Netkrom W24-AP11H User manual




















Table of contents
Other Netkrom Wireless Access Point manuals
Popular Wireless Access Point manuals by other brands

Extreme Networks
Extreme Networks WiNG AP-7612 installation guide

Compex
Compex NetPassage WP18 Quick install guide

Alcatel-Lucent
Alcatel-Lucent OAW-AP277 installation guide

Huawei
Huawei AP7052DN Hardware installation and maintenance guide

3Com
3Com 7608 quick start guide

NETGEAR
NETGEAR WAG102 - ProSafe Dual Band Wireless Access... installation guide

H3C
H3C WA2210-AG installation manual

TRENDnet
TRENDnet TPL-110AP - 125Mbps 802.11g Wireless Powerline Access... user guide

Cambium Networks
Cambium Networks XE5-8 Hardware installation guide

EnGenius
EnGenius ENS202EXT Quick installation guide

Knox
Knox MedVault 2.5 Admin & user guide
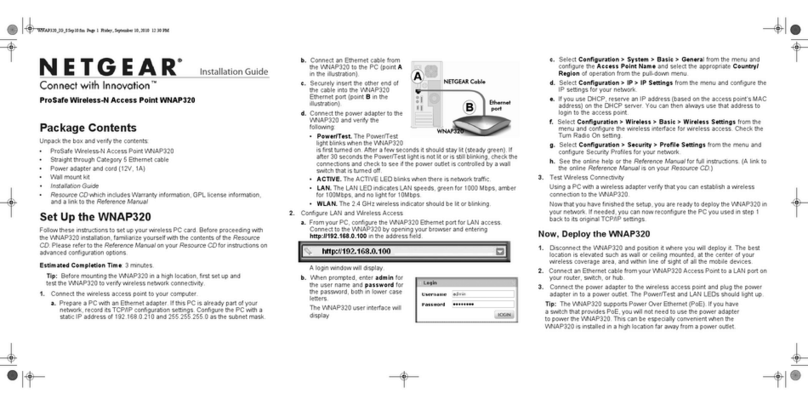
NETGEAR
NETGEAR ProSafe WNAP320 installation guide
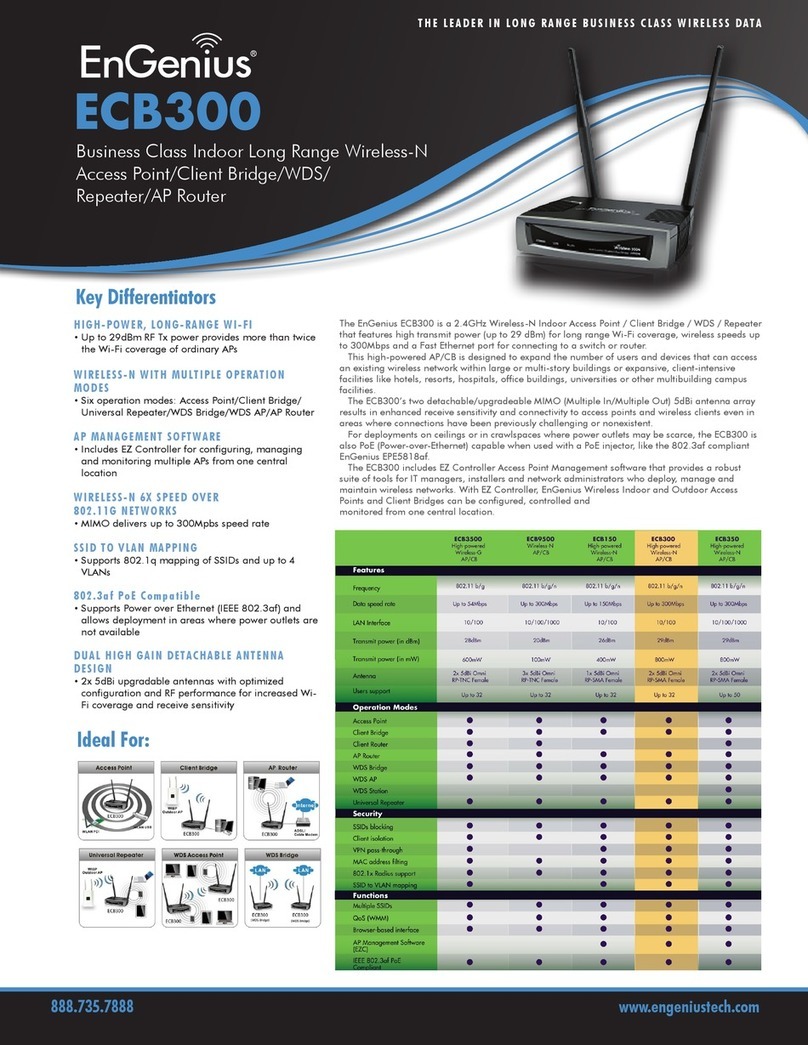
EnGenius
EnGenius ECB300 Technical specifications

Aruba Networks
Aruba Networks 340 Series installation guide

ExtremeWireless
ExtremeWireless WiNG AP7662i installation guide

Ruckus Wireless
Ruckus Wireless ZoneFlex 7762 datasheet

EnGenius
EnGenius EAP300 user manual

Gonet Systems
Gonet Systems GoBeam 6100 Quick installation guide




