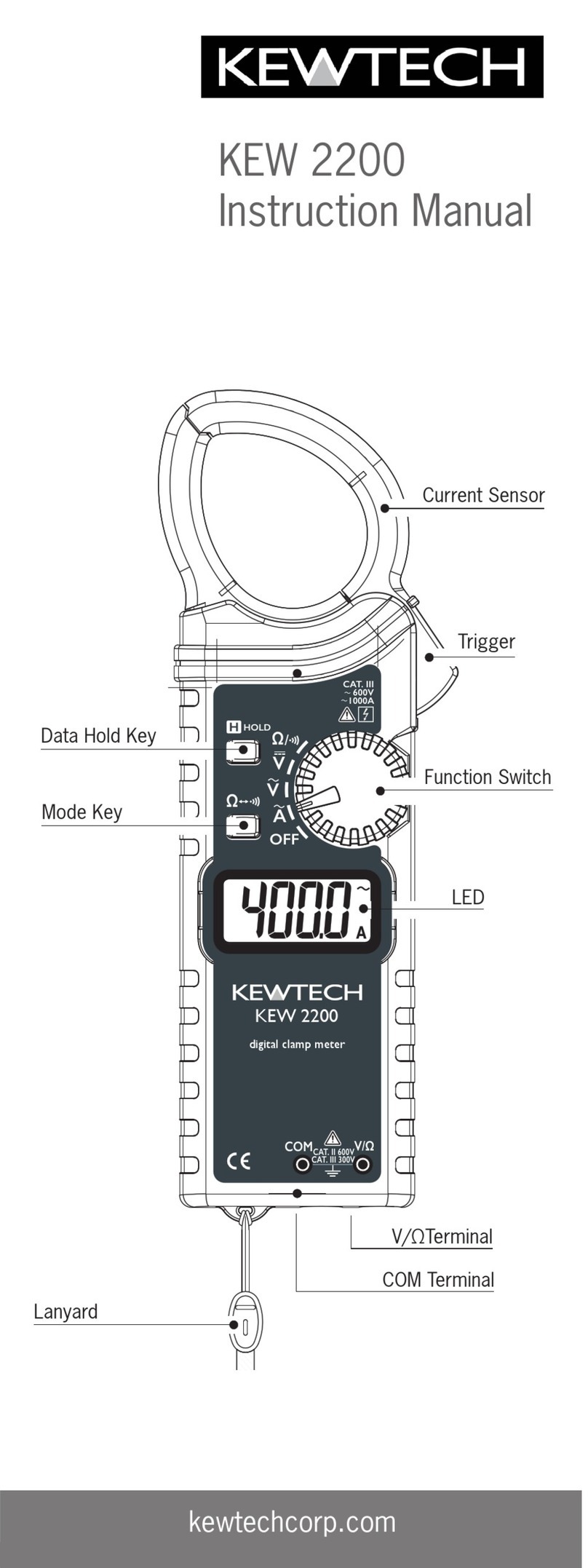
Electricity is dangerous and can cause injury and death. Always treat
it with the greatest of respect and care. If you are not quite sure how
to proceed, stop and take advice from a qualified person.
1 This instrument must only be used by a competent and trained person
and operated in strict accordance with the instructions. Kewtech will
not accept liability for any damage or injury caused by misuse or non-
compliance with the instructions or with the safety procedures.
2 It is essential to read and to understand the safety rules contained
in these instructions. They must always be observed when using the
instrument.
3 This instrument is designed to work in distribution systems where the line
to earth has a maximum voltage of 300V 50/60Hz and for some ranges
where line to line has a maximum voltage of 500V 50/60Hz.
Be sure to use it within this rated voltage.
For use in the continuity testing and insulation testing modes this
instrument must be used ONLY on circuits which are de-energized.
4 When conducting tests do not touch any exposed metalwork associated
with the installation. Such metalwork may become live for the duration of
the test.
5 Never open the instrument case (except for fuse and battery
replacement and in this case disconnect all leads first) because
dangerous voltages are present. Only fully trained and competent
electrical engineers should open the case. If a fault develops, return the
instrument to Kewtech for inspection and repair.
6 If the overheat symbol appears in the display disconnect the instrument
from the mains supply and allow to cool down.
7 If abnormal conditions of any sort are noted (such as a faulty display,
unexpected readings, broken case, cracked test leads, etc) do not use
the tester and return it to Kewtech for repair.
8 For safety reasons only use accessories (test leads, probes, fuses,
cases, etc) designed to be used with this instrument and recommended
by Kewtech. The use of other accessories is prohibited as they are
unlikely to have the correct safety features.
9 When testing, always be sure to keep your fingers behind the finger
guards on the test leads.
10 During testing it is possible that there may be a momentary degradation
of the reading due to the presence of excessive transients or discharges
on the electrical system under test. Should this be observed, the test
must be repeated to obtain a correct reading. If in doubt, contact
Kewtech.
1 Safe Testing