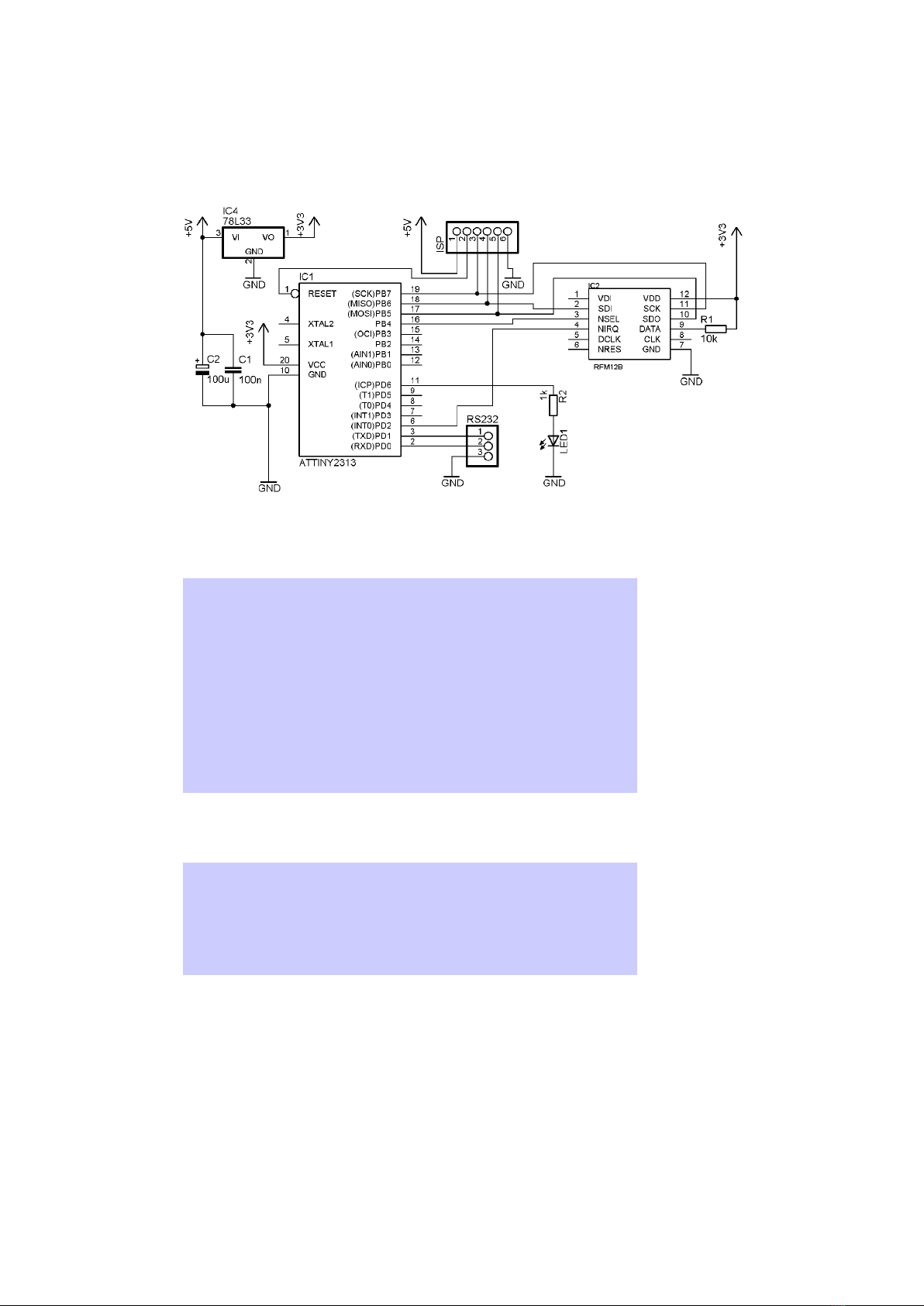
4 Receiver code
Here things get a little bit inconsistent with the ”Programming Guide”.
Macros, port initialization and SPI handling in the receiver part is the same
as before so I will omit some code. The easiest way to check received data
is to send it to the PC. To do this we need some RS232 handling functions.
#define BAUDRATE 25 // 19200 at 8MHz
void rsInit(unsigned char baud) {
UBRRL = baud;
UCSRC = (1<<UCSZ0) | (1<<UCSZ1); // 8N1
UCSRB = (1<<RXEN) | (1<<TXEN); // enable tx and rx
}
void rsSend(unsigned char data) {
while( !(UCSRA & (1<<UDRE)));
UDR = data;
}
unsigned char rsRecv() {
while( !(UCSRA & (1<<RXC)));
return UDR;
}
Initialization of the module is almost the same. Only difference is quite
obvious — we need to turn on the reveiver instead of the transmitter. Sur-
prisingly, it is not so obvious for authors of the ”Programming Guide”. Their
initialization is the same no matter what they want to do. It’s the chineese
way I guess... ;) Anyway I recommend to turn on the receiver this time
(command no. 2).
void rfInit() {
writeCmd(0x80E7); //EL,EF,868band,12.0pF
writeCmd(0x8299); //er,!ebb,ET,ES,EX,!eb,!ew,DC (bug was here)
writeCmd(0xA640); //freq select
writeCmd(0xC647); //4.8kbps
writeCmd(0x94A0); //VDI,FAST,134kHz,0dBm,-103dBm
writeCmd(0xC2AC); //AL,!ml,DIG,DQD4
writeCmd(0xCA81); //FIFO8,SYNC,!ff,DR (FIFO level = 8)
writeCmd(0xCED4); //SYNC=2DD4;
writeCmd(0xC483); //@PWR,NO RSTRIC,!st,!fi,OE,EN
writeCmd(0x9850); //!mp,90kHz,MAX OUT
writeCmd(0xCC17); //!OB1,!OB0, LPX,!ddy,DDIT,BW0
writeCmd(0xE000); //NOT USE
writeCmd(0xC800); //NOT USE
writeCmd(0xC040); //1.66MHz,2.2V
}
Now it’s time for receiving functions. They are totally different from what
you can find in the mentioned, glorious ”Programming Guide”. To be honest,
I have no idea how their code could work at all... So, referring to the
5