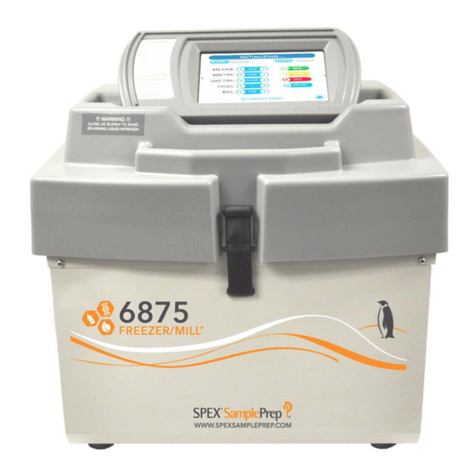
NanoSurface Cytostretcher Operation Manual ã2018 NanoSurface Biomedical, Inc.
INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................................................3
SECTION 1: SYSTEM OVERVIEW........................................................................................................4
A. THE NANOSURFACE CYTOSTRETCHER-LV ............................................................................................................ 4
B. REMOVING THE GLASS WINDOW ....................................................................................................................... 5
C. CYTOSTRETCHER CULTURE CHAMBER ...................................................................................................................... 6
Two Chamber Sizes ......................................................................................................................................... 6
Two Surface Options for Each Chamber Size .................................................................................................. 6
D. SOFTWARE ......................................................................................................................................................... 6
SECTION 2: USING THE CYTOSTRETCHER ......................................................................................7
A. PREPARATION OF THE CYTOSTRETCHER .................................................................................................................... 7
B. SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................................................... 7
C. FOCUS TILT ADJUSTMENT ................................................................................................................................. 8
Procedure ........................................................................................................................................................ 8
D. SOFTWARE OPERATION .................................................................................................................................... 9
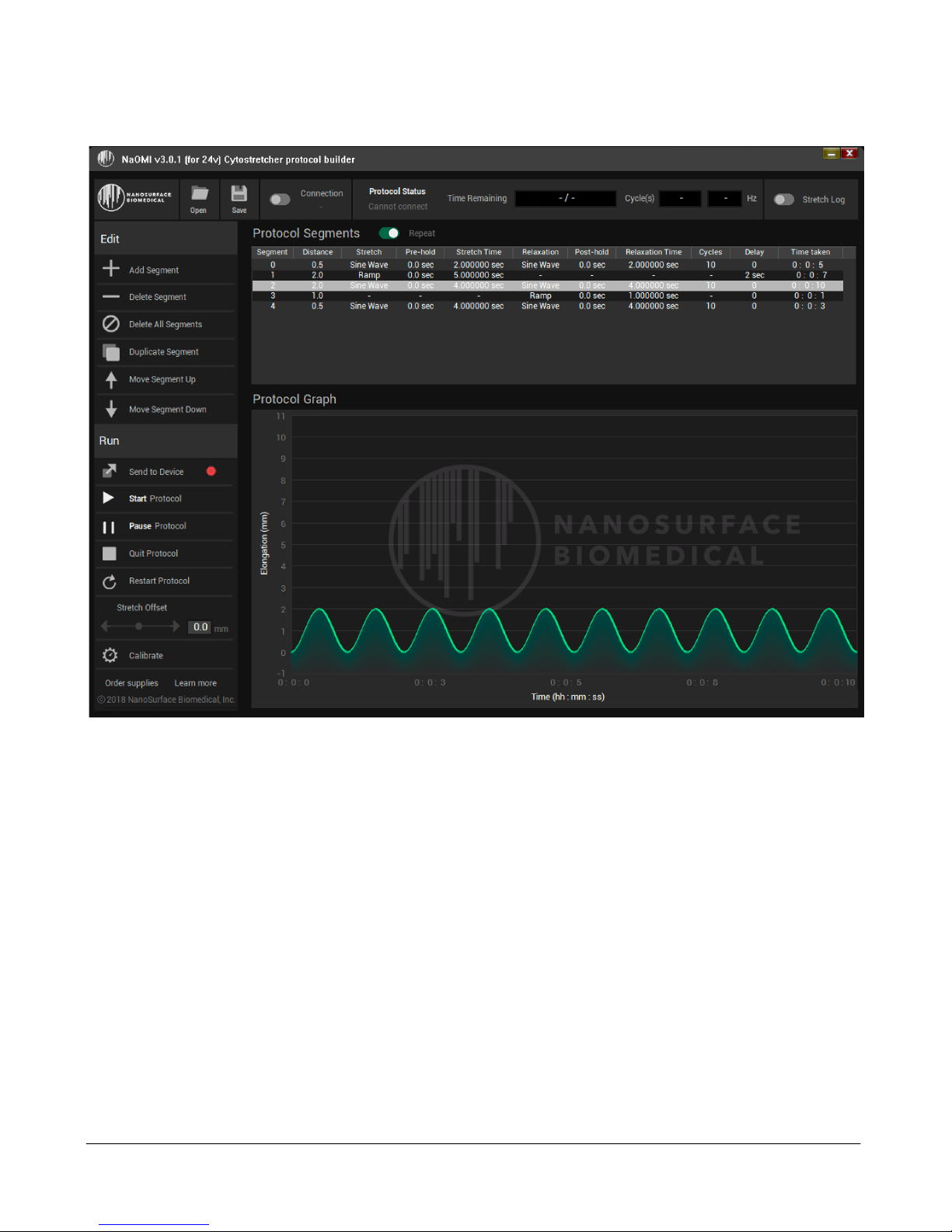
Overview: ........................................................................................................................................................ 9
Before starting: ............................................................................................................................................. 10
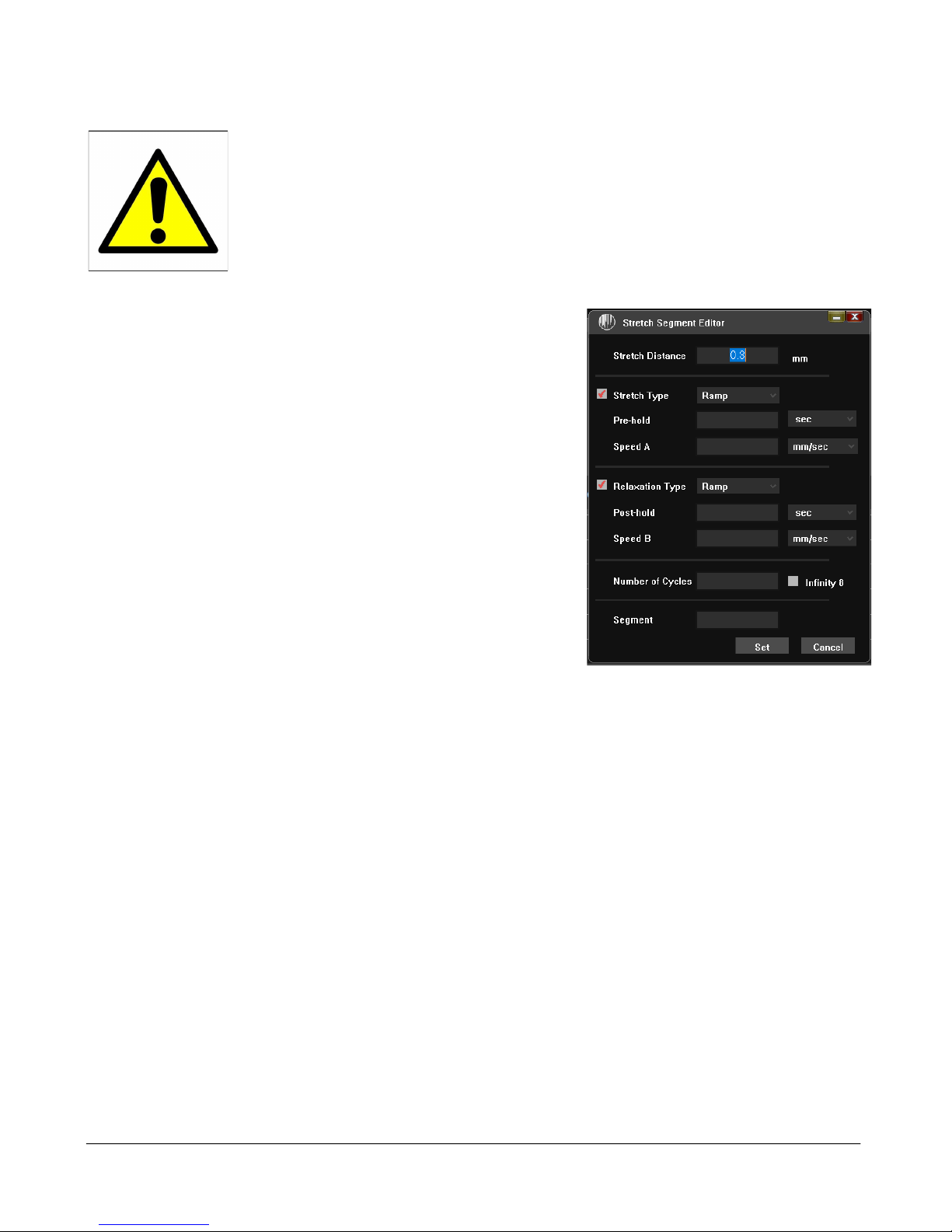
Working with Stretch Segments .................................................................................................................... 10
Offsets: .......................................................................................................................................................... 10
Calibration: ................................................................................................................................................... 10
Example- Symmetrical Repetitive Sine Stretch with no fixed time: 10%, 1Hz using a 12 mm chamber. ....... 11
Calculating Strain .......................................................................................................................................... 11
SECTION 3: CULTURING CELLS IN THE CYTOSTRETCHER CHAMBERS ...................................12
A. CHAMBER STERILIZATION .................................................................................................................................... 12
B. CELL ATTACHMENT ............................................................................................................................................ 12
Plasma Treatment (Recommended) ............................................................................................................. 12
Coating with ECM proteins without plasma treatment ................................................................................ 12
Chemical Modification .................................................................................................................................. 13
SECTION 4: WARRANTY & SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................. 14
WARRANTY .......................................................................................................................................................... 14
SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................................................................................... 14
APPENDIX A: INSTALLING THE FONT PACKAGE ..........................................................................15
REFERENCES .....................................................................................................................................16