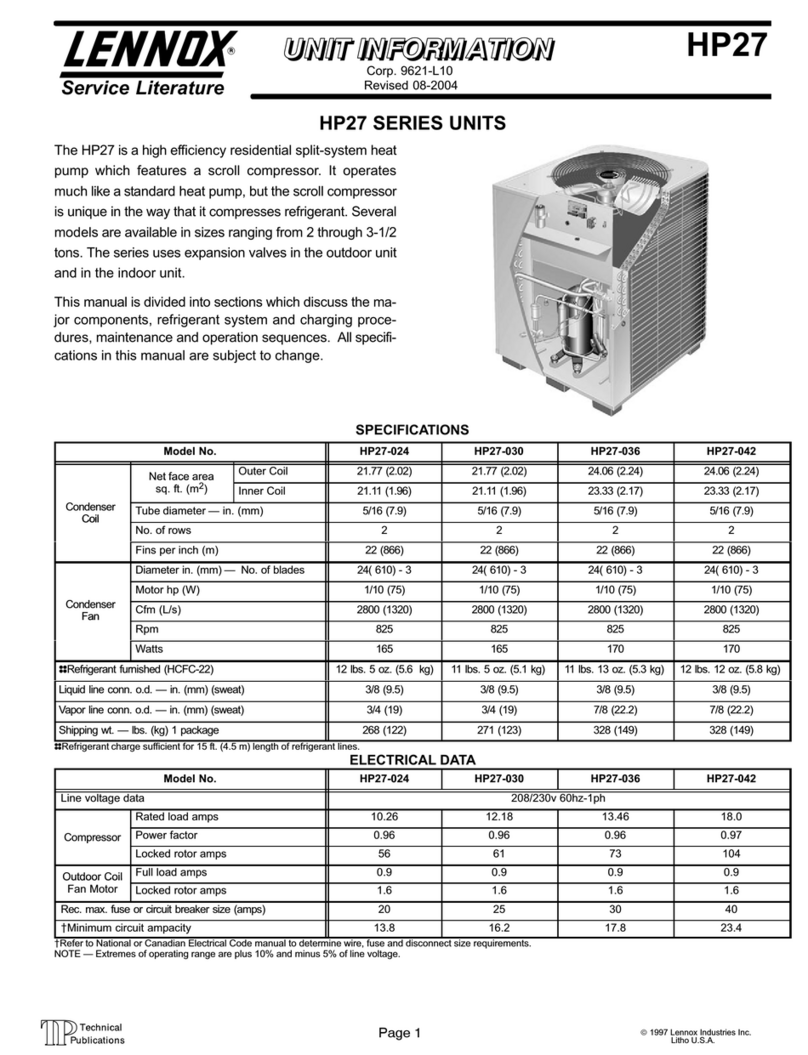
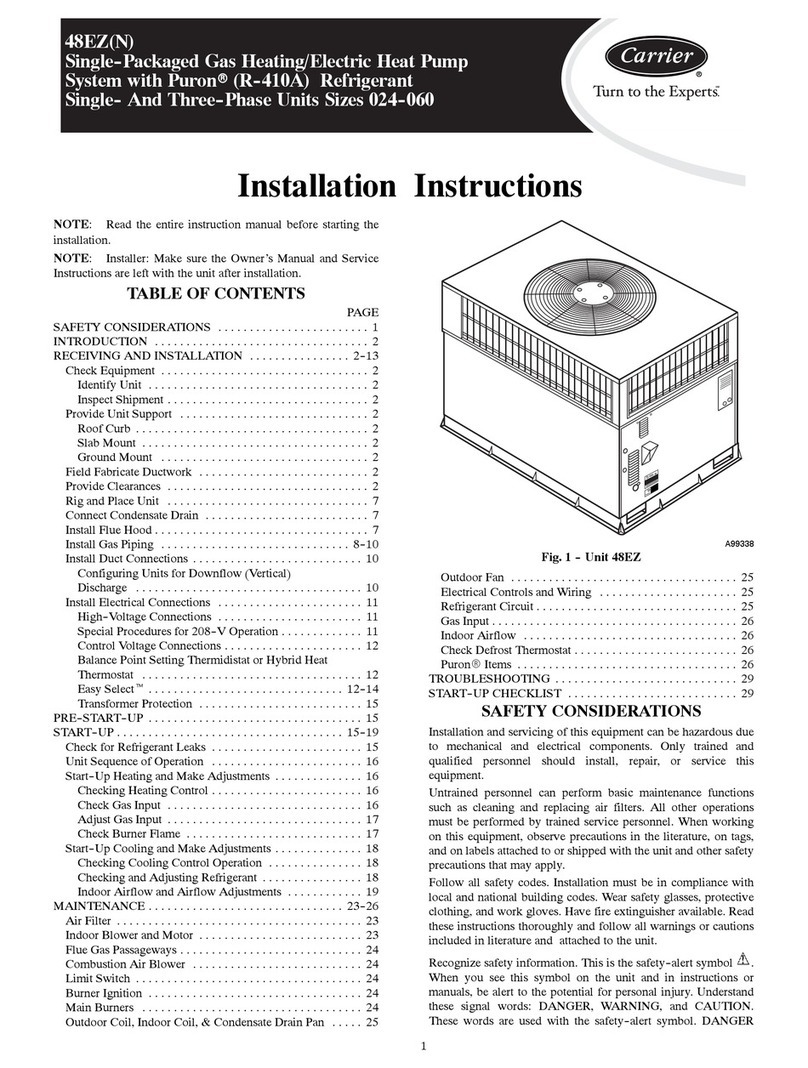
Page 10
Plumbing
Field re rigerant piping consists o liquid and vapor lines
rom the heat pump unit. Piping may be brought into the
unit through either side. Remove the knockouts on the
mullions and install the provided rubber grommets into the
piping holes. Remove the plugs rom the liquid and vapor
lines. Re er to table 1 or ieldĆ abricated re rigerant line
sizes or runs up to 50 linear eet (15 m).
TABLE 1
REFRIGERANT LINE SIZES
UNIT LIQUID LINE VAPOR LINE
HP29-090 5/8 in. (16 mm) 1-3/8 in. (35 mm)
HP29-120 5/8 in. (16 mm) 1-3/8 in. (35 mm)
Refrigerant Line Brazing Procedure
1 - End o re rigerant line must be cut square, kept round,
ree rom nicks or dents and deburred (I.D. and O.D.)
2 - Wrap a wet cloth around the valve body when brazing
to prevent possible heat damage to the valve core and
port.
3 - Install ilter drier, provided with unit, in the liquid line as
close as possible to the expansion device.
Refrigerant Line Limitation
Unit applications with line set lengths up to 50 linear eet
(15 m) (excluding equivalent length o ittings) may be
installed using re rigerant line sizes as outlined in table 1.
Refrigerant line from 50 to 100 linear feet (15 to 30 m)
hould be ized in accordance with the following ecĆ
tion. The maximum line length is 100 eet (30 m).
Maximum suction rise must not exceed 45 linear eet
(13.7 m) and maximum liquid head must not exceed 45
linear eet (13.7 m).
Re er to the re rigerant piping guideline manual (Corp.
9351-L9) i line lengths exceed 50 eet (15 m). In these
applications, you must install a liquid line solenoid valve
at the evaporator coil. In addition, use expansion valves
only (RFC and capĆtube expansion devices are not acĆ
ceptable). In applications where the lines exceed 75 eet
(23 m), install the solenoid valve with a nonĆrecycling
pumpĆdown control.
NOTE - When refrigerant line solenoid valves are installed,
velocities sho ld not exceed 300 fpm (1.5 m s) in order to
avoid liq id line hammer.
All units are equipped with a low ambient (head pressure)
control to allow or cooling down to 0°F (-18°C).
Due to the additional re rigerant required to ill the lines,
the likelihood o slugging is greatly increased with lines
that are over 50 eet (15 m) in length. An incremental inĆ
crease in liquid line size results in a 40 to 50 percent inĆ
crease in liquid to ill the line. There ore, it is desirable to
use the smallest liquid line size possible.
Pipe Sizing, Line Layout and De ign
[Line et length from 50 - 100 linear feet
(15 - 30 m)]
Start by making a sketch o the system showing relative
locations o the heat pump unit and the indoor coil, length o
each piping segment, elbows, tees, valves, etc. This in orĆ
mation will be used to determine the equivalent length o
the piping run. Also, take note o any di erence in elevation
between the outdoor and indoor units. Vapor and liquid li t
must be considered to ensure proper pipe sizing.
Liquid Line Function and De ign
The liquid line must convey a ull column o liquid rom the
outdoor unit to the metering device at the indoor coil withĆ
out lashing. In order to ensure this, liquid line pressure
drop and pressure across the expansion device and disĆ
tributor must be considered.
TABLE 2
HCFCĆ22 SATURATION TEMPERATURES
(Conden ing Temperature at Different Pre ure )
HCFCĆ22 Pre ure Temperature Table (P ig)
Degree F (°C) HCFC22 Degree F (°C) HCFC22 Degree F (°C) HCFC22 Degree F (°C) HCFC22 Degree F (°C) HCFC22
-40 (-41) 0.6 18 (-8) 41.1 36 (2) 63.3 75 (24) 133.4 120 (49) 262.5
-30 (-34) 4.9 20 (-7) 43.3 38 (3) 66.1 80 (27) 145.0 125 (52) 280.7
-20 (-28) 10.2 22 (-6) 45.5 40 (4) 69.0 85 (29) 157.2 130 (54) 299.7
-10 (-23) 16.6 24 (-4) 47.9 45 (7) 76.6 90 (32) 170.0 135 (57) 319.6
0 (-18) 24.1 26 (-3) 50.3 50 (10) 84.7 95 (35) 183.6 140 (60) 340.3
10 (-12) 32.9 28 (-2) 52.7 55 (13) 93.3 100 (38) 197.9 145 (63) 362.0
12 (-11) 34.9 30 (-1) 55.2 60 (16) 102.4 105 (41) 212.9 150 (66) 384.6
14 (-10) 36.9 32 (0) 57.8 65 (18) 112.2 110 (43) 228.6 155 (68) 406.3
16 (-9) 39.0 34 (1) 60.5 70 (21) 122.5 115 (46) 245.2 160 (71) 433.3