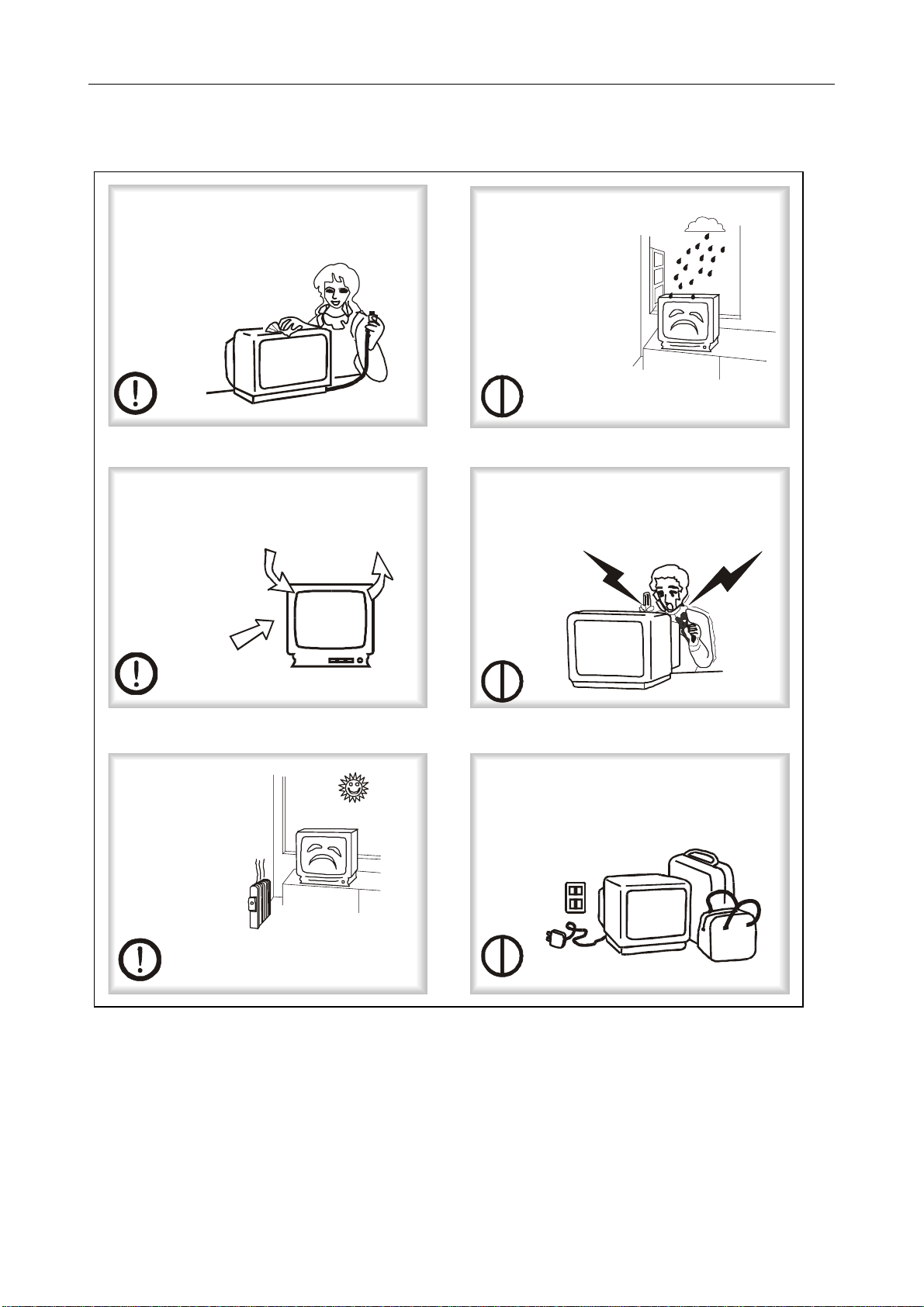
7
Explanation on the display tube
Generally, it is not needed to clean the tube surface. However, if necessary, its surface can
be cleaned with a dry cotton cloth after cutting off the power. Don’t use any cleanser. If
using hard cloth, the tube surface will be damaged.
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this service manual and its
supplements and addenda, read and follow the SAFETY PRECAUTIONS.
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the following servicing
precautions and any of the safety precautions, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember : Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power source before:
a.Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board module or any other assembly of
the receiver.
b.Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or other electrical connection.
c.Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong substitution part or incorrect installation polarity of electrolytic
capacitors may result in an explosion hazard.
d. Discharging the picture tube anode.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate high voltage meter or other
voltage-measuring device (DVM, FETVOM, etc.) equipped with a suitable high voltage
probe. Do not test high voltage by “drawing an arc”.
3. Discharge the picture tube anode only by (a) first connecting one end of an insulated
clip lead to the degaussing or kine aquadag grounding system shield at the point where
the picture tube socket ground lead is connected, and then (b) touch the other end of
the insulated clip lead to the picture tube anode button, using an insulating handle to
avoid personal contact with high voltage.
4. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its assemblies.
5. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, clean electrical contacts only by
applying the following mixture to the contacts with a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or
comparable nonabrasive applicator; 10% (by volume) Acetone and 90% (by volume)
isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION: This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of contacts is not required.
6. Do not defeat any plug / socket B+ voltage interlocks with which receivers covered by
this service manual might be equipped.
7. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its electrical assemblies unless
all solid-state device heat sinks are correctly installed.
Warning and Cautions