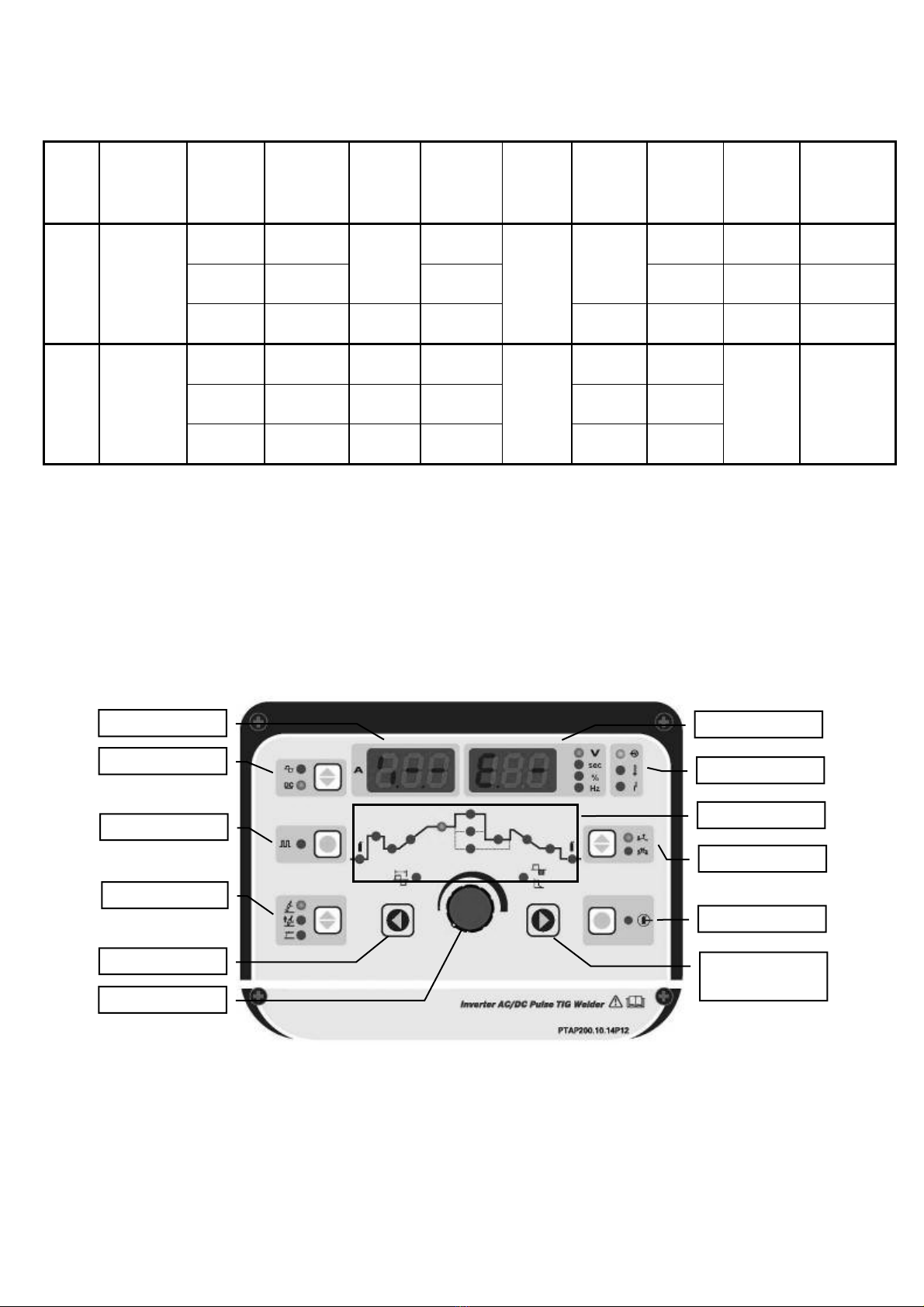
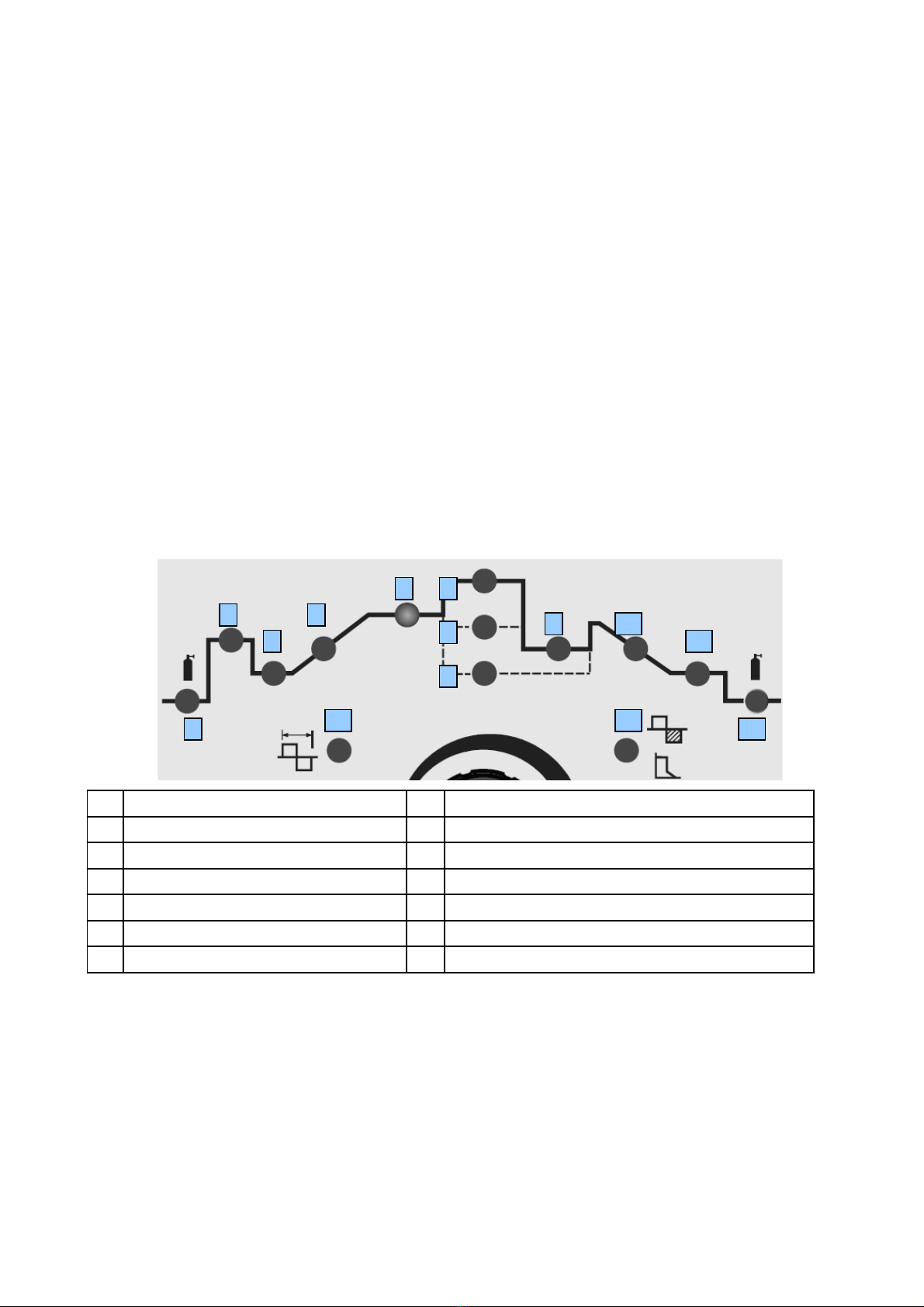
4
IR rays.
-Do not overuse or overheat your welder. Allow proper cooling time between duty cycles.
-Keep hands and fingers away from moving parts and stay away from the drive rolls.
-Do not point torch at any body part of yourself or anyone else.
-Always use this welder in the rated duty cycle to prevent excessive heat and failure.
1.4 Specific Areas of Danger, Caution or Warning
Electrical Shock
Electric arc welders can produce a shock that can cause injury or death. Touching electrically live parts can
cause fatal shocks and severe burns. While welding, all metal components connected to the wire are
electrically hot. Poor ground connections are a hazard, so secure the ground lead before welding.
-Wear dry protective apparel: coat, shirt, gloves and insulated footwear.
-Insulate yourself from the work piece. Avoid contacting the work piece or ground.
- Do not attempt to repair or maintain the welder while the power is on.
-Inspect all cables and cords for any exposed wire and replace immediately if found.
-Use only recommended replacement cables and cords.
-Always attach ground clamp to the work piece or work table as close to the weld area as possible.
-Do not touch the welding wire and the ground or grounded work piece at the same time.
-Do not use a welder to thaw frozen pipes.
Fumes and Gases
-Fumes emitted from the welding process displace clean air and can result in injury or death.
-Do not breathe in fumes emitted by the welding process. Make sure your breathing air is clean and safe.
-Work only in a well-ventilated area or use a ventilation device to remove welding fumes from the
environment where you will be working.
-Do not weld on coated materials (galvanized, cadmium plated or containing zinc, mercury or barium).
They will emit harmful fumes that are dangerous to breathe. If necessary use a ventilator, respirator with air
supply or remove the coating from the material in the weld area.
-The fumes emitted from some metals when heated are extremely toxic. Refer to the material safety data sheet
for the manufacturer’s instructions.
-Do not weld near materials that will emit toxic fumes when heated. Vapors from cleaners, sprays and
degreasers can be highly toxic when heated.
UV and IR Arc Rays
EMBED Word.Picture.8
The welding arc produces ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays that can cause injury to your eyes and skin.
Do not look at the welding arc without proper eye protection.
-Always use a helmet that covers your full face from the neck to top of head and to the back of each ear.
-Use a lens that meets ANSI standards and safety glasses. For welders under 160 Amps output, use a shade 10
lens; for above 160Amps, use a shade 12. Refer to the ANSI standard Z87.1 for more information.
-Cover all bare skin areas exposed to the arc with protective clothing and shoes. Flame-retardant cloth or
leather shirts, coats, pants or coveralls are available for protection.
-Use screens or other barriers to protect other people from the arc rays emitted from your welding.
-Warn people in your welding area when you are going to strike an arc so they can protect themselves.
Fire Hazards