USER MANUAL
ISC-178x
Monochrome/Color Smart Camera
This document contains detailed electrical and mechanical information for the National
Instruments ISC-178x.
Contents
Hardware Overview.................................................................................................................. 1
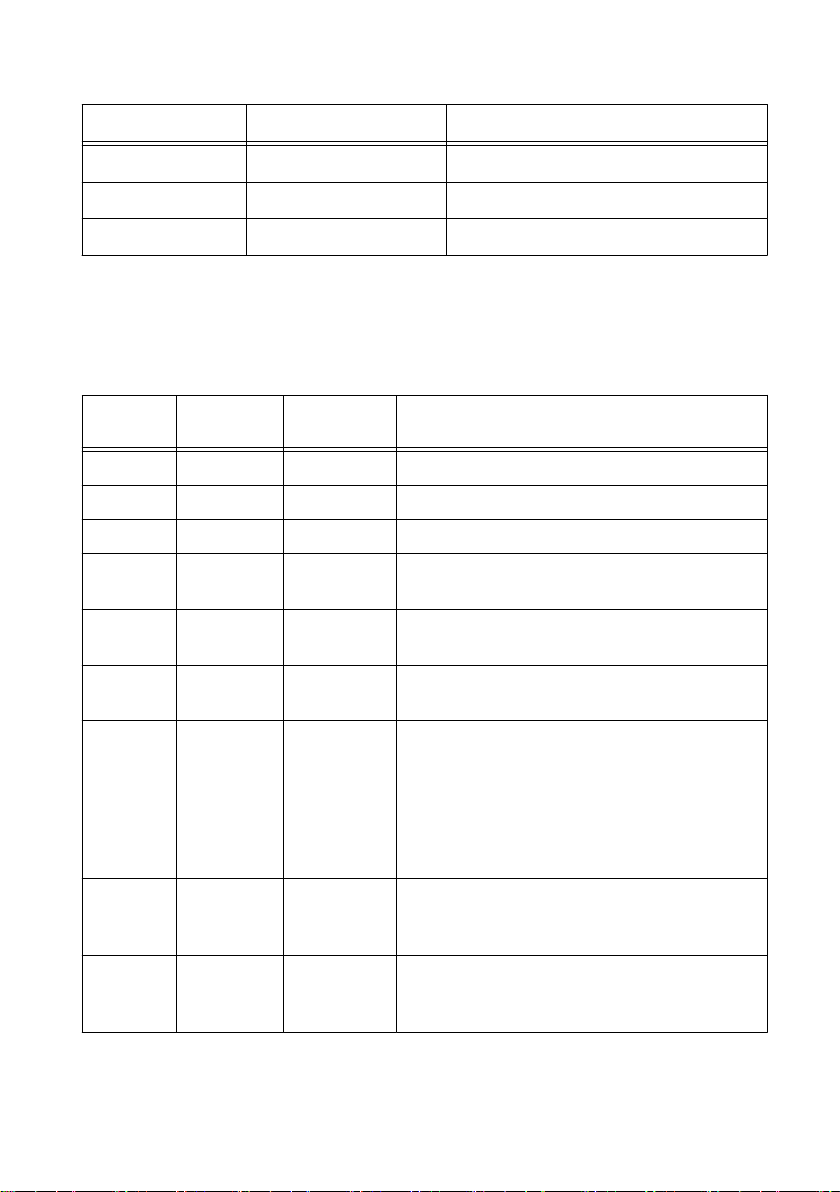
Connector Pinouts............................................................................................................. 3
LED Indications................................................................................................................ 8
Mounting the ISC-178x.................................................................................................... 9
Connecting to Lighting Devices............................................................................................. 12
Wiring the Isolated Inputs....................................................................................................... 13
Wiring the Isolated Outputs.................................................................................................... 14
Choosing a Pull-up Resistor....................................................................................................16
Safe Mode (NI Linux Real-Time)...........................................................................................16
Image Sensor...........................................................................................................................16
Acquiring Images....................................................................................................................20
Triggering........................................................................................................................20
Exposure and Lighting.................................................................................................... 24
Image Readout................................................................................................................ 25
Trigger Overlap............................................................................................................... 25
Reconfiguring During an Acquisition.............................................................................26
ISC-178x Software Attributes.................................................................................................26
Restoring the NI Linux Real-Time Operating System............................................................35
Restoring the Windows Operating System............................................................................. 36
Creating a Bootable USB Flash Drive............................................................................ 36
Reinstalling Windows..................................................................................................... 37
Where to Go Next................................................................................................................... 38
Worldwide Support and Services............................................................................................ 38
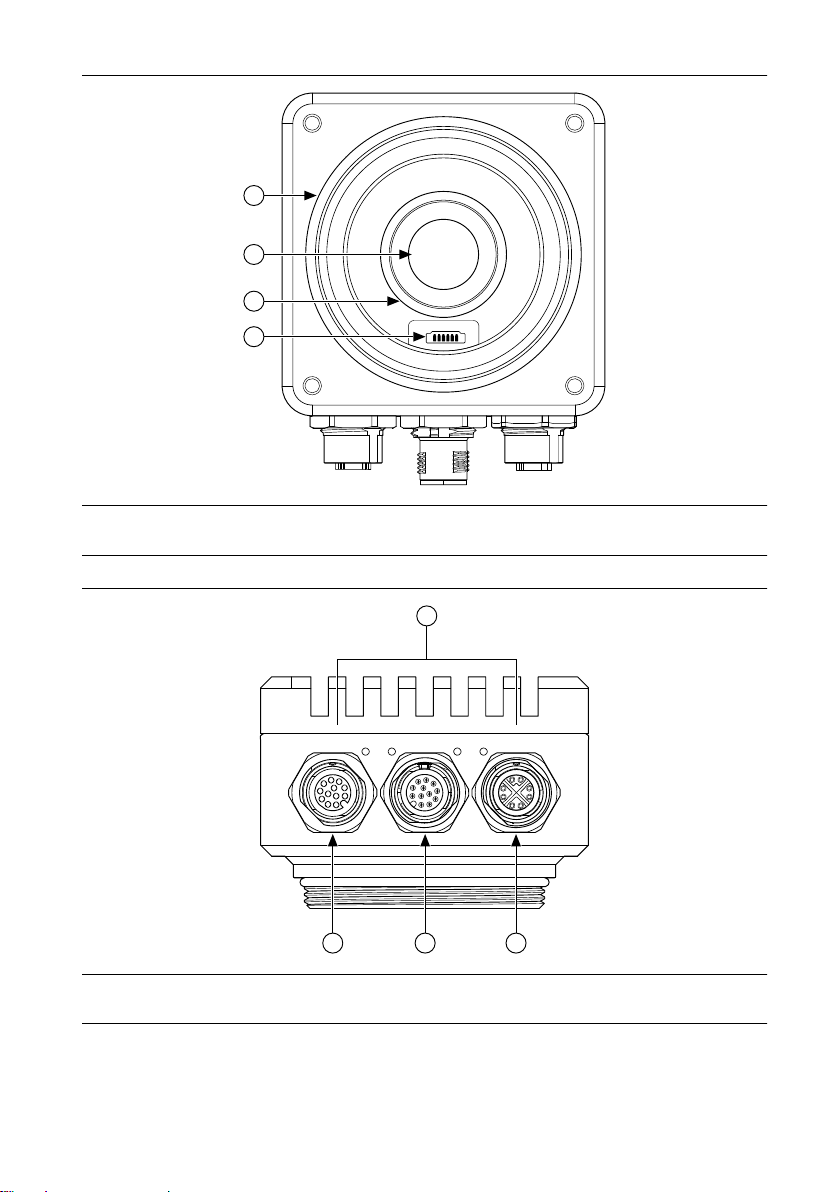
Hardware Overview
ISC-178x smart cameras incorporate a 1.58 GHz dual-core Intel Celeron processor, image
sensor, and digital I/O in a compact, IP67-rated housing.