KEPCO, INC. " 131-38 SANFORD AVENUE " FLUSHING, NY. 11355 U.S.A. " TEL (718) 461-7000 " FAX (718) 767-1102
090310 228-1532 REV 9 3
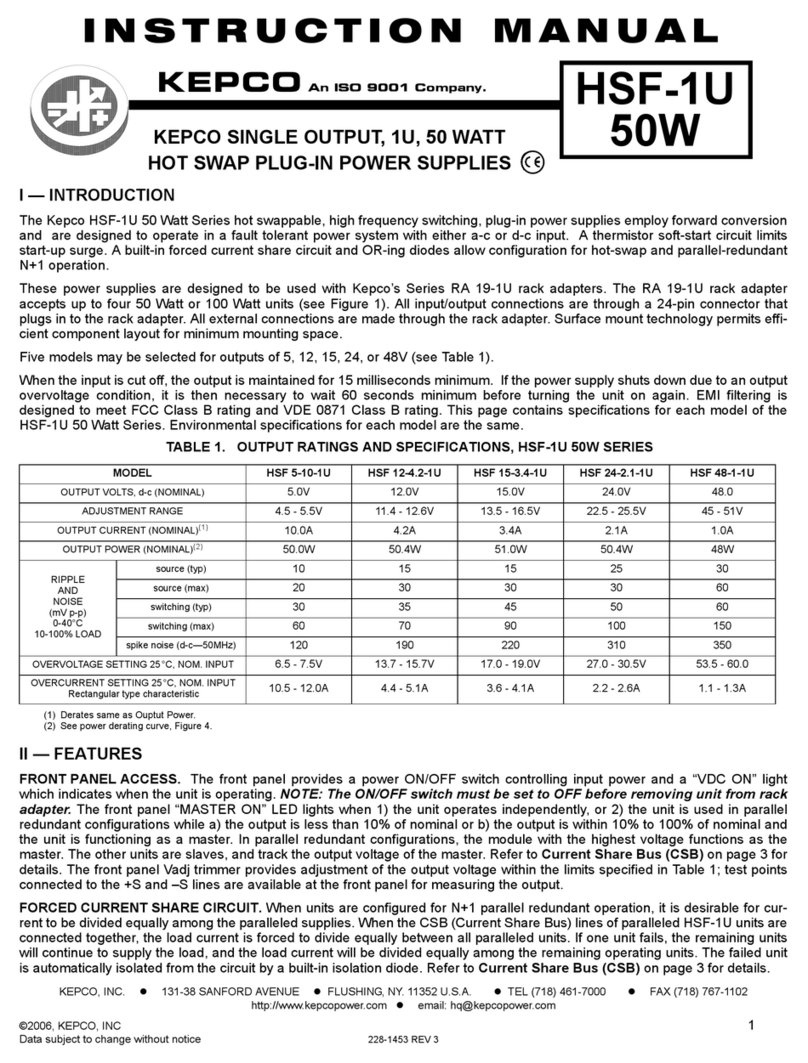
ALARM CIRCUIT. The HSF-PFC includes an isolated
internal relay offering normally closed and normally open
contacts referenced to an isolated common. These con-
tacts are rated for 1A at 30V d-c and 0.5A at 125V a-c.
These contacts may be used to configure “close on failure”
or “open on failure” alarm circuits. (Refer to the Series
RA 19-(X)B Manual for alarm configurations for multiple
HSF-PFC power supplies.) Any condition which causes the
unit to be out of specified voltage/current ranges (including
overvoltage, overcurrent, overtemperature, open sense
line, ac input line failure, etc.) results in an alarm.
KEYING. Keying of the HSF-PFC is established at the
factory. The output voltage determines which keyway is
open. When the corresponding rack adapter key (pin) is
installed by the user, only a power supply of the correct
voltage can be inserted in the rack adapter slot.
CONNECTIONS: The 24-pin I/O connector is designed
to mate with the corresponding connector in the Series RA
19-(X)B Rack Adapter.
FIGURE 3. % OUTPUT POWER RATING VS.
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
(+) SENSE, (–) SENSE: These lines are provided to com-
pensate for voltage drops in the load connecting wires. The
Sense lines must be connected to their respective (+) and
(–) output terminals, either at the load or at the rack
adapter (see Rack Adapter Manual). The connection
ensures the most accurate error tracking. Error compensa-
tion in the connecting wires is up to 0.25 Volts per lead for
all models.
NOTE:
The Sense lines must be connected for the
HSF-PFC Power supply to work properly!
OUTPUT (+), OUTPUT (–): HSF-PFC power supply d-c out-
put.
CURRENT SHARE BUS (CSB): (Not available on 3.3V
model.) Connecting the CSB lines of HSF-PFC power sup-
plies operating in a parallel configuration causes output
current to be shared equally. (See Rack Adapter Manual
for additional information on parallel configurations.). For
current sharing to work properly the outputs of all paralleled
units must be within 250 mV (max) of each other and each
unit must be operating at between 10% to 100% of rated
output. If current to the load goes below 10% for each unit
in current share mode, all MASTER ON lights may go on
(see load effect specifications); this indicates that forced
current share is no longer working, units are simply in cur-
rent share mode. (If forced current sharing at less than
10% nominal current per supply is needed, contact Kepco
application engineering.) Remote sensing is recom-
mended. For master/slave operation to work properly each
unit should be adjusted to 40 mV (optimum) less than the
next paralleled unit (unit 1 is adjusted to VOUT
, unit 2 to
VOUT – 40mV, and unit 3 to VOUT – 80mV, etc. If the master
fails, the unit 2 will become the new master). The 40 mV
difference can be reduced to a minimum of 25 mV as
needed to parallel many units and still keep all units within
250 mV of each other. Adjust the outputs using Vadj trim-
mer on front panel.
• Optimum difference among output voltages of par-
alleled units: 40mV
• Maximum difference among output voltages of
paralleled units: 250 mV
• Minimum difference among output voltages of par-
alleled units: 25 mV
ALARM: The Alarm NC (normally closed) - Open on Fail-
ure and Alarm NO (normally open) - Close on Failure lines
are relay contacts referenced to Alarm Common. If the unit
fails, the path between Alarm NC - Open on Failure and
Alarm Common opens, the path between Alarm NO - Close
on Fail and Alarm Common is a short circuit. Figure 4 illus-
trates typical Close on Fail and Open on Fail circuits to give
a failure indication if any one of a number of power supplies
fail.
INPUT POWER: Line (either a-c or d-c source power), Neu-
tral and Ground (chassis)