JasperMIDI guide
Using JasperMIDI
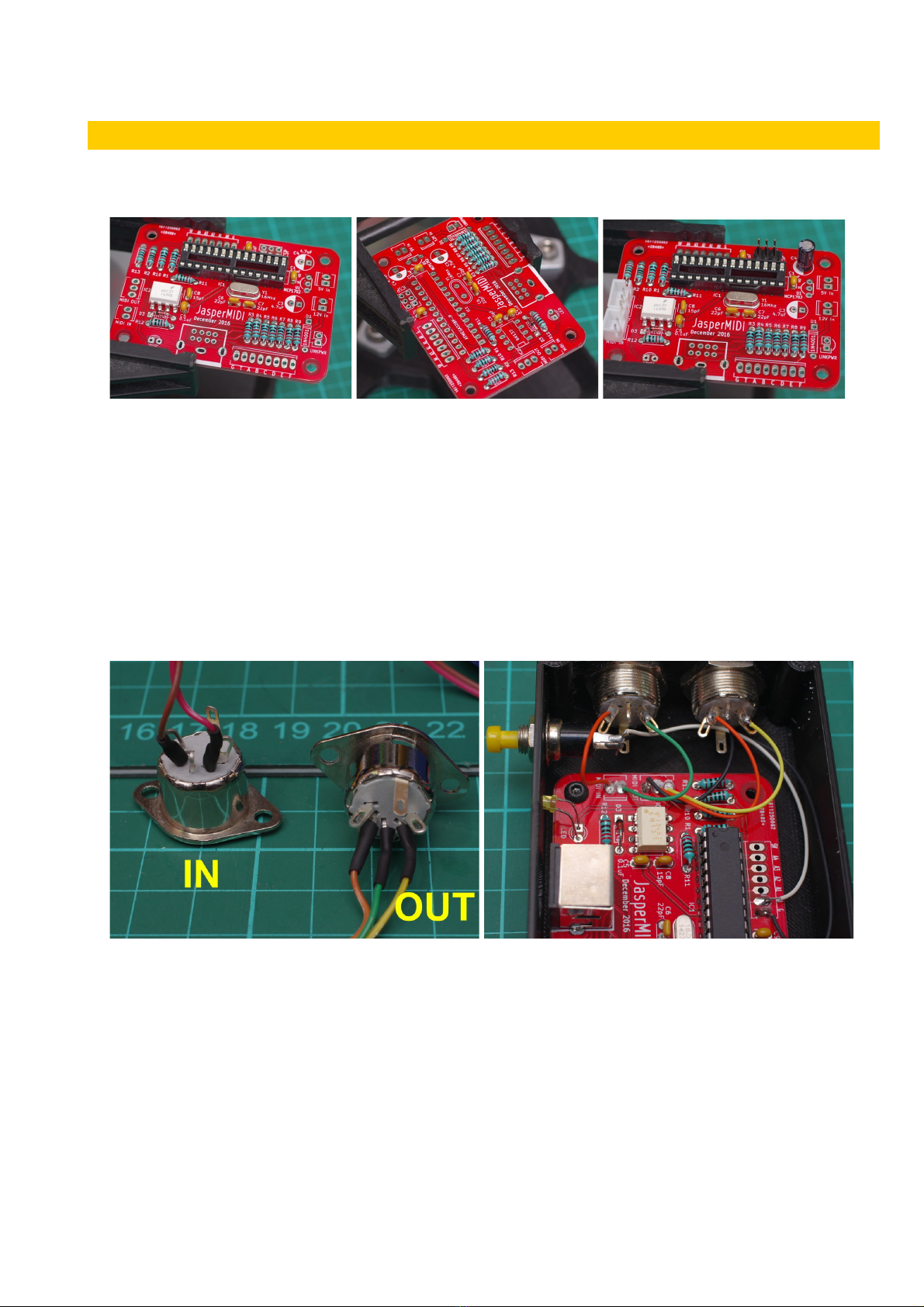
Use standard 5pin DIN MIDI cables to connect JasperMIDI to your other equipment. When
connecting to a Jasper synth with an 8 way mini-DIN connector, make sure you use straight-
through connected shielded cable. The shield must be connected at both ends as this provides the
GND reference for the circuits.
If you are using large 7pin DIN cables as used on original EDP equipment, do not get them mixed
up with the MIDI connectors – you may damage things.
JasperMIDI has a current draw of around 20mA to 23mA in use. If it is idle for a period of time, the
microcontroller goes to sleep drawing less than 8mA. Activity on the Link or MIDI input ports or a
press of the button will wake it up.
By default JasperMIDI will use MIDI channel 1. The only commands it responds to are NoteOn and
NoteOff (or NoteOn with velocity 0) commands for notes 3 -72 – 3 octaves from C0 to C3. The 2
octave Jasper/Wasp keyboard will produce notes in the top two of these octaves from C1 to C3.
Notes outside this range are ignored. Velocity or after-touch is ignored.
The Link port is purely monophonic – multiple synths connected together on a single Link bus will
simply play the same note at the same time. If you try to play two notes at the same time using a
Jasper keyboard and MIDI controller, glitchy results will occur as the different triggers try and
compete!
JasperMIDI keeps track of MIDI notes held down together, allowing for trilling and fast keyboard
playing. When playing a MIDI keyboard, the most recent key is played, even if other keys are held
down. When that key is released, the next most recent key still held down is played.
To change the MIDI channel, hold down the push-button for four seconds. This will put JasperMIDI
into a learning mode which lasts for 10 seconds. The LED will flash. The next MIDI command sent
from your controller will set the channel. This is saved in EEPROM, so will be persistent.
To reset it back to channel 1, hold down the button when the JasperMIDI is powered up.
MIDI output simply consists of NoteOn and NoteOff commands for the notes played over the Link
port. Jasper can be used as a very limited MIDI controller. JasperMIDI doesn’t pass through any
other MIDI data, but only outputs the notes played over the Link bus.
Due to limitations with the Wasp/Jasper envelope triggering circuitry you may find that fast
triggering of notes by MIDI won’t trigger the envelope. If using a keyboard (or Jasper’s touch
keyboard) you will find you have to lift your finger from the keyboard in order to retrigger envelope
on the next note. Likewise if using a sequencer, there should be a minimum of about 30mS
between notes sent over MIDI if you need the envelope to retrigger.
v1 Page 7 of 9 November 2017