Beamage SDK User Manual Revision 1 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENTEC-EO’S BEAMAGE SDK..........................................................................................................................5
1.1. WHAT IS THE BEAMAGE SDK ? .............................................................................................................................5
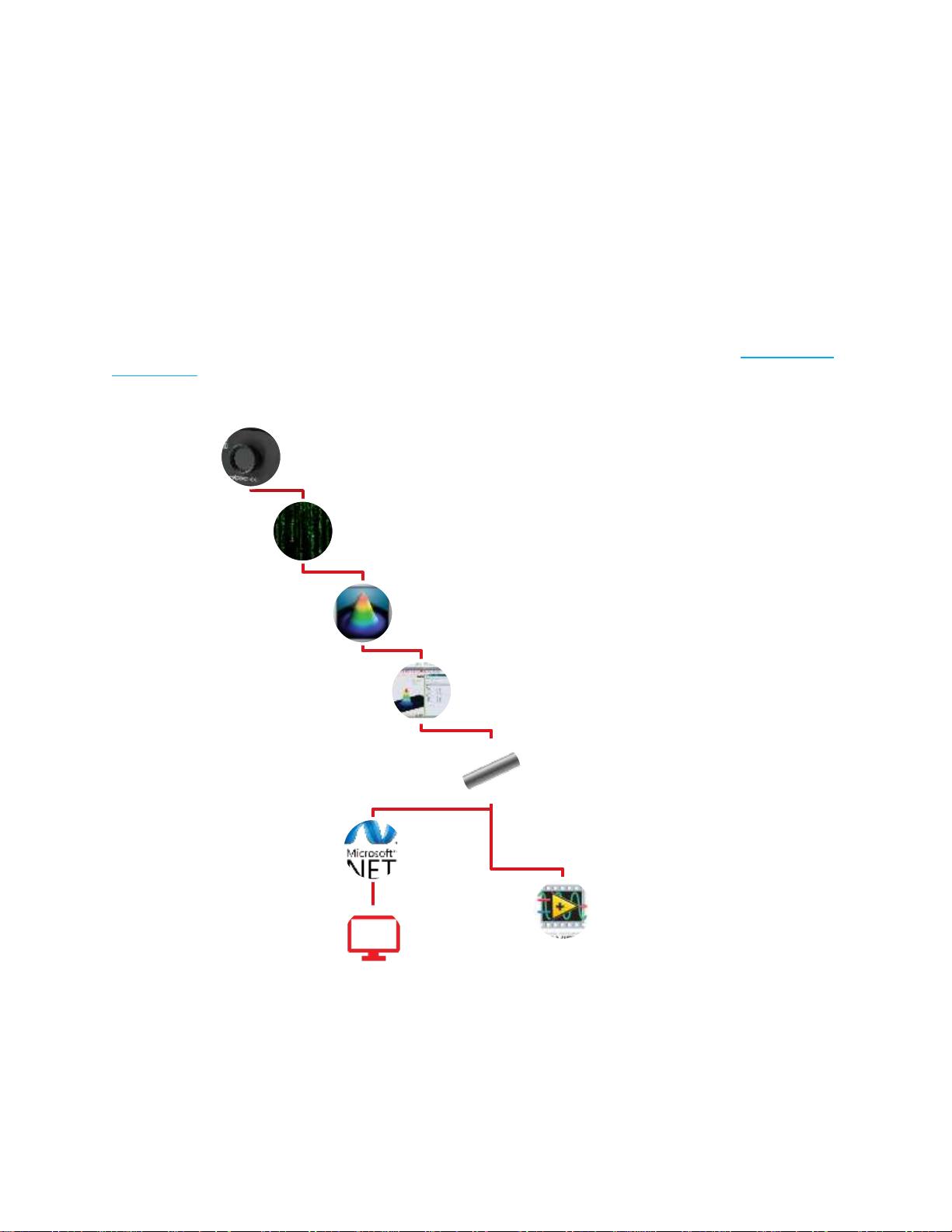
1.2. THE .NET COMPATIBLE PIPELINE FOR BEAMAGE CAMERAS..........................................................................................7
1.3. GETTING STARTED WITH THE BEAMAGE SDK............................................................................................................7
1.4. WHAT YOUR VISUAL STUDIO SOLUTION NEEDS .........................................................................................................8
1.5. UNDERSTANDING THE CODE..................................................................................................................................8
1.6. BEAMAGE SDK CLASS DIAGRAM .........................................................................................................................10
2. GET STARTED EXAMPLE................................................................................................................................ 11
2.1. FIRST EXAMPLE:C# EXAMPLE WITH VIEWER ...........................................................................................................11
2.1.1. GENERAL INFORMATION.....................................................................................................................................11
2.1.2. GRAB IMAGES ..................................................................................................................................................12
2.1.3. MATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS ON THE IMAGE BUFFER...............................................................................................13
2.1.4. EVENTS...........................................................................................................................................................14
2.2. SECOND EXAMPLE:C++ CONSOLE APPLICATION .....................................................................................................14
3. BEAMAGE API .............................................................................................................................................. 15
3.1. BCAM ............................................................................................................................................................15
Class declaration..................................................................................................................................................15
Properties.............................................................................................................................................................15
Events ..................................................................................................................................................................15
Functions..............................................................................................................................................................16
3.2. BCAMIMG.......................................................................................................................................................16
Class declaration..................................................................................................................................................16
Properties.............................................................................................................................................................16
Events ..................................................................................................................................................................17
Functions..............................................................................................................................................................17
3.3. BCAMPROPERTIES ............................................................................................................................................18
Class declaration..................................................................................................................................................18
Properties.............................................................................................................................................................18
Events ..................................................................................................................................................................18
Functions..............................................................................................................................................................18
3.4. BERRORSMANAGER..........................................................................................................................................18
Class declaration..................................................................................................................................................18
Properties.............................................................................................................................................................18
Events ..................................................................................................................................................................18
3.5. BSDK.............................................................................................................................................................19
Class declaration..................................................................................................................................................19
Properties.............................................................................................................................................................19
Events ..................................................................................................................................................................19
Functions..............................................................................................................................................................19
3.6. FUTURE CLASSES AND FUNCTIONS ........................................................................................................................20