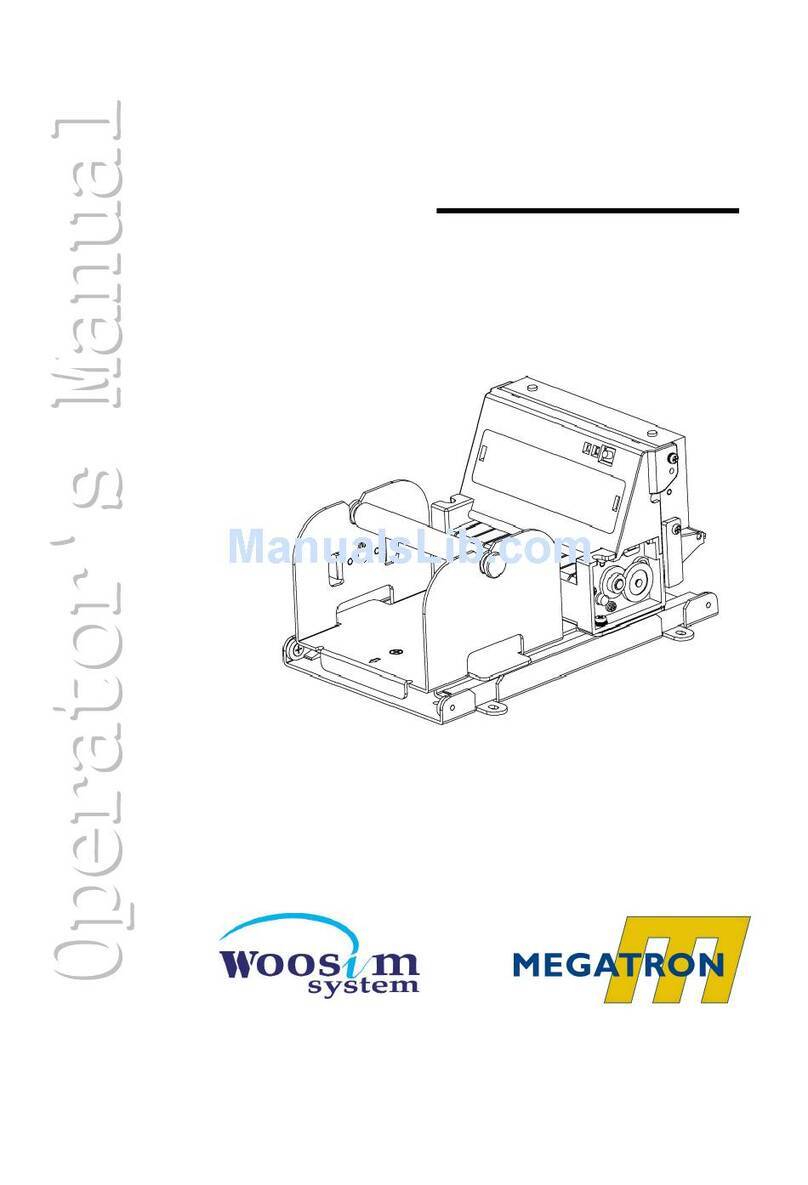
Megatron TP UP-NH User manual

24 25
TP UP-NH
Line Thermal Printer
User's Manual
April 1998
Contents
Introduction 1
Chapter 1 Features and Specifications 2
1.1 PrintingFeatures 2
1.2 PrintingPaper 2
1.3 PrintingCharacter 2
1.4 PrintingBufferSize 2
1.5 PrintingCommands 2
1.6 OperationFormat 3
1.7 Printer-head Energy Compensation Function 3
1.8 Printer-head Protection Function 3
1.9 Interface 3
1.10 Power Supply 3
1.11 Power Supply Control 4
1.12Dimension 4
1.13Weight 4
1.14 Operation Environment 4
Chapter 2 Installation and Operation 5
2.1 Appearance 5
2.2 Loading Printing Paper 6
2.3 PowerONandOFF 8
2-3-1 Connecting of Power 8
2-3-2 Auto Power OFF 10
2.4 Indicator and Function Key 11
2.5 Connecting of Parallel Interface 11
2.6 Connecting of Serial Interface 13
Chapter3 PrintingCommands 15
3.1 Summary 15
3.2 Paper Feed Command 15
3.3 Format Setting Commands 16
3.4 Character Setting Commands 18
3.5 User-defined Characters Commands 20
3.5.1 User-defined Characters Form I 20
3.5.2 User-defined Characters Form II 22
3.6 Graphics Printing Commands 23
3.6.1 Bit Map Graph Setting form I 23
3.6.2 Bit Map Graph Setting form II 23
3.7 Initialization Command 26
3.8 Data Control Command 27
3.9 Hexadecimal Printing Command 27
Appendix 1 Index of Printing Command 28

24 25
Introduction
TP UP-NH is a new type of line direct thermal printer. The special features of this
printer are small in size, light in weight, low noisy and high in printing quality and
reliability. It is suitable for printing receipt of cash register and data records of
medical instruments.
Chapter 1 Features and Specifications
1.1 Printing Features
- Printing Method: Line direct thermal
- Paper Width: 57.5 mm ±0.5 mm
- Printing Density: 8 dots/mm, 384dots/line
- Printing Speed: 12.5mm/sec. (DC9V 1A)
- Printing Width: 48mm
1.2 Printing Paper
- Thermal Paper Roll
Paper Width: 57.5 mm ±0.5mm
OD: 50 mm(max, Build-in)
I D: 10 mm(min)
Thickness: 53 - 64 g /m2
1.3 Printing Character
- IBM Character set 2
12 x 24 dots, 1.50 mm(w) x 3.00 mm(h)
8 x 16 dots, 1.00 mm(w) x 2.00 mm(h)
1.4 Data Buffer Size
- 10k bytes
1.5 Printing Commands
- ESC/P Commands
1.6 Operation
- Printing out text in ANK, graph and hexadecimal
- Self-test
- Paper feed
1.7 Printer-head Energy Compensation Function
- Temperature Control: by test of build-in thermal resistor.

24 25
- Voltage Control: by test of voltage
1.8 Printer-head Protection Function
- Stop warning for out of paper
- Stop warning for printer-head over/under the normal temperature
1.9 Interface
- Serial (compatible with RS232)
Baud Rate: 1200/2400/4800/9600, selected by DIP switch built-in
Handshaking: RTS/CTS or XON/XOFF protocol.
Data Structure: 7/8 Data Bits and even, odd or no Parity Bit
Connect Socket: D-Sub 25pin (femal in printer side)
Signal Level: EIA +/-3V to +/-12V
- Parallel (compatible with PC Printer port)
Handshaking: BUSY or ACK protocol
Connect Socket: D-Sub 25pin (male in printer side)
Signal Level: TTL
1.10 Power Supply
- DC9V 1A average printing current 2.6A, non-printing current 80mA.
- Power Socket: DC Jack type with center pin φ2.0mm
1.11 Power Supply Control
- Auto Power off Function
- Support Push Button and Interface Signal Control
1.12 Dimension
- 160 (w) x 106 (d) x 42 (h) mm
1.13 Weight
- 350g including paper roll
1.14 Operation Environment
- Operating temperature: 5 o - 50oC
- Relative humidity: 5 - 85% RH
Chapter 2 Installation and Operation
2.1 Appearance

24 25
Figure.2-1 Appearance
2.2 Loading Printing Paper
Paper roll can be put inside the case, Loading paper as follows:
1. push the removable upper cover plate forward till its off the printer like figure
2-2 below, figure 2-3 is not correct.
Figure 2-2
Figure 2-3
2. Cut the paper end like figure 2-4 below.
- for paper roll placed inside the case: Insert the paper end deep-down into paper
in slot on rear of printer mechanism like figure 2-5. Figure 2-6 is not correct.
- for paper roll hold outside the case: Insert the paper end through paper in slot
on the back of the printer first, then repeat the action above.
Figure 2-4
Figure 2-5 Figure 2-6
3. Lift the lever of the print mechanism and push the paper end forward out of the
mechanism. Turn on the power. Power indicator flashing while press SEL
button. Hold the LF button, paper will automatically move upwards to paper
out slot on top of printer mechanism for certain length , then release the button.

24 25
4. Pull the paper out through paper out slot on upper cover plate and then close
the plate like figure 2-7 below.
Figure 2-7 put upper cover plate back to the printer
2-3 Power On and OFF
This printer provides auto power cut off function to save energy.
2.3.1 Connecting of Power
After connecting the power supply, there are two methods of power connecting
namely: 1. by push button; 2. by interface.
1. By Push Button.
There are two push buttons on the control panel namely SEL & LF. Press SEL
button, power indicator will be in red to indicate the printer is on power..
2. By Interface
- Using Parallel Interface. The interface signal INIT is negative pulse signal and
will remain for at least 3ms to ensure power on. Power Indicator turns in red
to signal the printer is on power. Wait another 600ms to initialize printer before
sending data.
- Using Serial Interface. The interface signal DTR is EIA standard. It is logical
level from “1” to “0 ” and remain at least 3ms to ensure power connection. Power
indicator turns in red to signal the printer is on power. Wait another 600ms to
initialize printer before sending data.
3. Example of Using Parallel Interface (for PC)
BasicFormal Explanation
100 DEF SEG=&H40 : Bottom of BIOS
database.
200 prtr=PEEK (9) *256+PEEK (8) +2 : Get base address of
LPT1.
300 OUT prtr, 8 : Initialize printer by
negative signal through
INIT.
400 IF (INP (prtr-1) AND &H98)
<>&H98THEN 400 : Loop if check the printer
is BUSY.
500 . : Normal printing
procedure.
.
.
.
.
prtr-1 status register of parallel interface
BIT3: 0, printer error; 1, printer normal
BIT4: 0, printer off line;1, printer on line
BIT7: 0, printer busy; 1, printer not busy
prtr control register of parallel interface
BIT2: 0, initialize printer; 1, normal setting
BIT3: 0, make printer off line; 1, normal setting
4. Example of Using Serial Interface (for PC)
Basic Program Explanation
100 baseaddress = &H2f8 : Set base address of serial port.
: &H3F8 for COM1 and &H2F8
for COM2.
200 OUT baseaddress +4, &H1 : DTR (data terminal ready) set
high.
300 IF (INP (baseaddress+6) AND
&HB0) <> &HB0 THEN 300. : Loop if check printer is not
READY.
400 . : Execute normal printing
procedure
.
.
.
.
baseaddress+4: Control register of modem of the PC serial port
COM1 or COM2.
BIT0: DTR (data terminal ready) set 1 for valid.
baseaddress +6 Status register of modem of the PC serial port

24 25
COM1.
BIT4: CTS allow for transmitting” input high (ok).
BIT5: DSR data ready” input high (ok).
BIT7: RLSD receipt route signal testing” input high(ok).
2.3.2 Auto Power Off
This printer provides auto power cut off function. If no paper feed and printing
function performed more than 10 seconds, power will be automatically cut off.
2.4 Indicator & Function Key
There are two indicators and two switch buttons on the panel of TP UP-NH printer.
Power Indicator marked with P and Status indicator marked with SEL. When SEL
indicator in light or flash , it means printer is wrong otherwise means printer is
normal. For power connection, press SEL button; for paper feed press LF button.
see figure 2-8 below:
Figure 2-8
1. Self-test
To start self-test, press and hold down LF button and SEL button as well while
power on, when power indicator light, release both buttons, then self-test sample
will be printed.
2. Paper feed
Press and hold down LF button to start paper feeding and release it to stop paper
feeding.
2.5 Connecting of Interface (parallel port)
TP UP-NH adopts DB-25 parallel port which is compatible with PC ′s printer port.
1. The Pin Assignment of DB-25 is shown as follows:
PinN
o Signal I/O Description
1 /STB In Strobe pulse, to read data. Reading occurs at falling edge.
2 D0 In Data line: D0
3 D1 In Data line: D1
4 D2 In Data line: D2
5 D3 In Data line: D3
6 D4 In Data line: D4
7 D5 In Data line: D5
8 D6 In Data line: D6
9 D7 In Data line: D7
10 /ACK Out Acknowledge pulse. Printer is ready to accept data. It takes no less
than 10µs to change from high level to low level.
11 BUSY Out High level signal indicates that the printer is Busy and can not
receive data while low level is able to receive data.
12 PE Out High level signal indicates that paper running out. Low level signal
indicates
otherwise.
13 SLCT Out Selection, pull up to 5V.
14 ------- ----- No connection.
15 /ERRO
R Out Pull up to 5V
16 /INIT In Low level signal (no less than 3ms) for control of printer power.
17 ------- ----- No connection.
18
- ------- ----- Grounding.
25
2. The signal timing chart in parallel port is as follows:
Figure 2-9 Signal timing chart of parallel port
2.6 Connecting of Interface (serial port)
TP UP-NH adopts serial port which is compatible with RS232C for DB-25 socket
(female type in printer side)
1. DIP Switch Setting
K1-K6 for setting of baud rate, data bit, stop bit and parity. Default settings are
all on off position, users can change setting according to the following tables:

24 25
Baud Rate (BPS) Parity Check
ON ■■
OFF □□
1 2
1200
ON ■□□
OFF □■■
4 5 6
8 bit
odd parity
ON □■
OFF ■□
2400
ON □■□
OFF ■□■
8 bit
even parity
ON ■□
OFF □■
4800
ON □□□
OFF ■■■
8 bit
non-parity
ON □□
OFF ■■
9600
ON ■□■
OFF □■□
7 bit
odd parity
ON □■■
OFF ■□□
7 bit
even parity
ON □□■
OFF ■■□
7 bit
non-parity
DIP Switch Handshaking Default Setting
ON □□□□□□
OFF □□■□□□
1 2 3 4 5 6
XON/XOFF
ON □□□□□□
OFF ■■■■■■
1 2 3 4 5 6
ON □□■□□□
OFF □□□□□□
1 2 3 4 5 6
RTS/CTS
Figure 2-10 DIP Switch Setting
Pin Assignment of DB25
Pin No. Signal Source Description
2 TXD Host Printer receive data from host.
3 RXD Printer Printer transmit data. Printer transmit XON/XOFF
code to host while in use of handshaking of
XON/XOFF.
5 CTS Printer There are two states of this signal, "Mark" and
"Space". "Mark" indicates that the printer is busy
and unable to receive data; "Space" indicates that
printer is ready to receive data.
7 GND Printer Signal ground
20 DTR Host In SPACE” status for not less than 3ms, for control
of printer power.
Chapter 3 Printing Commands
3.1 Summary
TP UP-NH provides ESC/P commands:
1. define format
2. enlarge characters
3. print bit map graphs
4. choice character sets
5. define user-defined characters
6. others
Each command is described in following format:
Printingcommand Function
Format: ASCII: the standard ASCII characters sequence.
Decimal: the decimal numbers sequence.
Hexadecimal: the hexadecimal numbers sequence.
Explanation: What the command does and how to use it.
3.2 Paper Feed Commands
LF Line Feed
Format ASCII : LF
Decimal : 10
Hexadecimal: 0A
Explanation:
Print data in buffer of the printer and feed one line forward. Feed one
line forward only if no data in buffer of the printer.

24 25
ESC J 'n' Dot Line Feed
Format ASCII : ESC J n
Decimal : 27 74 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 4A n
Explanation:
print data in buffer of the printer and feed 'n' -dot line forward. The value of n is
between 0 and 255.
Line space will be automatically adjusted when using commands ESC V & ESC W
for enlarge characters.
ESC 1 Set n’ dot line spacing
Format ASCII : ESC 1 n
Decimal : 27 49 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 31 n
Explanation:
The line spacing is set to n dot lines for future Line Feed command. The value of n
is between 0 and 255. Default setting n=10 for text printing, n=0 for bit map
printing when using ESC K command.
3.3 Format Setting Commands
ESC D Set Horizontal Tabs
Format ASCII : ESC D n1 n2 ... NUL
Decimal : 27 68 n1 n2 ... 0
Hexadecimal: 1B 44 n1 n2 ... 00
Explanation:
The tab positions are entered as n1 , n2and so on. These n1 , n2 should be within the
line width of the printer. For character set A 12x24 dots,
the maximum value n=32; for character set B 8x16 dots, the maximum value n=48.
NUL character is added to indicate the end of command.
All settings can be cleared by using command ESC D NUL.
HT Horizontal Tab
Format ASCII : HT
Decimal : 9
Hexadecimal: 09
Explanation:
The printing position is advanced to the next horizontal tab.
HT command will not execute if the current print position exceeds the last
horizontal tab.
ESC f Print Blank Characters or Lines
Format ASCII : ESC f m n
Decimal : 27 102 m n
Hexadecimal: 1B 66 m n
Explanation:
If m=0, command ESC f NUL will print n blank characters. The value n should be
within the line width of the printer (see command ESC D in the chapter).
If m=1, command ESC f n will print n blank lines. The value of n should be within
the range between 0 to 255.
ESC I Set Left Margin
Format ASCII : ESC I n
Decimal : 27 108 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 6C n
Explanation:
This command sets start printing position as n character from left.
The value of n should be within the line width of the printer. For character set A,
n=32 and character set B, n=48. Default value n=0, This means no left margin.
The command sets an absolute position and is not affected by character enlarge
command ESC U or ESC W.
3.4 Character Setting Commands
ESC U Enlarge Width
Format ASCII : ESC U n
Decimal : 27 85 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 55 n
Explanation:
Characters or graphics following this command are printed atn times normal width.
The value n should be in the range 1- 2. Default value n=1, that means normal
width.
ESC V Enlarge Height
Format ASCII : ESC V n
Decimal : 27 86 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 56 n
Explanation:

24 25
Characters or graphics following this command are printed atn times normal height.
The value n should be within the range 1-2. Default value n=1, that means normal
height.
ESC W Enlarge Width & Height
Format ASCII : ESC W n
Decimal : 27 87 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 57 n
Explanation:
Characters or graphics following this command are printed at n times normal width
and height. The value n should be in the range 1-2. Default value n=1, that means
normal width and height.
ESC - Turn Underline on/off
Format ASCII : ESC - n
Decimal : 27 45 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 2D n
Explanation:
Underlining is turned on if n=1, all characters are underscored including spaces.
Underline is turned off if n=0.
ESC 6 Select Font A
Format ASCII : ESC 6
Decimal : 27 54
Hexadecimal: 1B 36
Explanation:
Characters following this command are printed using the Font A. There are two
fonts available in the TP UP-NH printer. Font A is selected at power on or on ESC
@ command.
ESC 7 Select Font B
Format ASCII : ESC 7
Decimal : 27 55
Hexadecimal: 1B 37
Explanation:
Characters following this command are printed using the font B (see ESC 6).
SO Select Double-width Printing
Format ASCII : SO
Decimal : 14
Hexadecimal: OE
Explanation:
Characters following this command on the same line n the print buffer are printed at
twice their normal width. The command is canceled by a Carriage Return or using
DC4 command.
DC4 Cancel Double-width Printing
Format ASCII : DC4
Decimal : 20
Hexadecimal: 14
Explanation:
Double-width printing is canceled if it has been set using SO. This command does
not cancel enlarge width printing selected using ESC U or ESC W.
ESC c Turn Inverse Printing on/off
Format ASCII : ESC c n
Decimal : 27 99 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 63 n
Explanation:
Inverse printing is turned on if n=1; inverse printing is turned off if n=0. Default
value n=0
3.5 User Defined Characters Commands
There two forms of user defined characters which can be recognized by printer
automatically.
3.5.1 User Defined Characters Form 1
Support user defined characters for 101 DPI horizontal and 68 DPI vertical.
Compatible with TPuP-T printer.
ESC & Define User Defined Characters
Format ASCII : ESC & m n1 n2 ... n6
Decimal : 27 38 m n1 n2 ... n6
Hexadecimal: 1B 26 m n1 n2 ... n6
Explanation:
This command allows a character to be defined. The value m is the code of this
user-defined character and ranges from 32 to 255. The value n1,n2,...n6 are codes
for structure defined characters. Character size is 6 x 8 dot matrix. That means
there are six codes, each code define one row of character for 8 rows.
User-defined characters are stored in printer RAM until power off. It can print out
according to 101 DPI horizontal and 68 DPI vertical.
If many ESC & commands use same m value, only the last one is
effective. The maximum number of user-defined characters is 32. Also

24 25
see ESC% and ESC: commands.
ESC % Replace with User Defined Characters
Format ASCII : ESC % m1n1 m2n2 ... mknk NUL
Decimal : 27 37 m1n1 m2n2 ... mknk 0
Hexadecimal: 1B 25 m1n1 m2n2 ... mknk 00
Explanation:
This command is used to replace font characters n with user-defined characters m.
m1, m2, ... mk are codes of user-defined characters.
n1, n2, ... nk are codes of the characters in the current font - the replaced characters.
The values m and n should be in the range 32 to 255. The subscript k ranges from 1
to 32. The maximum number of replaced characters is 32.
The NUL character is added to indicate the end of the commands. Also refer ESC &
ESC: commands.
ESC : Reinstate the Font Characters
Format ASCII : ESC :
Decimal : 27 58
Hexadecimal: 1B 3A
Explanation:
The command reinstates the original characters in the font replaced by user-defined
characters using ESC % command. User-defined characters, however, are not
deleted from the RAM in printer and may be brought back again with ESC %.
3.5.2 User Defined Characters Form 2
Support user defined high density characters for 203 DPI horizontal and vertical.
Compatible with printer using ESC/POS commands.
.ESC % Select User Defined Characters
Format ASCII : ESC % n
Decimal : 27 37 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 25 n
Explanation:
This command can select /cancel user-defined characters. n should be in the range 0
-1.
If n =<00000001> B the user-defined characters are selected.
If n=<00000000> B the regular characters are selected.
Default setting is regular characters. Using ESC & command to define
user-defined characters.
ESC & Define User Defined Characters
Format ASCII : ESC & s n m [a [p] s x a ]m-n+1
Decimal :27 38 s n m [a [p] s x a ]m-n+1
Hexadecimal: 1B 26 s n m [a [p] s x a ]m-n+1
Explanation:
This command allows characters to be defined. s = 3, 32< = n < m < = 126, 0 < = a
< = 12 (for font A), 0 < = a < = 9 (for font B), 0 < = p < = 255.
- s stands for number of bytes in vertical. S = 3.
- n stands for starting ASCII code of user-defined character.
- m stands for ending ASCII code of user-defined character.
When define only one character n=m. The maximum number of user-defined
characters is 50 and the maximum number of times for different
user-defined characters is 50 for each Font A & Font B.
- a stands for number of dots horizontal.
- p stands for data of user-defined characters, there are s x a character codes for each
character for defining m-n+1 characters.
- user-defined characters are valid till re-definition or return back to start position or
power off.
3.6 Graphics Printing Commands
3.6.1 Bit Image Graph Setting Form I
Only support bit map 101 DPI horizontal and 68 DPI vertical.
ESC K Bit Image Graph Printing
Format ASCII: ESC K n1 n2 ... data ...
Decimal: 27 75 n1 n2 ... data ...
Hexadecimal: 1B 4B n1 n2 ... data ...
Explanation:
This command is designed to print n1 x 8 bitimage. The width of this bit map is n1
+ n2 x 256 dots and the height is 8 dots.
Each column has 8 dots and can be presented by a byte (8 bits and bit 7 presents the
highest dot in the column). The data are the bytes of relative columns in the graphics
sequential from left to right.. The number of bytes should be n1 + n2 x 256.
3.6.2 Bit Map Graph Setting Form II
ESC * Set Bit Map
Format ASCII : ESC * m n1 n2 [d] k.
Decimal : 27 42 m n1 n2 [d] k
Hexadecimal: 1B 2A m n1 n2 [d] k
Explanation:
This command is for setting bit map by using m and n1,n2. The bit map graph can
be printed by either followed LF command or the width of the graph exceeds the
width of the line. So, this command allows to print both characters and graphics in
same line.
m = 0, 1, 32, 33. n1 = 0 - 255, n2 = 0 - 3, d = 0 - 255.
k = n1 + 256 x n2 (m = 0, 1)

24 25
k = (n1 + 256 x n2) x 3 (m = 32,33)
- The number of horizontal dots of the graphics is n1 + 256 x n2.
- The width of bit map data should be within the line width, excess parts will be
ignored.
- d presents bit map data, and k presents number of bit map data.
m for the setting of bit map. The definition of m is shown as below:
m mode vertical horizontal
dot dot density dot density max dot
0 8 dot single
density 8 68 DPI 101 DPI 192
1 8 dot double
density 8 68 DPI 203 DPI 384
32 24 dot single
density 24 203 DPI 101 DPI 192
33 24 dot double
density 24 203 DPI 203 DPI 384
GS * Define Down-load Bit Map Graph
Format ASCII : GS * n1 n2 [d] k.
Decimal : 29 42 n1 n2 [d] k
Hexadecimal: 1D 2A n1 n2 [d] k
Explanation:
This command sets a down-load bit map graph.
n1 = 1 - 48, n2 = 1 - 255, n1 x n2 < 9600, k = n1 x n2 x 8.
- d presents bit map data.
- The horizontal size of this graph is n1 x 8 dots and vertical is n2 x 8 dots
- This setting will be lost while resetting or return back to start position.
Bit Map format is showing as follows:
GS / Print Down-load Bit Map Graph
Format ASCII : GS / n
Decimal : 29 47 n
Hexadecimal: 1D 2F n
Explanation:
This command print out the down-load bit map graph set by command GS *.
n for selection of bit map. n = 0 - 3.
The relative graph sizes are listed as follows:
n graph size density in vertical density in horizontal
0 normal 203 DPI 203 DPI
1 double width 203 DPI 101 DPI
2 double height 101 DPI 203 DPI
3 double height & width 101 DPI 101 DPI
ESC ′Print Curving Lines
Format ASCII : ESC ′m n1 n1′... nk nk′CR
Decimal : 29 39 m n1 n1′... nk nk′CR
Hexadecimal: 1B 27 m n1 n1′... nk nk′CR
Explanation:
This command is designed to print curving graphic lines along with the paper feed
direction. (vertically). The value m is the number of lines to be printed, and should
be within the range of 1 to 384. In a horizontal line, there are m dots of m curving
line. The value n1, n1′, n2, n2′... nk, nk′represents the position of dot of m line.
The quantity of nk should be equal m and each nk should be fall on the largest dot in
each line. The last CR (carriage return) lets printer print this one horizontal dot line
out and carriage return to next dot line. So a set of horizontal dot lines will be
printed out to form m curving graphic lines. base on the data of n1, n1′, n2, n2′, ...,
nk, nk′.’.

24 25
3.7 Initialization Command
ESC @ Initialize Printer
Format ASCII : ESC @
Decimal : 27 64
Hexadecimal: 1B 40
Explanation:
This command initialize printer in following aspects:
- clear data in printing buffer.
- reinstate default value.
- select internal character font A.
- clear user defined characters.
3.8 Data Control Command
CR Carriage Return
Format ASCII : CR
Decimal : 13
Hexadecimal: OD
Explanation:
When a Carriage Return is sent to the printer, any data in the buffer is printed and
paper is fed one line. Same as LF command.
NUL Null
Format ASCII : NUL
Decimal : 0
Hexadecimal: 00
Explanation:
NUL is used as the final code in some commands such as ESC B, ESC D. NUL
command is ignored by printer when used alone.
3.9 Hexadecimal Printing Command
ESC ” Turn Hexadecimal Dump Printing on/off
Format ASCII: ESC ” n
Decimal: 27 34 n
Hexadecimal: 1B 22 n
Explanation:
Hexadecimal Dump print mode is turned on if n = 1, and turned off if n = 0. If you
execute programs or list program in Hexadecimal Dump print mode, all data sent
from the host computer will be printed out in hexadecimal.
Printing in the Hexadecimal Dump mode is performed only when the printer is in
the line buffer-full state.
Appendix 1 Index of Printing Command
Decimal Hexadecimal Command Description Page No.
0 00 NUL Nil 27
9 09 HT Horizontal Tab 17
10 0A LF Line Feed 15
13 0D CR Carriage Return 27
14 0E SO Select Double-width Printing 19
20 14 DC4 Cancel Double-width Printing 20
27 34 1B 22 ESC ” n On/off Hexadecimal Printing 27
27 38 1B 26 ESC & m n1 Define User-defined
n2..n6 Characters 20
27 37 1B 25 ESC % m n1 n2 Replace with User Defined
..mk nk NUL Characters 21
27 42 1B 2A ESC * Set Bit Map Graph 23
27 58 1B 3A ESC : Reinstate the Font Characters 21
27 37 1B 25 ESC % n (n<2) Selection of self-defined
Character Sets 22
27 38 1B 26 ESC & s n m Define User-defined
[a[p]sxa]m-n+1 Characters 22
27 39 1B 27 ESC ′m n1 n1′Print Curving Lines
....nk nk′’ CR 26
27 45 1B 2D ESC - n On/off Underline Printing 19
27 49 1B 31 ESC 1 n Set n’ dot line Spacing 16
27 54 1B 36 ESC 6 Select Character set A 19
27 55 1B 37 ESC 7 Select Character Set B 19
27 64 1B 40 ESC @ Initial the Printer 26
27 68 1B 44 ESC D Set Horizontal Tab 16
27 74 1B 4A ESC J n Line Feed 16
27 75 1B 4B ESC K n1 n2
...data Bit Map Graph Printing 23
27 85 1B 55 ESC U n Character Width Enlarge 18
27 87 1B 57 ESC W n Character Width & Height
Enlarge 18
27 86 1B 56 ESC V n Character Height Enlarge 18
27 99 1B 63 ESC c n On/Off Inverse Printing 20
27 102 1B 66 ESC f m n Print Blank Characters or Lines 17
27 108 1B 6C ESC I n Set Left Margin 17
29 42 1D 2A GS * n1 n2 [d] k Define Down-load Bit Map
Graph 24
29 47 1D 2F GS / n Print Down-load Bit Map graph 25
Table of contents
Other Megatron Printer manuals

Megatron
Megatron GeBE-COMPACT Plus User manual
Megatron
Megatron PORTI-T380 User manual

Megatron
Megatron WSP-i350 User manual

Megatron
Megatron PORTI-T380 User manual

Megatron
Megatron WSP-R241 User manual

Megatron
Megatron WSP-R240 User manual

Megatron
Megatron MTH-2500 User manual

Megatron
Megatron WSP-CP260 User manual

Megatron
Megatron WSP-i250 User manual

Megatron
Megatron UP-PN-II User manual