7
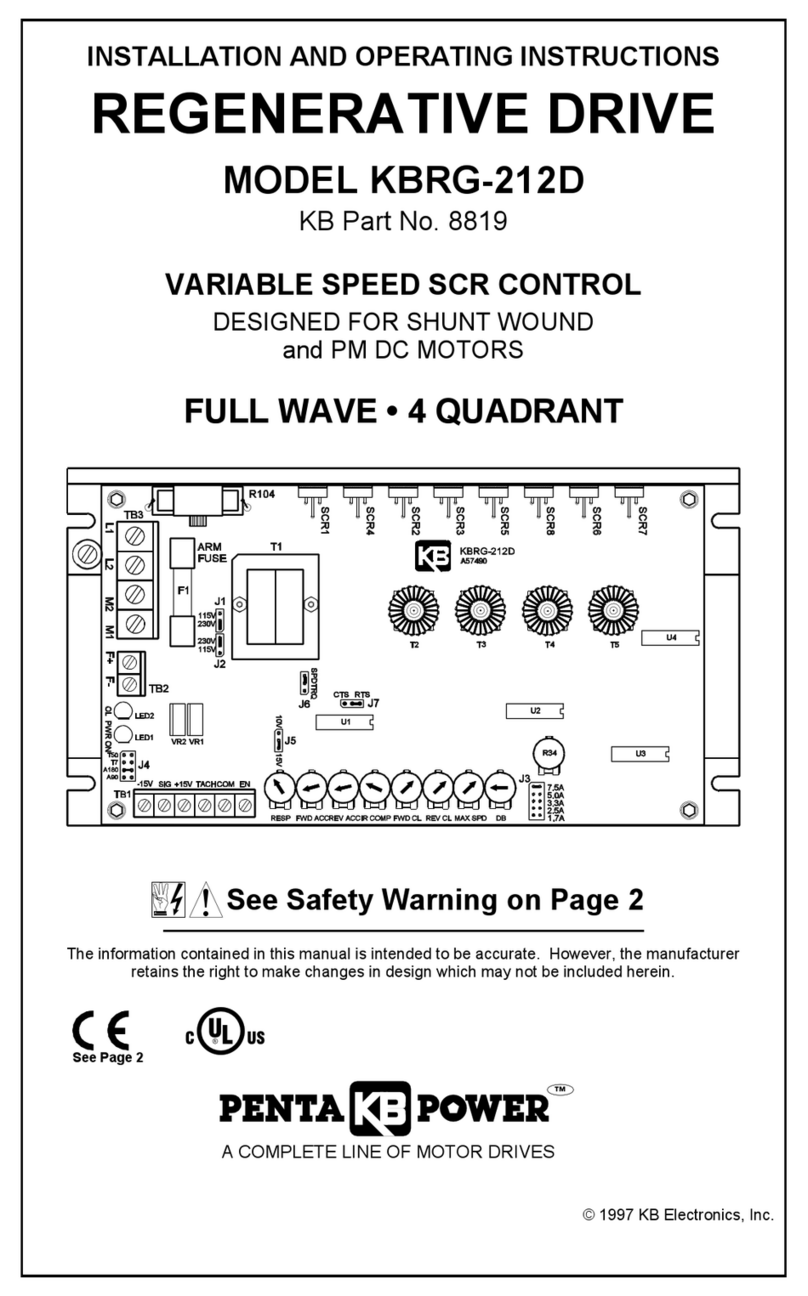
TABLE 1 – STANDARD FEATURES
Feature Description
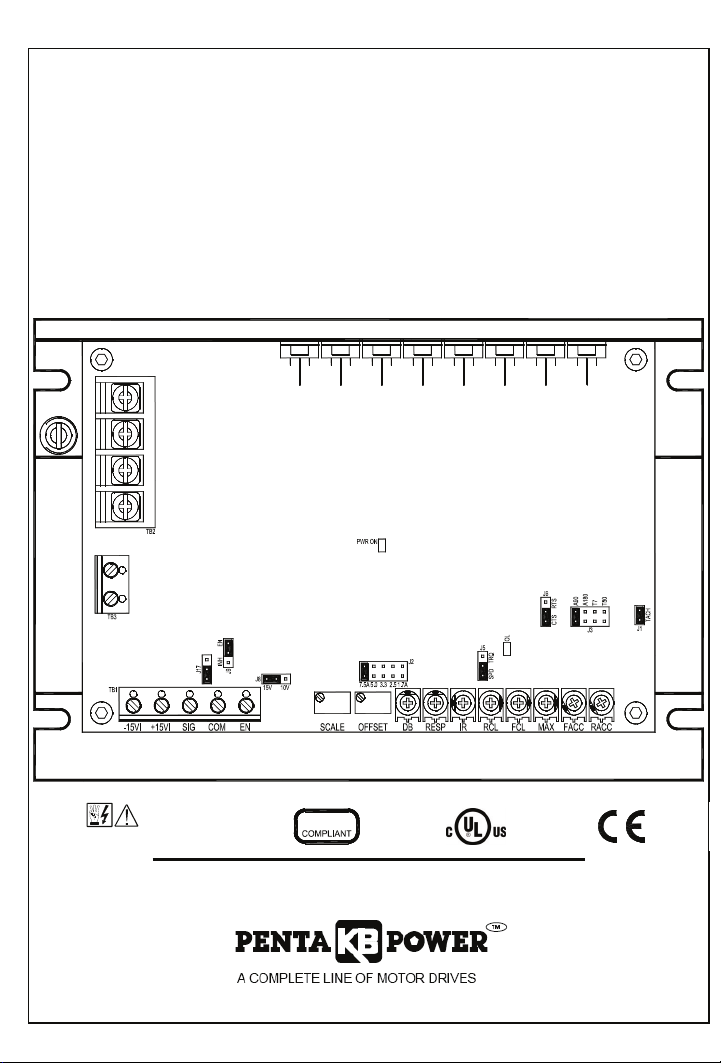
Terminal Blocks
(See Section 6, on page 13.)
Facilitates wiring of AC line, motor armature and field,
TB1 (-15V, +15V, SIG, COM, EN), TB2 (L1, L2, M2, M1), TB3
(F+, F-).
Connectors
(See Section 7, on page 19.)
J1, Tach-Generator Input – Connection point for an external
Tach-Generator.
Selectable Jumpers
(See Section 7, on page 19.)
J2 - Motor Armature Current
J3 - Motor Armature Voltage
J5 -SPD / TRQ – (Speed / Torque)
J6 -CTS/RTS – (Coast to Stop / Regenerate to Stop)
J8 -Signal Input Source (15V or 10V)
J9 - Enable (EN) / Inhibit (INH)
J17- Analog Signal Input (Voltage/Current)
Trimpots
(See Section 10, on page 25.)
Provide adjustment for Forward Acceleration (FACC), Reverse
Acceleration (RACC), Maximum (MAX), Forward Current Limit
(FCL), Reverse Current Limit (RCL), IR Compensation (IR),
Response (RESP), Deadband (DB), Offset (OFFSET), and
Scale (SCALE).
Diagnostic LEDs
(See Section 11, on page 30.)
For Power On (ON), and Current Limit (OL) indications.
(Current Overload gives indication that the control will trip).
TABLE 2 – SELECTABLE JUMPERS (See Section 7, on page 19)
Feature Description
J2-Motor Current, Refer to Section 7.1, on page
19. For selection of the motor current being used.
J3 – Motor Armature Voltage, Refer to Section
7.2, on page 20.
For selection of the motor voltage being
used.
J5-SPD / TRQ, Speed or Torque, Refer to
Section 7.3, on page 20.
Jumper position is selectable for either Speed
(SPD) or Torque (TRQ) modes.
J6-CTS/RTS. Refer to Section 7.4, on page 21.
For selection of Coast to Stop (CTS) and
Regenerate to Stop (RTS). Works in
conjunction with the Enable circuit.
J8-Signal Input (15V or 10V). Refer to Section
7.5, on page 22.
Used for selection of potentiometer (15V) or
use if the control is to be used from a
0 – ±10/±15VDC.
J17-Signal Input. Refer to Section 7.6, on page
22.
Input signal connection for the use with the
Main Speed Potentiometer. Used for
accepting a 0 – ±10V or 0 – ±25V signal or
4 – 20 ma.
J9-EN (Enable) / INH (Inhibit). Refer to Section
7.7, on page 22.
For selection of electronically starting and
stopping the motor. Used in conjunction with
J6, CTS/RTS.