InHand InRouter900 Series User manual

2
Preface
Thanks for choosing InRouter900 series industrial routers! This user’s manual will guide you in
detail on how to configure InRouter900.
The preface includes the following contents:
Readers
Conventions in the Manual
Obtaining Documentation
Technical Support
Readers
Information Feedback
This manual is mainly intended for the following engineers:
Network planners
On-site technical support and maintenance personnel
Network administrators responsible for network configuration and maintenance
Conventions in the Manual
1. Format Conventions on Command Line
Format Significance
Bold Keywords of command line (the part that should be remained unchanged in
command and be entered as it is) are expressed with bold font.
Italic The parameters of command line (the part that must be replaced with the actual
value in command) are expressed in italic.
[ ] Indicating that the part in “[]” is optional in command configuration.
{ x | y | ... } Indicating to select one from multiple options.
[ x | y | ... ] Indicating to select one or not to select from multiple options.
{ x | y | ... } * Indicating to select at least one from multiple options.
[ x | y | ... ] * Indicating to select one or more or not to select from multiple options.
&<1-n> Indicating that the parameter in front of the symbol & can be repeatedly entered
for 1~n times.
#The lines starting from no. “#” are comment lines.
2. Format Conventions on Graphic Interface
Format
Significance

3
<> The content in angle brackets "<>" indicates button name, e.g. "click <OK>
button.”
[ ] The content in square brackets "[]" indicates window name, menu name or data
sheet, e.g. “pop-up the [New User] window”.
/Multi-level menu is separated by "/". For example, the multi-level menu [File /
New / Folder] indicates the menu item [Folder] under the submenu [New] under
the menu [File].
3. Various Signs
The manual also uses a variety of eye-catching signs to indicate the places to which special
attention should be paid in operation. The significances of these signs are as follows:
It indicates matters to be noted. Improper operation may cause
data loss or damage to the device.
The necessary complement or description on the contents of
operation.
Obtaining Documentation
The latest product information is available on the website of InHand (www. inhandnetworks.com):
The main columns related to product information on the website of InHand are described as
follows:
[Service Support / Document Center]: Product information in terms of hardware installation,
software upgrade, configuration, etc., is available.
[Product Technology]: Documents on product introduction and technology introduction
including relevant introduction on product, technical introduction, technical white papers, etc.,
are available.
[Service Support / Software Download]: The supporting information on software version is
available.
Technical Support
E-mail: support@inhandneworks.com
Website: www.inhandnetworks.com
Information Feedback
If you have any question on product information in use, you can feed back through the following
ways:
Thanks for your feedback to let us do better!

4
CONTENTS
1. INROUTER900 INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................................7
1.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................................................7
1.2 Product Features.........................................................................................................................................................7
2. LOGIN ROUTER....................................................................................................................................................... 11
2.1 Establish Network Connection ................................................................................................................................ 11
2.1.1 Automatic acquisition of IP address (recommended) ..........................................................................................11
2.1.2 Set a static IP address ..........................................................................................................................................14
2.2 Confirm that the network between the supervisory PC and router is connected ...............................................15
2.3 Cancel the Proxy Server...........................................................................................................................................16
3. WEB CONFIGURATION .........................................................................................................................................18
3.1 Login the Web Setting Page of Router....................................................................................................................19
3.2 Management..............................................................................................................................................................19
3.2.1 System .................................................................................................................................................................20
3.2.2 System Time........................................................................................................................................................21
3.2.3 Admin Access......................................................................................................................................................24
3.2.4 AAA.....................................................................................................................................................................28
3.2.5 Configuration Management.................................................................................................................................32
3.2.6 SNMP..................................................................................................................................................................33
3.2.7 Alarm...................................................................................................................................................................37
3.2.8 System Log..........................................................................................................................................................41
3.2.9 System Upgrading ...............................................................................................................................................42
3.2.10 Reboot ...............................................................................................................................................................43
3.2.11 Device Management..........................................................................................................................................43
3.3 Network .....................................................................................................................................................................45
3.3.1 Ethernet Port........................................................................................................................................................45
3.3.2 Dialup Port...........................................................................................................................................................48
3.3.3 PPPoE..................................................................................................................................................................52
3.3.4 Loopback.............................................................................................................................................................53
3.3.5DHCP service.......................................................................................................................................................53
3.3.6 DNS Services.......................................................................................................................................................57
3.3.7 Dynamic Domain Name ......................................................................................................................................58
3.3.8 SMS.....................................................................................................................................................................61

5
3.4 Link Backup..............................................................................................................................................................62
3.4.1 SLA .....................................................................................................................................................................62
3.4.2 Track Module.......................................................................................................................................................63
3.4.3 VRRP...................................................................................................................................................................64
3.4.4 Interface Backup..................................................................................................................................................69
3.5 Routing ......................................................................................................................................................................73
3.5.1 Static Route .........................................................................................................................................................73
3.5.2 Dynamic Routing.................................................................................................................................................75
3.5.3 Multicast Routing................................................................................................................................................84
3.6 Firewall......................................................................................................................................................................87
3.6.1 Access Control.....................................................................................................................................................87
3.6.2 NAT .....................................................................................................................................................................92
3.7Qos ..............................................................................................................................................................................96
3.7.1QoS.......................................................................................................................................................................97
3.7.2 QoS Application Example ...................................................................................................................................99
3.8VPN.............................................................................................................................................................................99
3.8.1IPSec...................................................................................................................................................................100
3.8.2GRE....................................................................................................................................................................107
3.8.3 DMVPN.............................................................................................................................................................109
3.8.4L2TP................................................................................................................................................................... 117
3.8.5OPENVPN.......................................................................................................................................................... 118
3.8.6 Certificate Management ....................................................................................................................................122
3.9 Industrial.................................................................................................................................................................123
3.9.1 DTU...................................................................................................................................................................123
3.9.2 IO.......................................................................................................................................................................130
3.10 Tools .......................................................................................................................................................................130
3.10.1PING.................................................................................................................................................................130
3.10.2 Routing detection.............................................................................................................................................131
3.10.3 Link Speed Test ...............................................................................................................................................132
3.11 Configuration Wizard...........................................................................................................................................132
3.11.1 New LAN ........................................................................................................................................................132
3.11.2New WAN.........................................................................................................................................................133
3.11.3 New Cellualr....................................................................................................................................................133
3.11.4 New IPSce Tunnel ...........................................................................................................................................134
3.11.5 New Port Mapping...........................................................................................................................................135
3.12 Network Mode.......................................................................................................................................................135
3.12.1 Cellular Dialup ................................................................................................................................................135
3.12.2 WAN ................................................................................................................................................................135
APPENDIX 1 TROUBLESHOOTING.......................................................................................................................137

6
APPENDIX 2 INSTRUCTION OF COMMAND LINE ...........................................................................................139
APPENDIX 3 GLOSSARY OF TERMS.....................................................................................................................145
APPENDIX 4 DESCRIPTION OF LEDS..................................................................................................................147

7
1. InRouter900 Introduction
This chapter includes the following parts:
Overview
Product Features
1.1 Overview
Thanks for choosing IR900 series industrial router. InRouter900 (“IR900” thereinafter) is the new
generation of industrial router developed by InHand Networks for M2M in 4G era.
Integrating 4G LTE and various broadband WANs, IR900 provides uninterrupted access to internet.
With the features of complete security and wireless service, IR900 can connect up to ten thousand
devices. IR900 has also been built for rapid deployment and easy management, which enables
enterprises to quickly set up large scale industrial network with minimized cost and time.
There are currently three IR900 series: IR9x2, IR9x5, IR9x8, which can provide up to 8 intelligent
ports and they support LAN/WAN protocol. IR900 products not only offer more options on WAN
port access, but also effectively save additional purchasing cost on switch equipments.
1.2 Product Features
Uninterrupted Access to Internet from Anywhere
Redundant WAN connection, 2 Ethernet ports, 3G/4G embedded, various DSL, InRouter 900 is
built to support various WAN and ensure network availability. Whether the device is located in
commercial region or wild field, it can always keep on line with broadband service or
widespread 3G/4G connection. Furthermore, InRouter 900 can automatically switch over
between broadband and 3G/4G when one link is failed, so as to ensure uninterrupted WAN
connection. With InRouter 900, your business is always online.
Support Large Scale Deployment
In your M2M application, there are thousands of remote machines, or tens of thousands of VPN
connection, which turns out to be a big challenge for network management. InRouter 900 make
large scale deployment much easier with following features:
Multiple configuration tools including Web and CLI, enable administrator to rapidly
configure thousands of InRouter

8
Remote Network Management: InRouter 900 works with network management platforms
installed in application center or headquarter. To remotely batch configure, download and
upload configuration file, upgrade firmware, monitor status of connection and VPN
tunnel… all these become essential for operating a M2M system especially when a large
number of devices scatter widely with limited field staff or even totally unattended.
InRouter 900 supports industrial standard SNMP and 3rd
InRouter 900 also collaborates with InHand Device Manager to handle cellular specialty of
network management. InHand Device Manager can be cloud based or installed within
enterprise’s intranet. InHand Device Manager improves for cellular circumstance to
monitor cellular data flow, signal strength on site, location of the device. Even better,
there’s no need to apply costly private network from telecomm operator, and you can build
your worldwide M2M system across multiple operators.
SNMP software platform, so as to
integrate into enterprise level IT management system.
Multiple diagnostic tools, supporting 3G/4G modem status, IMEI, IMSI and registration
status of cellular networks, help engineer out of complex network circumstance.
Support dynamic routing of RIP, OSPF, automatically update routing of whole network,
largely increase efficiency of large scale deployment.
Support Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DM VPN), greatly reduce workload to configure
thousands of remote InRouter 900. Establishing a large & secured remote network never
made so easy!
Robust Security
Secured VPN Connections
Support GRE, L2TP, IPSec VPN, DMVPN, OpenVPN; CA, ensure data security
Security of Network
Support firewall functions to protect from network attacks, such as: Stateful Packet
Inspection (SPI), Access Control List (ACL), resist DoS attack, intrusion protection, attack
protection, IP/MAC Binding and etc.
Security of Devices
Support AAA, TACACS, Radius, LDAP, local authentication, and multi levels user
authority, so as to establish a secured mechanism on centralized authentication and
authorization of device access.

9
High Reliability
Redundancy
WAN Redundancy: support link backup, VRRP to support automatic switch over between
WANs.
Dual SIM cards: backup between different mobile operators to ensure networks availability
and bargaining power on data plan.
Automatic Link Detection & Recovery
PPP Layer Detection: keep the connection with mobile network, prevent forced hibernation,
able to detect dial link stability.
Network connection Detection: automatic redial when link broken, keep Long Connection.
VPN Tunnel Detection: sustain VPN tunnel, to ensure availability of business.
InRouterAuto-recovery
InRouter embeds hardware watchdog, able to automatically recover from various failure,
ensure highest level of availability.
Entirely Ruggedized
InRouter 900 inherits InHand Networks’ legacy on best-in-class ruggedized design. From
component selection to circuit layout, InRouter 900 satisfies electric power and industrial
applications on EMC, IP protection, temperature range and etc. InRouter 900 is designed to last
in harshest circumstances.
High Performance, High Bandwidth
Equipped with powerful Cortex-A8 processor and 256MB memory, support more
application needs
Support 4G/LTE (100Mbps downlink and 50Mbps uplink) and HSPA+ (21Mbps downlink
and 5.76Mbps uplink)
InHand Network Operation System: INOS 2.0
InHand Network Operation System (INOS) has been built as the highly reliable & real-time
basis for all network functions, as well as easy-to-use configuration interface via Web, CLI or
SNMP. INOS is in modular design, expandable, and adaptable to various M2M applications.
Embed WIFI AP and Client, Easy to Establish Versatile Wireless Network
Support 802.11 b/g/n standard, fulfill the need to connect WLAN devices, up to 150Mbps

10
throughput
Easily establish wireless LAN, support WEP/WPA/WPA2 for network security
WIFI can be the backup WAN link for 3G/4G
11
2. Login Router
This chapter mainly contains the following contents:
Establish Network Connection
Confirm that the connection between supervisory PC and router
Cancel the Proxy Server
2.1 Establish Network Connection
2.1.1 Automatic acquisition of IP address (recommended)
Please set the supervisory computer to "automatic acquisition of IP address" and "automatic
acquisition of DNS server address" (default configuration of computer system) to let the router
automatically assign IP address for supervisory computer.
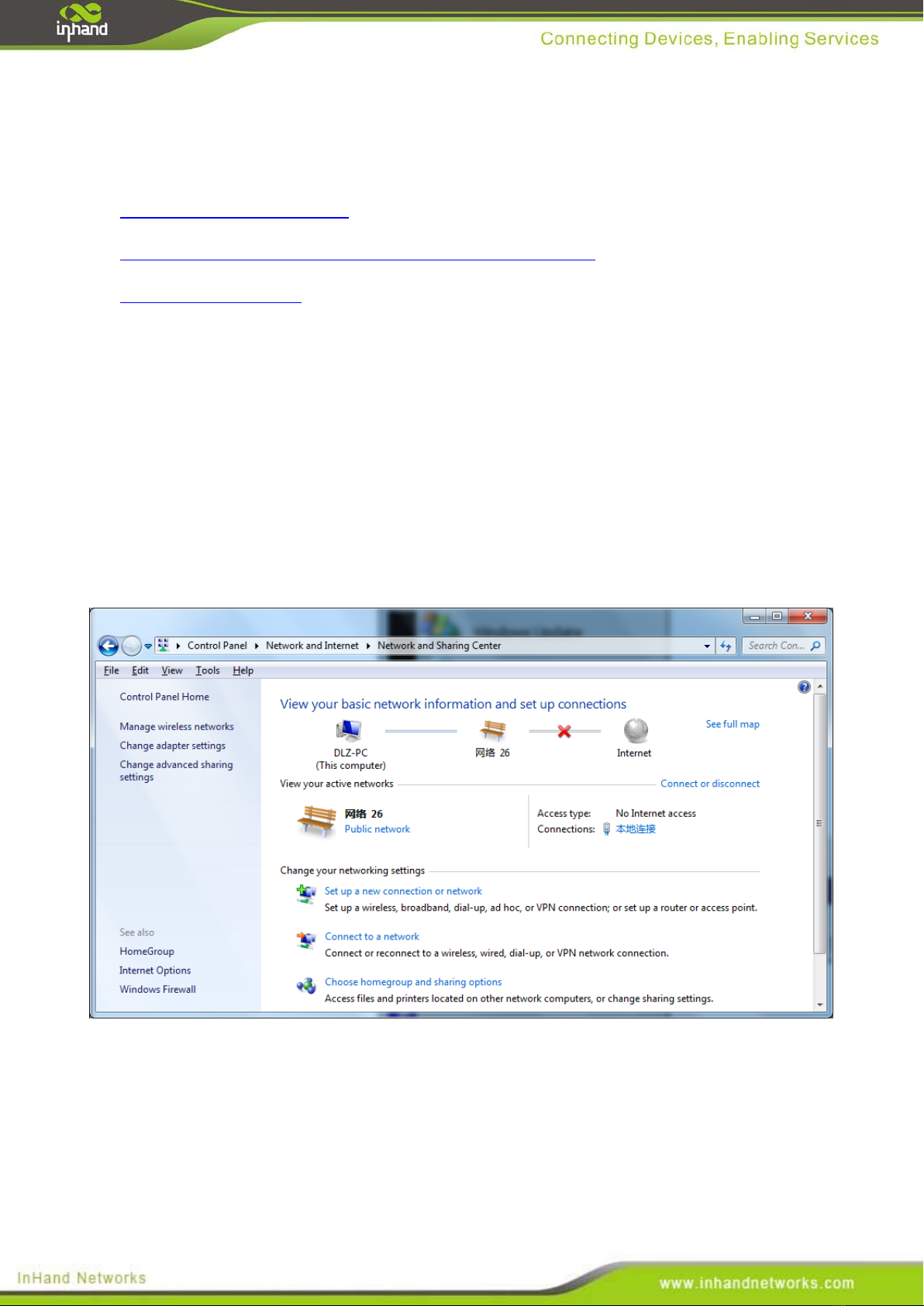
1) Open “Control Panel”, double click “Network and Internet” icon, enter “Network and Sharing
Centers”
2) Click the button <Local Connection> to enter the window of "Local Connection Status”

12
3) Click <Properties>to enter the window of "Local Connection Properties”, as shown below.

13
4) Select “Internet Portocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4)”, click <Properties> to enter “Internet Portocol
Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)Properties” page. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and
“Obtain DNS Server address automatically”, then click <OK> to finish setting, as shown
below.

14
2.1.2 Set a static IP address
Enter “Internet Portocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)Properties” page, select “Use the following IP
address”, type IP address (arbitrary value between 192.168.2.2~192.168.2.254), Subnet Mask
(255.255.255.0), and Defafult Gateway (192.168.2.1), then click <OK>to finish setting, as shown
below.

15
2.2 Confirm that the network between the supervisory PC and router is
connected
1) Click the button <Start> at the lower left corner to research “cmd.exe”, and run cmd.exe
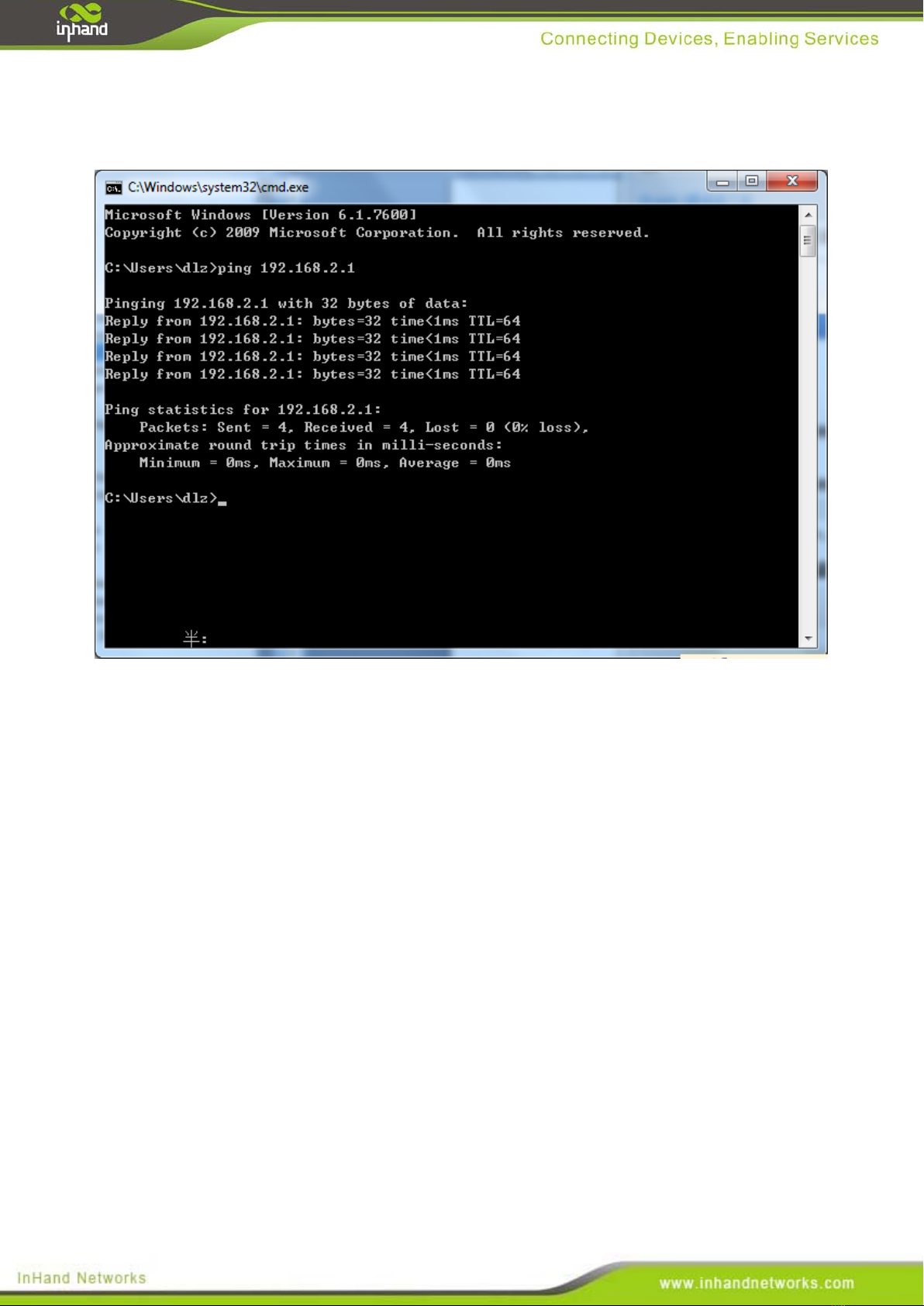
16
2) Enter "ping 192.168.2.1 (IP address of router; it is the default IP address), and click the
button <OK>. If the pop-up dialog box shows the response returned from the router side, it
indicates that the network is connected; otherwise, check the network connection.
2.3 Cancel the Proxy Server
If the current supervisory computer uses a proxy server to access the Internet, it is required to
cancel the proxy service and the operating steps are as follows:
(1) Select [Tools/Internet OPtions] in the browser to enter the window of [Internet Options]
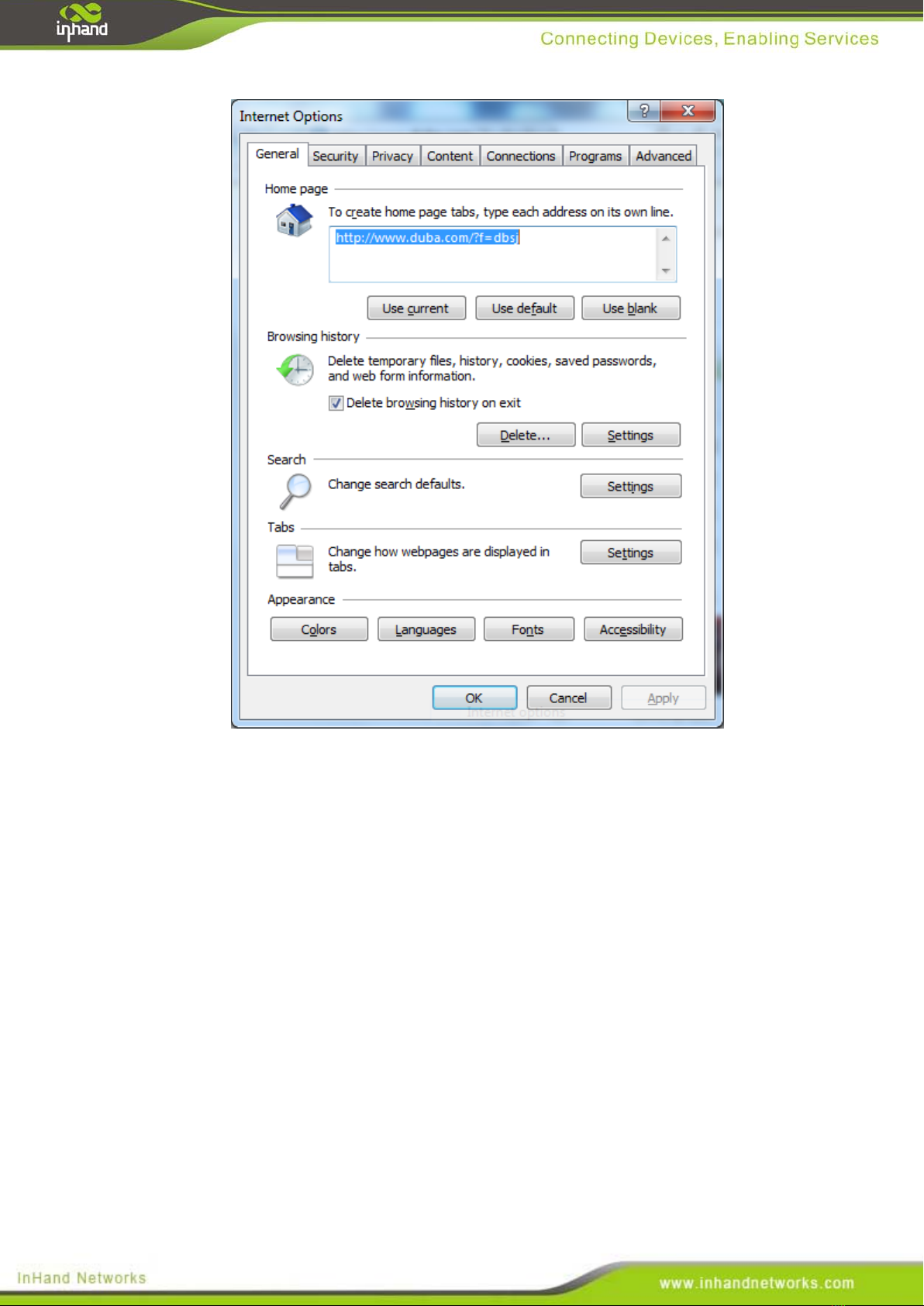
17
(2) Select the tab”Connect” and click the button<LAN Setting(L)> to enter the page of “LAN
Setting”.Please confirm if the option”Use a Proxy Server for LAN” is checked;if it is
checked,please cancel and click the button<OK>.

18
3. Web Configuration
19
This chapter includes the following parts:
Login/out Web Configuration Page
Management
Network
Link Backup
Routing
Firewall
QOS
VPN
Tools
Installation Guide
3.1 Login the Web Setting Page of Router
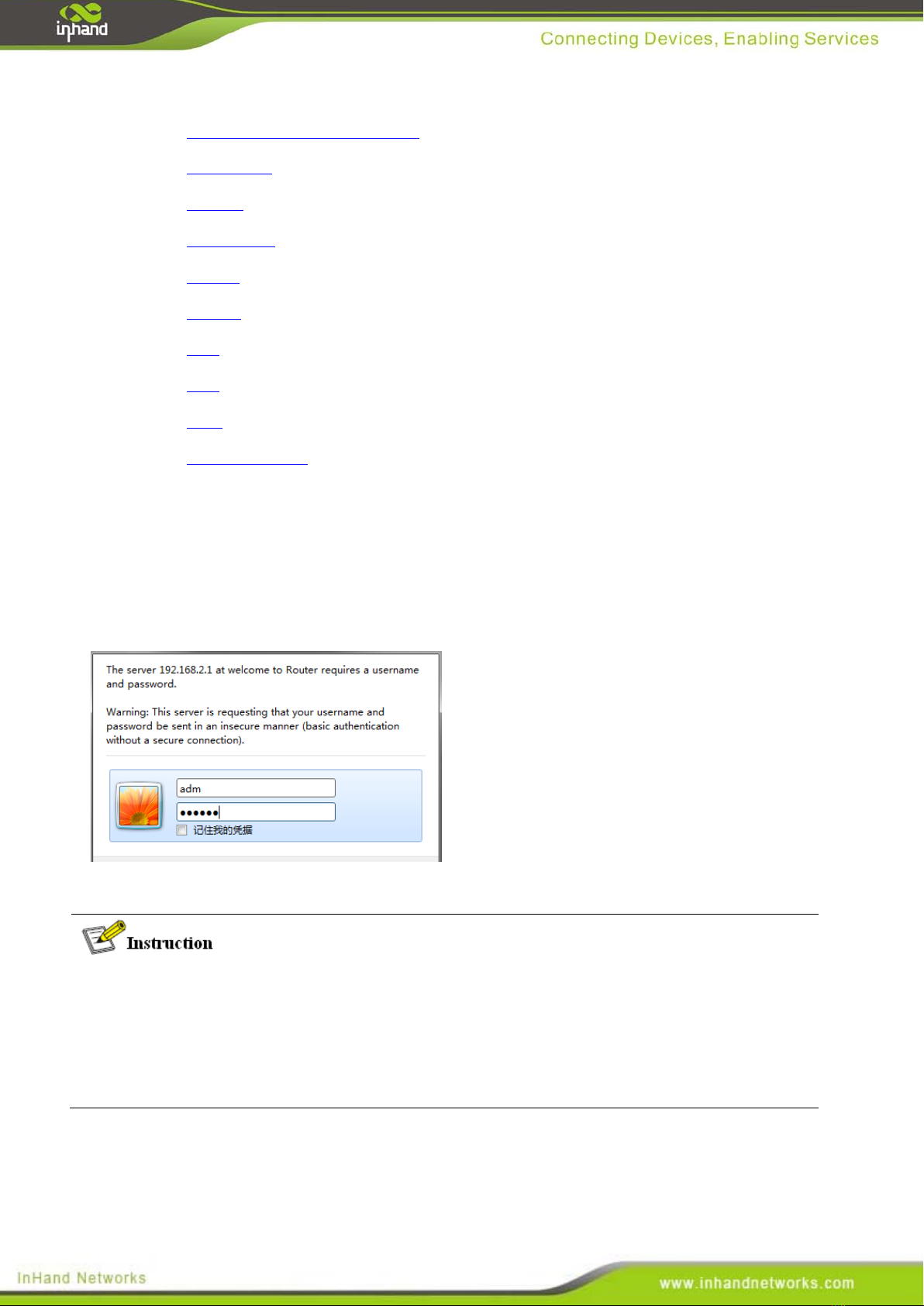
Run the Web browser, enter “http://192.168.2.1” in the address bar, and press Enter to skip to
the Web login page, as shown in Figure 3-1. Enter the “User Name” (default: adm) and “Password”
(default: 123456), and click button <OK> or directly press Enter to enter the Web setting page.
At the same time, the router allows up to four users to manage through the Web setting page.
When multi-user management is implemented for the router, it is suggested not to conduct
configuration operation for the router at the same time; otherwise it may lead to inconsistent
data configuration.
For security, you are suggested to modify the default login password after the first login and
safe keep the password information.
3.2 Management
20
3.2.1 System
3.2.2.1 System Status
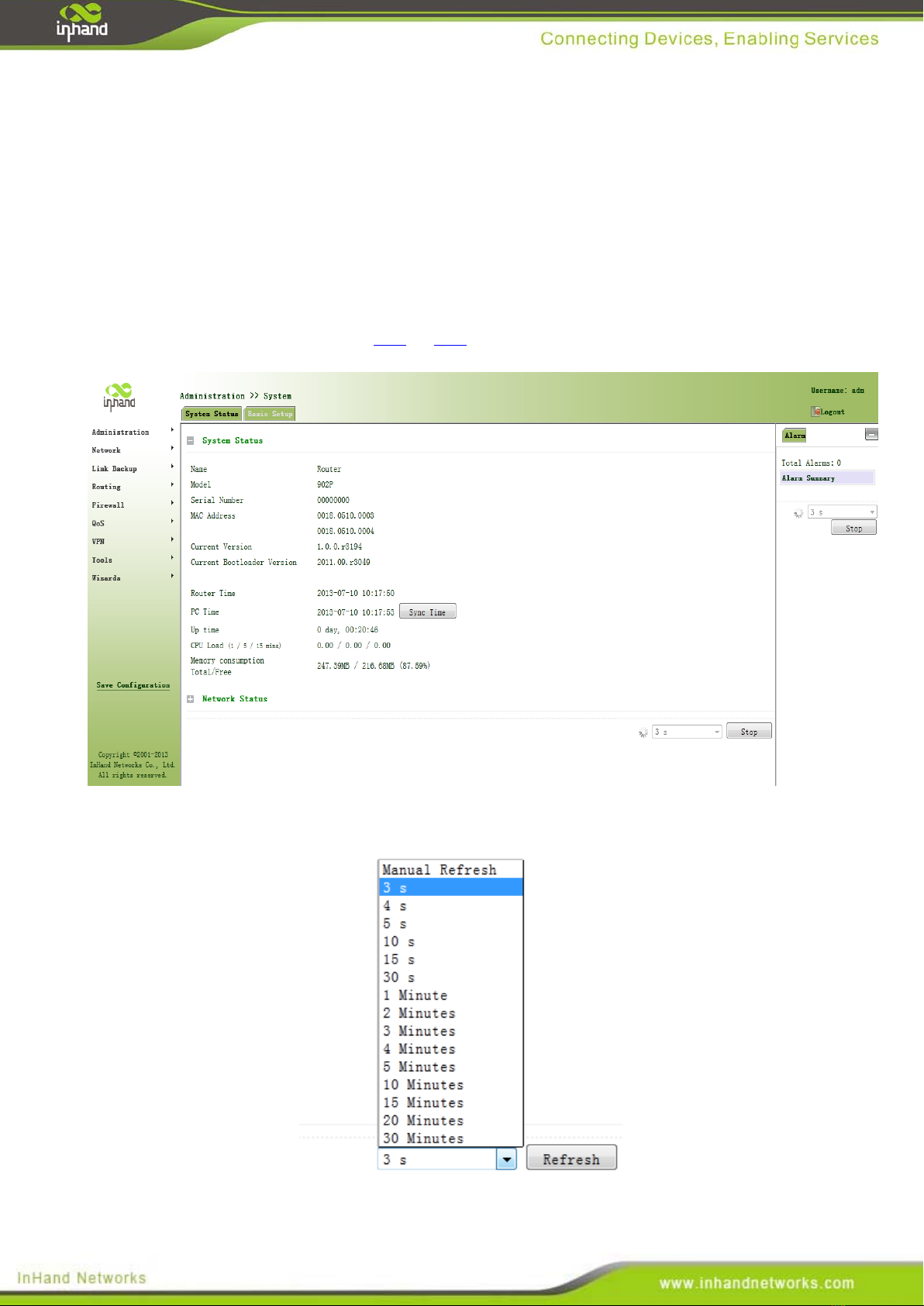
From the left navigation panel, select Administration << System, then enter “System Status” page. On this page
you can check system status and network status, as shown below. In system status, by clicking <Sync Time>you
can make the time of router synchronized with the system time of the host. Click the “Set” behind Cellular1,
Fastethernet 0/1 and Fastethernet 0/2 respectively on network status to enter into the configuration screen directly.
For configuration methods, refer to Section 3.3.1and 3.3.2.
User can define the refresh interval of the screen through the drop down list at the lower right corner of the screen.
Other manuals for InRouter900 Series
1
Table of contents