Water level sensor signal signal ground 0.5A
3 blue 24awg Pump relay activation (ground switch) ----------
4 black 24awg Water level sensor ground ----------
--------------------------------
9 Red 12awg 12V Power cable to water pump relay 38A @12V max.
10 lack 12awg 0v ground for water pump 38A @12V max
Green Harness to EMS (2M): Direct, P&H Injection systems, Common Rail Diesel Interface
1 red 24awg Fuel injector (+) signal detection 600V 8mS dc<50%
2 green 24awg Fuel injector (-) signal detection 600V 8mS dc<50%
3 blue 24awg Spare port for custom interface ------------
4 yellow 24awg Flow sensor signal (analogue 0-5V) 0.5 - 4.5V @1mA
5 white 24awg Water/Methanol IDC monitor (analogue) output 0 - 5V @1ma.
6 black 24awg Signal ground 0.2A max.
Other ERL Water System manuals
Popular Water System manuals by other brands
Everpure
Everpure CG5-20S Replacement Cartridge DEV9108-27 Specification sheet

Everpure
Everpure Quad-MC EV9628-28 Specification sheet

Xylem
Xylem CentriPro Aquavar SOLO 2 Frequently asked questions

HeatLink
HeatLink PEX-a installation guide

Culligan
Culligan MEDALLIST SERIES Service manual

Intex
Intex Krystal Clear Saltwater System owner's manual

Geekpure
Geekpure RO4 Installation and maintenance manual

Elkay
Elkay HATENBOER WATER VRCGNDWS C Series Installation and use manual

Everpure
Everpure QL2-OCS2 Specification sheet

Istore
Istore 180L installation manual

EINHELL
EINHELL 41.731.90 Original operating instructions

Marco
Marco FRIIA HC instruction manual