MultiSmart Integrator Guide
Page 6 of 20 MultiSmart_Integrator_Guide_R01.doc
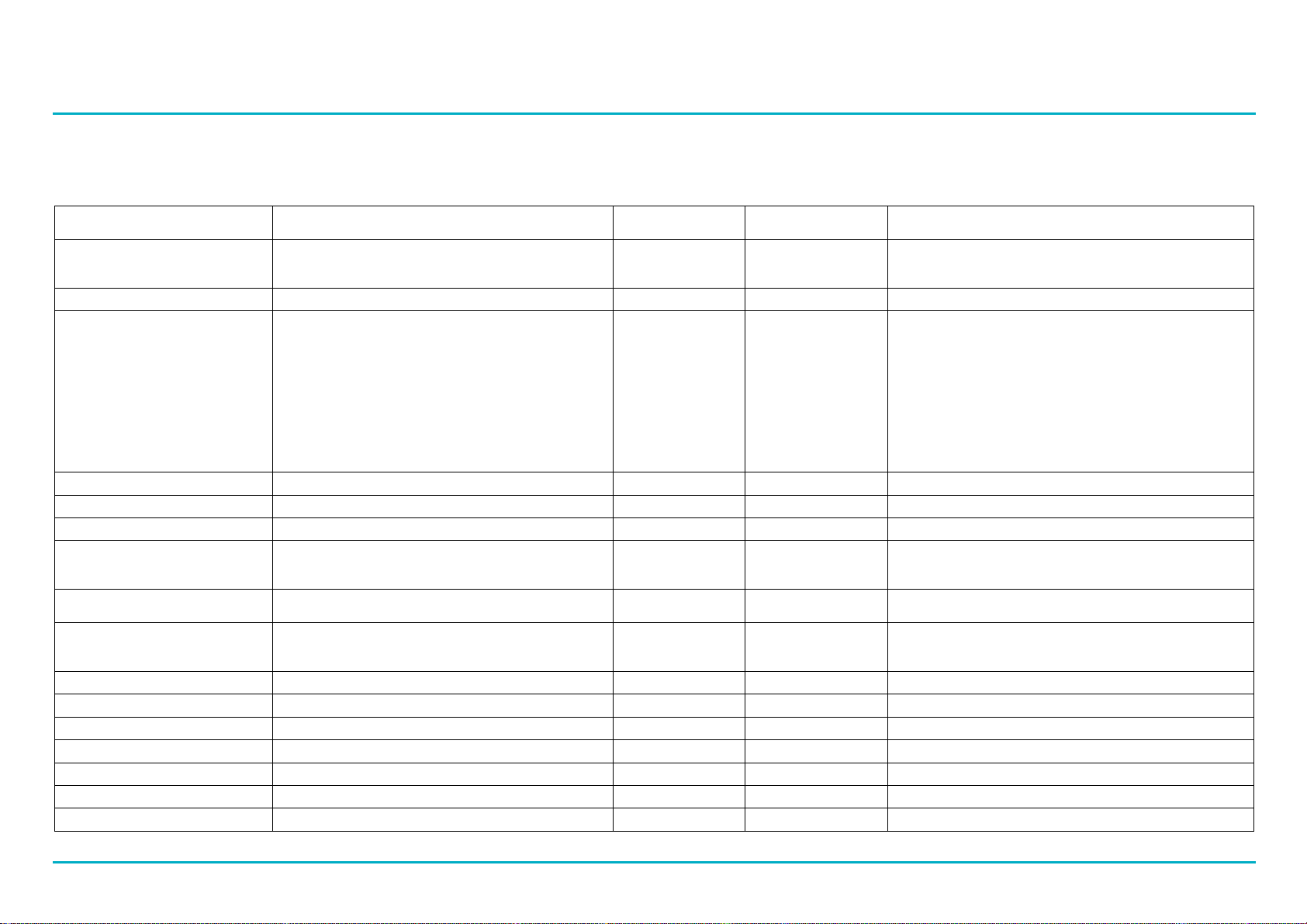
5.4 Basic 2-pump application (1 well) – 18 tags
Description Tag ID DNP ID (default) Modbus ID
(default) Comments
Pump 1 Running (called) PumpControl._1.Running Binary Input 70 Discrete Input 62 This means that the output control relay has been
asserted. Feedback from the contactor can be brought
back, details in section 5.5)
Pump 2 Running (called) PumpControl._2.Running Binary Input 130 Discrete Input 122
Pump 1 Unavailable PumpControl._1.FaultStatus.UnavailableActive Binary Input 73 Discrete Input 65
The pump can be unavailable when supply faults are
present as well as when pump faults exist.
A pump fault does not have to make the pump
unavailable, e.g. the default configuration for a seal
fault.
Any fault can be defined to be a display only fault, an
auto reset fault (pump becomes available when fault
condition clears), or a manual reset fault (pump only
becomes available when manual or SCADA reset takes
place)
Pump 2 Unavailable PumpControl._2.FaultStatus.UnavailableActive Binary Input 133 Discrete Input 125
Pump 1 Active Fault Fault.Pump._1.Active See note 1 See note 1
Pump 2 Active Fault Fault.Pump._2.Active See note 1 See note 1
Level PumpControl.Well._1.CurrentLevel or
PumpControl.Well._1.ScaledLevel Analog Input 10 or
Analog Input 12
Input Register 38 or
see Note 3 (section
5.5)
Currentlevel = level in %, ScaledLevel can be defined
by the user so it displays on the MultiSmart screen, e.g.
0-5m, 0-10ft
High Level alarm Faults.Well._1.HighLevel.Status.Active Binary Input 32 Discrete Input 30 There are 2 high level alarms available. High and High-
High. See Note 2.
Supply fault – Under-voltage
Over-voltage
Phase imbalance
Faults.Station.UnderVoltage.Status.Active
Faults.Station.OverVoltage.Status.Active
Faults.Station.VoltsPhaseImbalance.Status.Active
Binary Input 0
Binary Input 2
Binary Input 4
Discrete Input 0
Discrete Input 2
Discrete Input 4
Supply, phase AB IO.Unit._1.TopBoard.Vin._1.VoltsAb Analog Input 47 Input Register 113
Supply, phase BC IO.Unit._1.TopBoard.Vin._1.VoltsBc Analog Input 48 Input Register 114
Supply, phase CA IO.Unit._1.TopBoard.Vin._1.VoltsCa Analog Input 49 Input Register 115
Inflow Flow.InflowRate Analog Input 4 Input Register 21
Pump 1 Flow rate Flow.Pump._1.FlowRate Analog Input 21 Input Register 63
Pump 2 Flow rate Flow.Pump._2.FlowRate Analog Input 31 Input Register 93
Station volume Flow.VolumePumped Counter 4 Input Register 22
Lobley St SPS SP331 General (Electrical Manual (MPA) Multismart Manual Multitrode System Integrator Guide) General