1. This trailer was built to carry cargo within the
limitations of weight ratings shown on the
certification label. These ratings, GAWR and
GVWR are:
a. The GAWR (gross axle weight rating) is the
structural capability of the lowest rated
member of the running gear components:
suspension system, hubs, wheels, drums,
rims, bearings, brakes, axles, or tires.
b. The GVWR (gross vehicle weight rating) is
the structural capability of the trailer when
supported by the upper coupler and axles
with the load uniformly distributed through-
out the cargo space. CAUTION! The
maximum load indicated on the certification
label may or may not be a legal load on the
highway you plan to use.
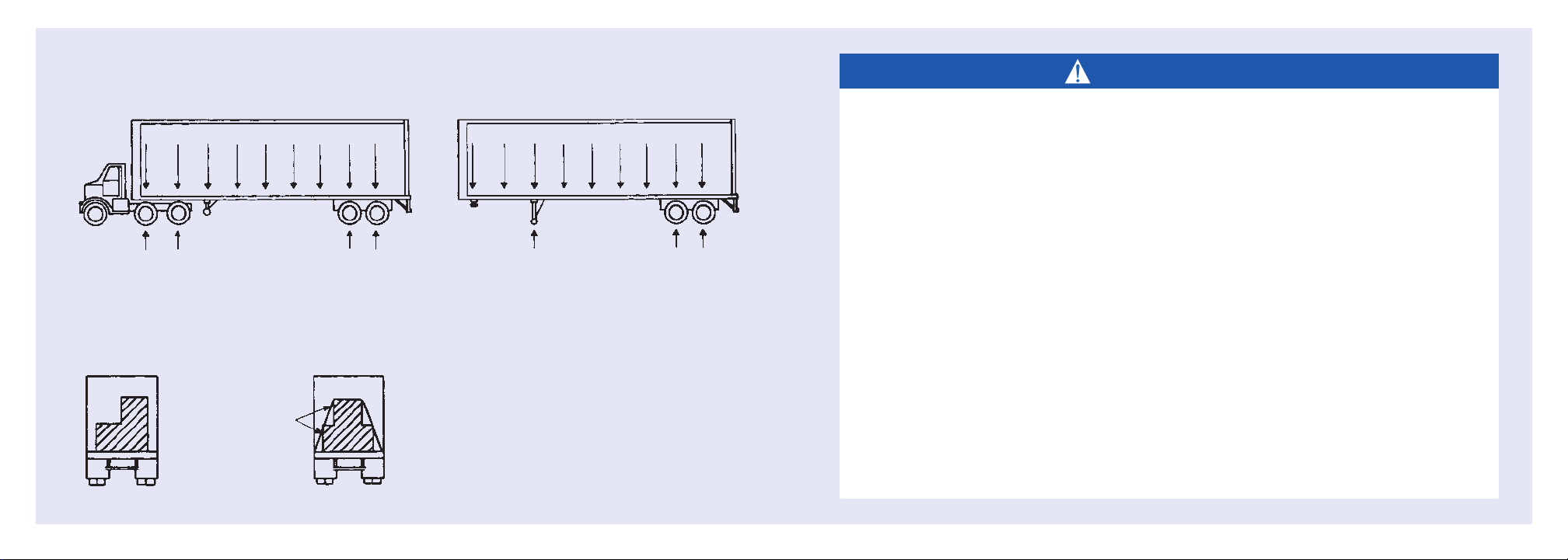
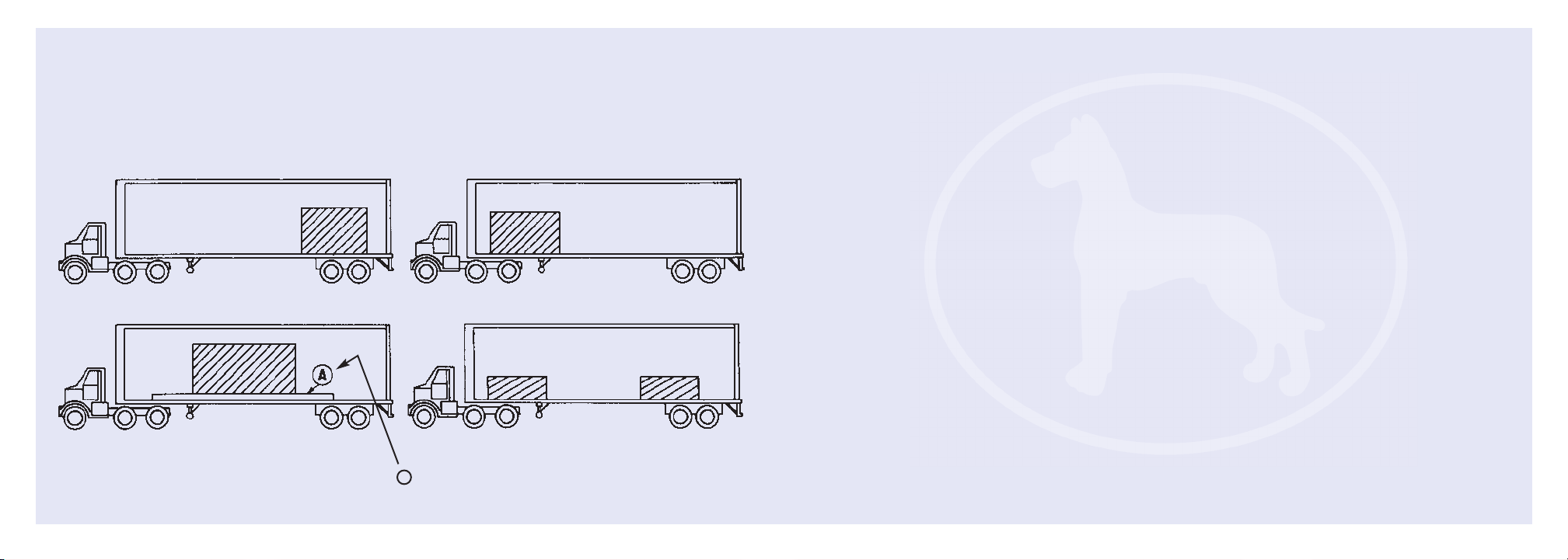
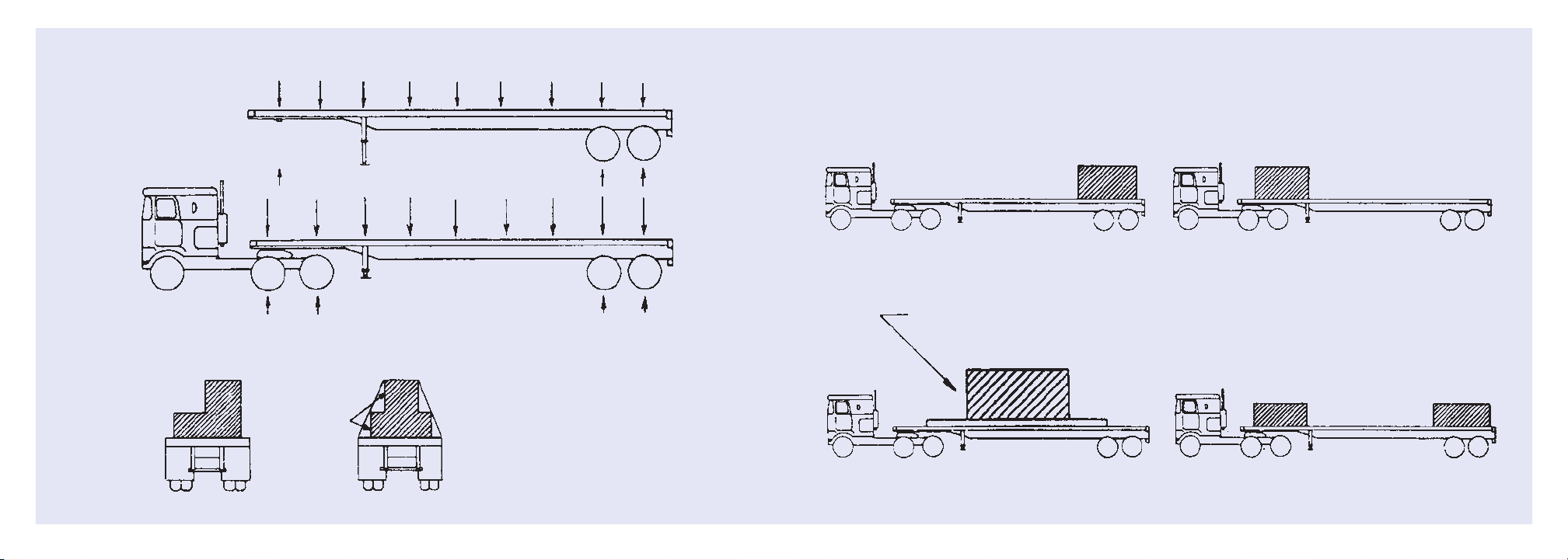
2. This trailer will carry a total payload equal to
the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) less
the weight of the trailer. The load must be
uniformly distributed, or it must be uniformly
distributed except for up to 25,000 pounds
that must be evenly distributed in any 10 linear
feet of trailer length. Recommended payload
distributions are shown in Figures 1, 2, and 3.
3. NOTE: Exceptions to the above are meat rail
trailers. For the maximum allowable suspended
load, see the vehicle certification label.
4. The cargo should be properly loaded, blocked,
and braced to prevent load shifts and to
comply with the following sections of the
Department of Transportation Federal Motor
Carriers Safety Regulation, Subpart 1 –
Protection Against Shifting or Falling Cargo:
Section 393.100 – General rules for protection
against shifting or falling cargo.
Section 393.102 – Securement systems.
Section 393.104 – Blocking and bracing.
Section 393.106 – Front-end structure.
n rmal use
10
ACCESS FROM THE TRACTOR
If the tractor is not equipped with adequate steps, handholds and slip-resistant deck plate to the rear
of the cab, Do Not Attempt Access To The Trailer Steps From The Tractor. Use “Access From The
Ground” method. If the tractor is properly equipped with steps, handholds and a deck plate and the
tractor is coupled and locked to the trailer, it is most important that the tractor be in a partial “jackknife”
orientation. The tractor must be positioned such that the deck plate is directly beneath the lowest step.
9
warning: Walk carefully in the trailer. The
floor may be slippery. Enter and leave only from a
dock as high as the floor or by means of a substan-
tial ladder. Advise others of these precautions.
cauti n: Operation of the trailer outside
the limitations of this manual is against federal law
and Great Dane Trailers’ design criteria. Any opera-
tion exceeding the limitations stated will void any
responsibility of Great Dane Trailers for the results.
1. DO NOT climb on steps not firmly attached and properly maintained.
2. DO NOT climb on steps with any item in your hands.
3. DO NOT use a tractor not equipped with a safe, adequate climbing system to access the
trailer’s front wall steps.
4. DO NOT step on tires, fenders, tractor frames, or mudflap supports.
5. DO NOT step over air and electrical lines between the tractor and the trailer. Disconnect and
properly store if necessary.
6. DO NOT use any portion of the tractor in conjunction with any portion of the trailer
simultaneously in a “spread-eagle” hold or stance for support.
7. DO NOT use an access system if wet, iced, or for any reason seems to be slippery.
8. DO NOT use a trailer’s front wall access system to start, inspect, or maintain any heating or
cooling unit.
9. DO NOT climb higher than necessary to open, secure or close the vent door.
10. DO NOT remain on a trailer’s access system while the trailer is being coupled to or uncoupled
from a tractor.
11. DO NOT jump from the trailer to the ground.
warning:
his Great Dane trailer was designed for operation within legal highway speed limits on reasonable
road surfaces in accordance with the following: