3
DEUTSCH
,
1. Zuerst lesen! ...............................3
2. Sicherheitshinweise ...................3
2.1 Bestimmungsgemäße V
erwendung ....................................3
2.2 Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise ...3
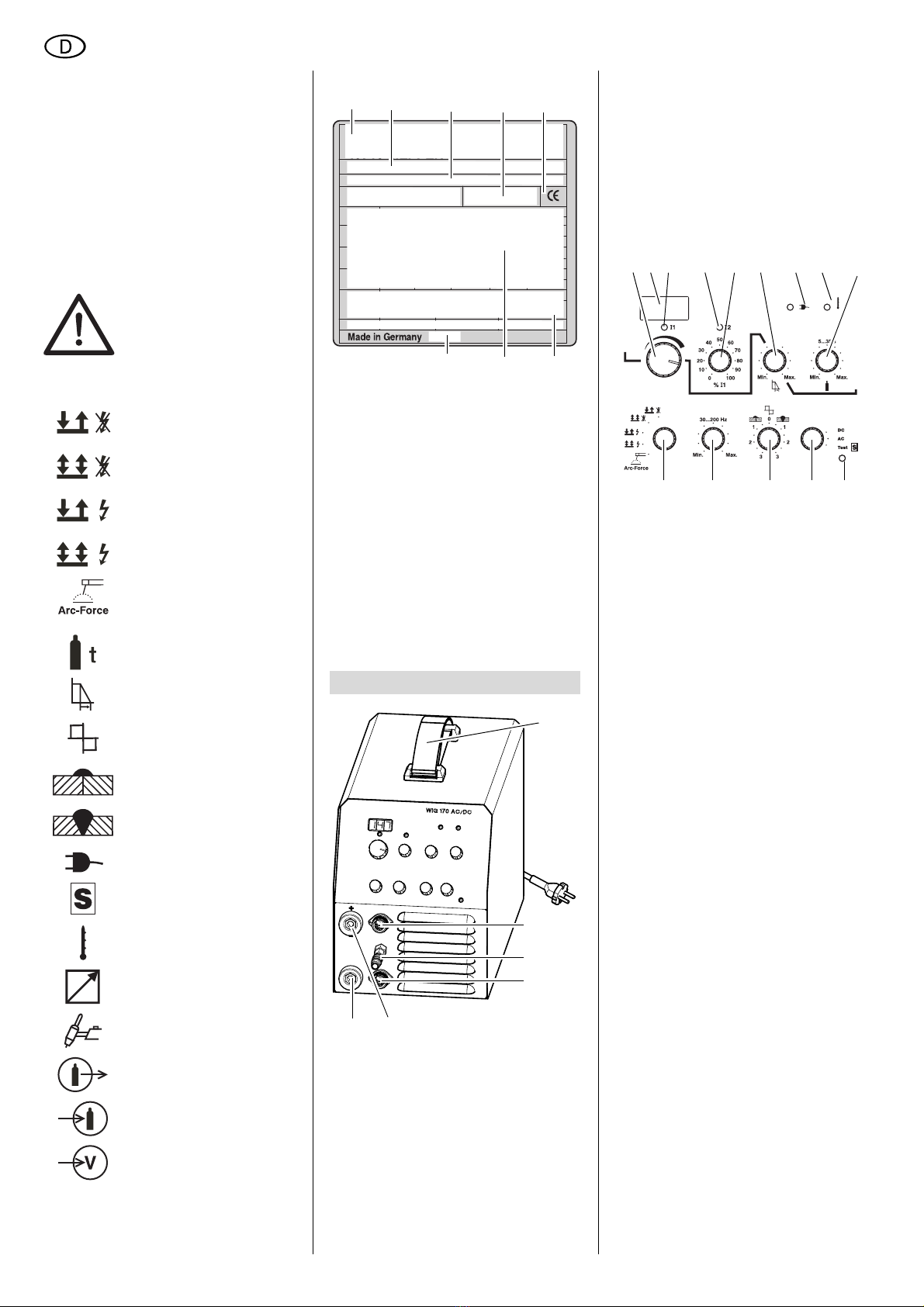
2.3 Symbole auf dem Gerät................4
3. Bedienelemente ..........................4
4. Betriebsvorbereitung .................5
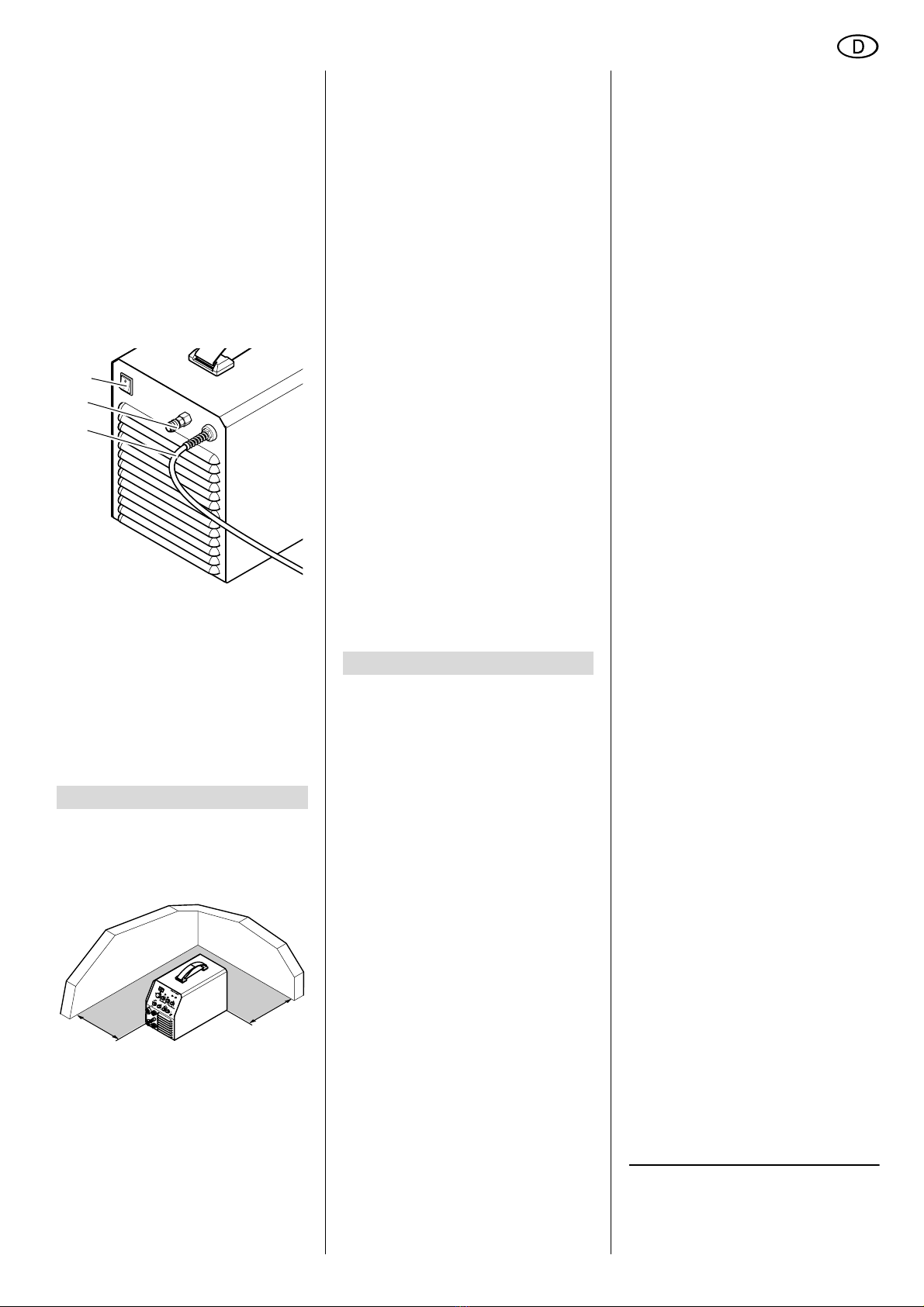
4.1 Aufstellen......................................5
4.2 Übrige Anschlüsse........................5
5. Bedienung ...................................5
5.1 Betriebsarten ................................5
5.2 Parameter.....................................6
5.3 Betrieb starten ..............................6
5.4 Betrieb beenden ...........................7
6. Wartung .......................................7
7. Lieferbares Zubehör..............7/59
8. Reparatur.....................................7
9. Umweltschutz..............................7
10. Störungen....................................7
11. Störungsbehebung.....................7
12. Technische Daten.......................8
Diese Betriebsanleitung wurde so
erstellt, dass Sie schnell und sicher mit
Ihrem Gerät arbeiten können. Hier ein
kleiner Wegweiser, wie Sie diese
Betriebsanleitung lesen sollten:
−Lesen Sie diese Betriebsanleitung
vor der Inbetriebnahme ganz durch.
Beachten Sie insbesondere die
Sicherheitshinweise.
−Diese Betriebsanleitung richtet sich
an ausgebildete Lichtbogenschwei-
ßer oder Fachkräfte mit ähnlicher
Qualifikation.
−Bewahren Sie alle mit diesem Gerät
gelieferten Unterlagen auf, damit
Sie sich bei Bedarf informieren kön-
nen. Bewahren Sie den Kaufbeleg
für eventuelle Garantiefälle auf.
−Wenn Sie das Gerät einmal verlei-
hen oder verkaufen, geben Sie alle
mitgelieferten Geräteunterlagen mit.
−Für Schäden, die entstehen, weil
diese Betriebsanleitung nicht beach-
tet wurde, übernimmt der Hersteller
keine Haftung.
Die Informationen in dieser Betriebsan-
leitung sind wie folgt gekennzeichnet:
Gefahr!
Warnung vor Personen-
schäden oder Umwelt-
schäden.
Stromschlaggefahr!
Warnung vor Personen-
schäden durch Elektrizi-
tät.
Achtung!
Warnung vor Sach-
schäden.
Hinweis:
Ergänzende Informationen.
−Zahlen in Abbildungen (1, 2, 3, ...)
−kennzeichnen Einzelteile;
−sind fortlaufend durchnumme-
riert;
−beziehen sich auf entspre-
chende Zahlen in Klammern (1),
(2), (3) ... im benachbarten Text.
−Handlungsanweisungen, bei denen
die Reihenfolge beachtet werden
muss, sind durchnummeriert.
−Handlungsanweisungen mit beliebi-
ger Reihenfolge sind mit einem
Punkt gekennzeichnet.
−Auflistungen sind mit einem Strich
gekennzeichnet.
2.1 Bestimmungsgemäße
Verwendung
Das Schweißgerät ist bestimmt für das
Verschweißen aller Metalle.
Es entspricht bei Auslieferung den ein-
schlägigen Bestimmungen.
Das Schweißgerät ist bestimmt für den
Gebrauch durch ausgebildete Lichtbo-
genschweißer oder Fachkräfte mit ähnli-
cher Qualifikation.
Zugelassene Schweißverfahren:
−WIG AC/DC (Wolfram-Inert-Gas),
für alle Metalle
−Elektrodenschweißen
Beim Schutzgasschweißverfahren ist
sicherzustellen, dass die Schutzglocke
des Schutzgases nicht durch Zugluft
weggeblasen wird.
Geräteleistungen siehe „Technische
Daten“.
Jede andere Verwendung gilt als
bestimmungswidrig und ist verboten.
Durch bestimmungswidrige Verwen-
dung, Veränderungen am Gerät oder
durch den Gebrauch von Teilen, die
nicht vom Hersteller geprüft und freige-
geben sind, können unvorhersehbare
Schäden entstehen!
2.2 Allgemeine Sicherheits-
hinweise
•Beachten Sie beim Gebrauch die-
ses Gerätes die folgenden Sicher-
heitshinweise, um Gefahren für Per-
sonen oder Sachschäden auszu-
schließen.
•Beachten Sie die speziellen Sicher-
heitshinweise in den jeweiligen
Kapiteln.
•Beachten Sie die gesetzlichen
Richtlinien oder Unfallverhütungs-
Vorschriften für den Umgang mit
Lichtbogenschweißgeräten.
BGefahr!
Elektrische Spannung.
•Setzen Sie das Gerät nur in Innen-
räumen und in trockener Umgebung
ein.
•Schließen Sie das Gerät nur an eine
Stromquelle an, deren Schutzein-
richtungen einwandfrei funktionie-
ren.
Wenden Sie sich im Zweifelsfall an
eine Elektrofachkraft!
•Reparaturen und Eingriffe in die
Geräte dürfen nur von ausgebilde-
ten Elektrofachkräften durchgeführt
werden.
•Vor Öffnen des Gerätes müssen Sie
die Netzverbindung trennen.
AGefahr!
•Tragen Sie bei Schweißarbeiten
unbedingt ausreichende Schutz-
kleidung.
•Verwenden Sie unbedingt Schutz-
schild und Schutzhandschuhe.
Sie schützen sich dadurch vor Fun-
kenflug und Lichtbogenstrahlung.
•Alle Metalldämpfe sind schädlich!
Sorgen Sie bei Arbeiten in geschlos-
senen Räumen immer für eine
ausreichende Belüftung und Absau-
gung, damit die maximalen Schad-
stoffkonzentrationen am Arbeits-
platz nicht überschritten werden.
Die Dämpfe von Blei, Cadmium,
Kupfer, Chrom, Nickel, Zink und
Beryllium sind besonders gefährlich!
AAchtung!
•Schweißen Sie niemals ein
Schweißgut, das geerdet ist.
Sie vermeiden so eine eventuelle
Beschädigung der Schutzleiter
durch vagabundierende Schweiß-
ströme (Potentialverschleifungen).
•Benutzen Sie das Schweißgerät nie-
mals zum Auftauen von Rohren.
•Befestigen Sie die Klemme der
Schweißstromrückleitung immer
direkt am Schweißgut und so nah
wie möglich an der Schweißstelle.
•Tragen Sie das Schweißgerät
immer am Tragegurt, wenn Sie es
transportieren.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
1. Zuerst lesen! 2. Sicherheitshinweise
XS0018D.fm Betriebsanleitung DEUTSCH