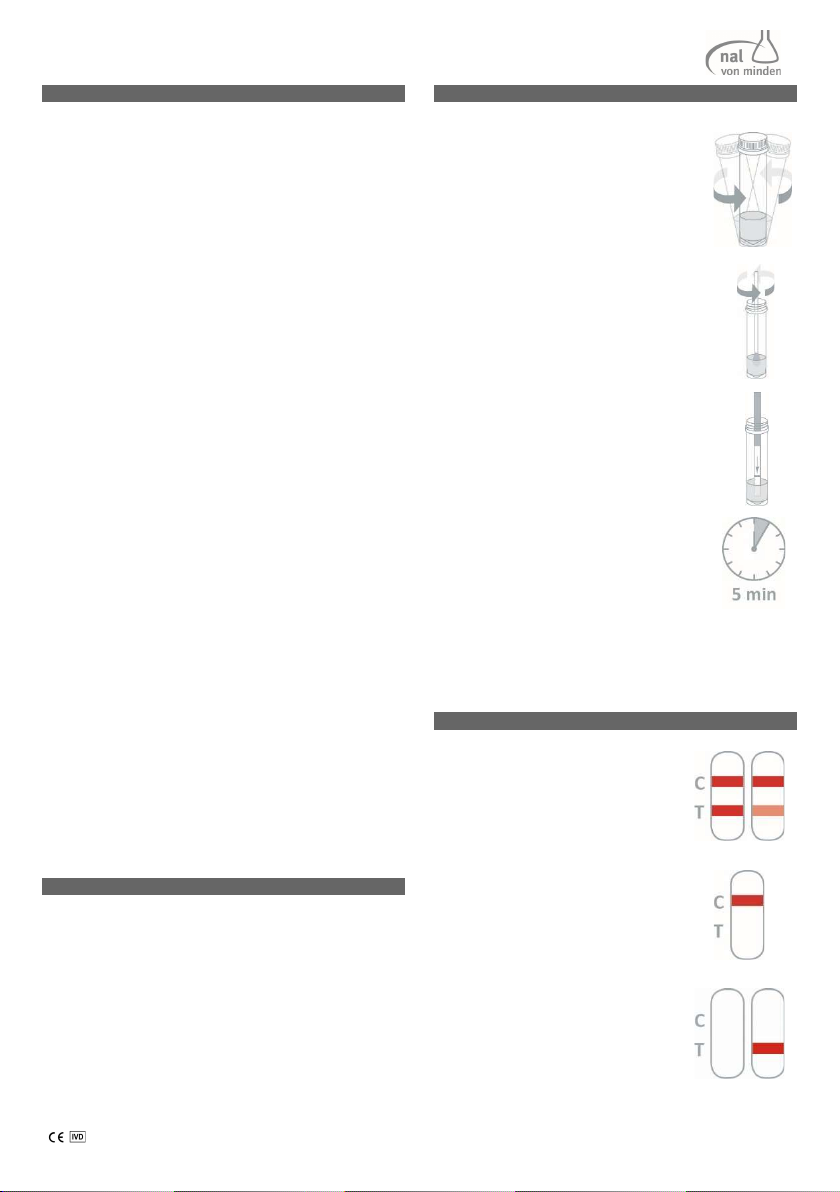
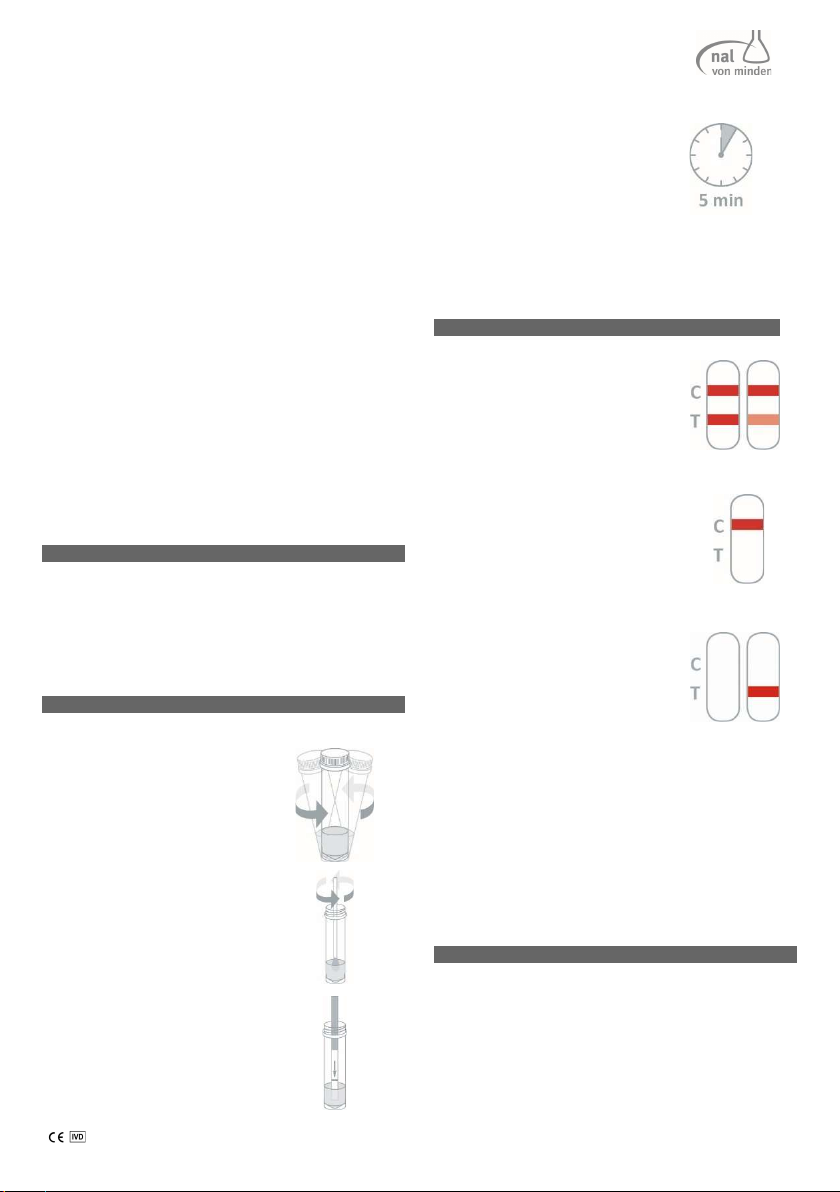
ENGLISH NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid Test
(Ref. 431006N-01/431006N-03/431006N-10/431006N-20)
nal von minden GmbH • Carl-Zeiss-Strasse 12 • 47445 Moers • Germany • [email protected]m • www.nal-vonminden.com 8 12. Limitations
The NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid Test is for professional
in-vitro diagnostic use and should be only used for the
qualitative detection of IGFBP-1.
The NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid Test only detects the
presence of IGFBP-1 in the specimen and should not be
used as the sole criterium for the diagnosis of PROM.
• In pregnant women, the IGFBP-1 concentration in the blood
is much lower than in the amniotic fluid, meaning that a
definitive diagnosis is normally possible. However, if the
sample material has been contaminated by blood, false
positive results may occur which cannot be attributed to
membrane rupture.
The epithelial cells in the cervix may contain IGFBP-1
concentrations which may cause a false positive test result
even without the presence of premature rupture of
membranes. This also applies to non-pregnant women, as
IGFBP-1 is a major protein in the endometrium around mid-
cycle.
According to existing theories (e.g. 'double sac'), ruptures
can occur which may lead to a temporary loss of amniotic
fluid. Tests carried out at different times can therefore
deliver different results.
If the test result is negative and clinical symptoms persist,
additional testing using other clinical methods is
recommended.
As with all diagnostic tests, a confirmed diagnosis should
only be made by a physician after all clinical and laboratory
findings have been evaluated.
13. Performance Characteristics
Sensitivity
The analytical sensitivity of the NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid
Test is 5 ng/mL IGFBP-1.
Accuracy
The results obtained using the NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid
Test were compared to those of another commercially
available PROM rapid test in a multi-center clinical evaluation.
The results of the study demonstrated 97.7% accuracy of the
NADAL® PROM Amniotic Fluid Test when compared to the
PROM rapid test of a different manufacturer.
PROM rapid test of a different
manufacturer
NADAL®
PROM
Amniotic
Fluid Test
Positive Negative Total
Positive 83 3 86
Negative 2 133 135
Total 85 136 221
Sensitivity: 97.6%
Specificity: 97.8%
Overall agreement: 97.7%
Interfering substances/microorganisms
The following substances and microorganisms have been
evaluated at the concentrations listed below. None of them
were found to affect the test performance of the NADAL®
PROM Amniotic Fluid Test.
Substance/microorganism Concentration
Pevaryl® 30 mg/mL
GYNO-TROSYD® 20 mg/mL
Flagyl® 100 mg/mL
Canesten® 40 mg/dL
Glucose 8 mg/mL
Candida albicans 11.2 x 10
CFU/mL
Gardnerella vaginalis 8.6 x 10
CFU/mL
Neisseria gonorrhoeae 10.6 x 10
CFU/mL
Baby powder 10 mg/mL
Vagisan® Myco Kombi (Creme) 1 mg/mL
Baby oil 1 mg/mL
Medical silicone oil 13 g/mL
Note: blood of pregnant women may cause false positive
results.
Intra-lot and inter-lot variability
Negative and positive controls at concentrations of 5 ng/mL
and 25 ng/mL were tested in 10 replicates with 3 independent
lots on 3 consecutive days. Each control was recognized
correctly.
14. References
1. Friedman ML, McElin TW. Diagnosis of ruptured fetal membranes. Am J Obstet
Gynecol 1969:104:544-550
2. Steinman G, Kleiner GJ, Greston WM. Spontaneous rupture of membranes. NY St. J
Med 1979:1849-1851
3. Koninckx PR, Trappeniers H, van Assche FA. Prolactin concentration in vaginalfluid:
a new method for diagnosing ruptured membranes. Br J Obstet Gynaecol
1981;88:607–610
4. Rochelson BL, Richardson DA, Macri JN. Rapid assay: possible application in the
diagnosis of premature rupture of the membranes. Obstet Gynecol 1983;62:414–
418
5. Bell SC, Hales MW, Patel SR, Kirwan PH, Drife JO, Milford-Ward A. Amniotic fluid
concentrations of secreted pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha1 and alpha2
globulins (alpha1 and alpha2 PEG). Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1986:93:909-915
6. Suikkari AM, Rutanen EM, Seppällä M. Circulating levels of immunoreactive insulin-
like growth factor-binding protein in non-pregnant women. Hum Reprod
1987:2:297-300
7. Bell SC, Keyte JW; N-terminalo amnio acid sequence of human pregnancy-
associated endometrial alpha1-globulin, an endometrial insulin-like growth factor
(IGF) binding protein – Evidence for two small molecular weight IGF binding
proteins. The Endoc Soc 1988:1202-1204
8. Rutanen EM, Pekonen F, Kärkkainen T. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-1 in cervical/vagonal secretions: comparison with the ROM-check
membrane immunoassay in the diagnosis of ruptured fetal membranes. Clin Chim
Acta 1993:214:73-81
9. Medina TM, Hill DA. Preterm premature rupture of membranes: diagnosis and
management. Am Famil Physic 2006:73: 659-664
10. Lockwood CJ, Wein R, Chien D, Ghidini A, Alvarez M, Berkowitz RL. Fetal membrane
rupture is associated with the presence of insulin-like growth factor-binding
protein-1 in vaginal secretions. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:146–150
11. Guibourdenche J, Luton D, André E, Noël M, Porquet D. Détection rapide de
l’Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 et de la fibronectine fœtale dans les
sécrétions cervico-vaginales pour le diagnostic de la rupture prématurée des
membranes. Ann Clin Biochem 1999 :36 :388-390
12. Sucak A, Moroy P, Cakmak P, Mungan T, Mollamahmutoglu L, Danisman N. Insulin-
Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-I; a rapid detection of amniotic fluid leakage
after amniocentesis. Turk J Med Sci 2005:35:157-161
13. Talabani H, Recoules A, Grenier S, Luton D, Paper T, Porquet D, Oury JF,
Guibourdenche J. L’alpha1-microglobuline placentaire dans les sécrétions
vaginales : un nouveau marqueur de la rupture prématurée des membranes. Act
Pharm Biol Clin 2005 :12 :233-240
14. Akercan F, Cirpan T, Kazandi M, Terek MC, Mgoyi l, Ozkinay E. The value of insulin-
like growth factor binding protein-1 in the cervical-vagonal secretion detected by
immunochromatographic dipstick test in the prediction of delivery in women with
clinically unconfirmed preterm premature rupture of membranes. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Rep Biol 2005:121:159-163
15. Schuman W. Double sac with secondary rupture of the bag of waters during labor;
a clinical entity, and its explanation from examination of the membranes. Am J
Obstet Gynecol 1951;62:633–8.