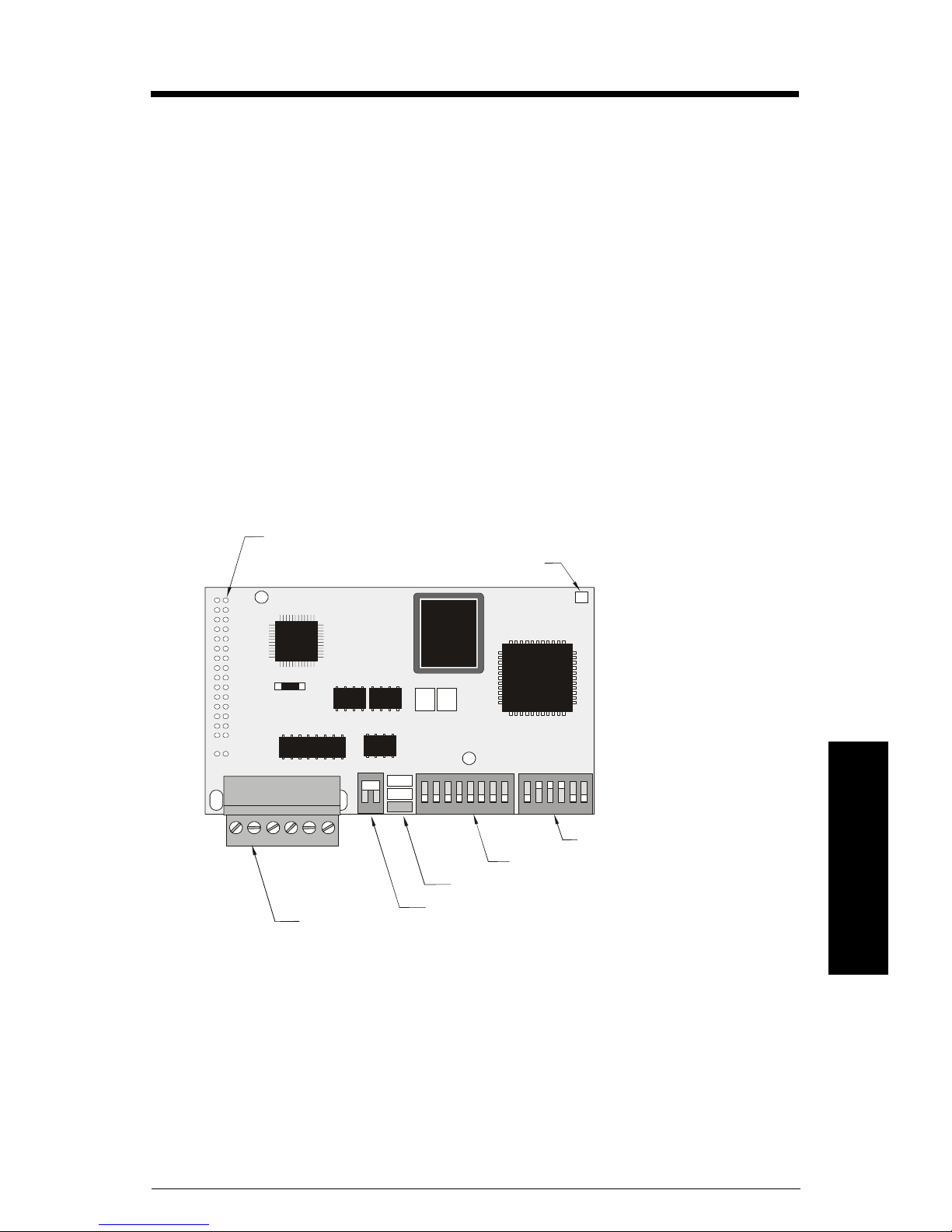
© Siemens MilltronicsProcessInstruments Inc. 2004
Safety Guidelines
Warning notices must be observed to ensure personal safety as well as that of others, and to
protect the product and the connected equipment. These warning notices are accompanied
by a clarification of the level of caution to be observed.
Qualified Personnel
This device/system may only be set up and operated in conjunction with this manual.
Qualified personnel are only authorized to install and operate this equipment in accordance
with established safety practices and standards.
Warning: This product can only function properly and safely if it is correctly transported,
stored, installed, set up, operated, and maintained.
Note: Always use product in accordance with specifications.
Copyright Siemens Milltronics Process
Instruments Inc.2004.AllRights ReservedDisclaimer of Liability
This document is available in bound version and in
electronic version. We encourage users to
purchase authorized bound manuals, or to view
electronic versions as designed and authored by
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc. will
not be responsible for the contents of partial or
whole reproductions of either bound or electronic
versions.
While we have verified the contents of
this manual for agreement with the
instrumentation described, variations
remain possible. Thus we cannot
guarantee full agreement. The
contents of this manual are regularly
reviewed and corrections are included
in subsequent editions. We welcome
all suggestions for improvement.
Technical data subject to change.
MILLTRONICS®is a registered trademark of Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
Contact SMPI Technical Publications at the following address:
Technical Publications
Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments Inc.
1954 Technology Drive, P.O. Box 4225
Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, K9J 7B1
Email: techpubs@siemens-milltronics.com
For the libraryof SMPI instruction manuals, visitour Web site: www.siemens-milltronics.com