2 pmg511en21p01
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2. SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................................................................................. 4
2.1 General Data.................................................................................................................................................................. 4
2.2 Accessories .................................................................................................................................................................... 5
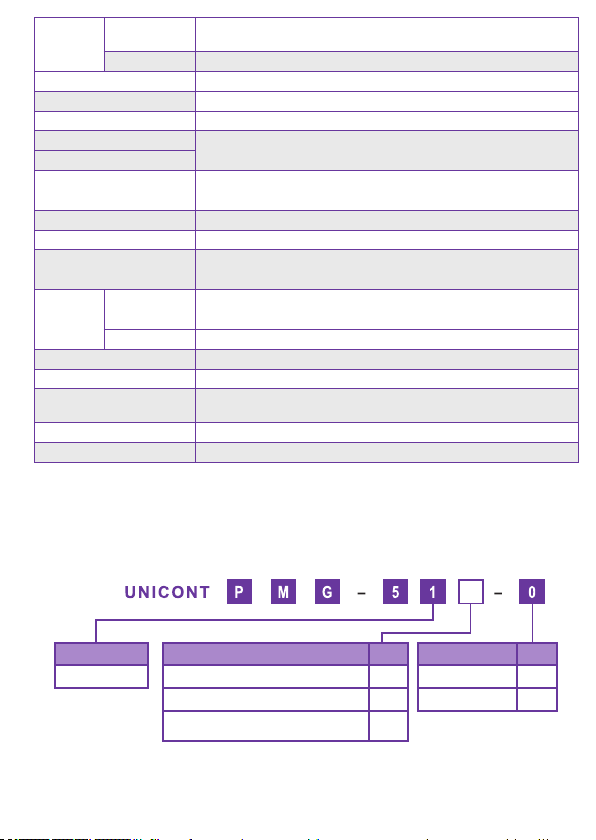
2.3 Order Code..................................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.4 Outlines and Dimensions .............................................................................................................................................. 6
3. MOUNTING............................................................................................................................................................................ 6
4. WIRING .................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
5. PROGRAMMING ................................................................................................................................................................... 7
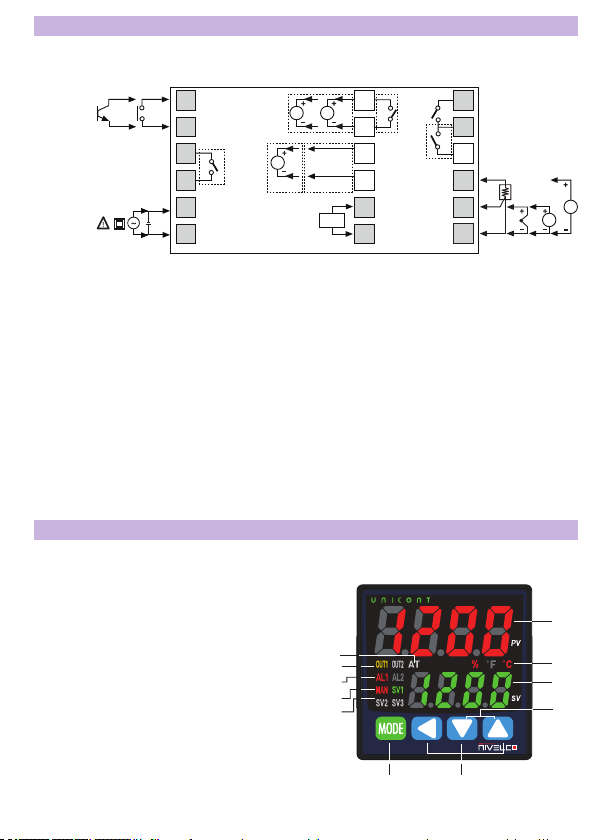
5.1 Parts and Display ........................................................................................................................................................... 7
5.2 Startup............................................................................................................................................................................ 9
5.3 Input Settings [PAR3 → IN-T]........................................................................................................................................ 9
5.3.1 Input Types [PAR3 → IN-T].................................................................................................................................. 9
5.3.2 Sensor Temperature Unit .................................................................................................................................... 10
5.3.3 Analog Input Scale Value Settings ...................................................................................................................... 10
5.3.4 Low-Limit Input Value [PAR3 → L-RG]............................................................................................................... 11
5.3.5 Upper-Limit Input Value [PAR3 → H-RG]........................................................................................................... 11
5.3.6 Scale Decimal Point Position [PAR3 → DOT].................................................................................................... 11
5.3.7 Lower Limit Scale Value [PAR3 → L-SC] ........................................................................................................... 11
5.3.8 Upper Limit Scale Value [PAR3 → H-SC]........................................................................................................... 11
5.3.9 Input Offset Correction [PAR3 → IN-B] .............................................................................................................. 11
5.3.10 Input Digital Filter [PAR3 → MAvF] .................................................................................................................. 12
5.3.11 Upper Limit [PAR3 → H-SV] and Lower Limit of Set Value (SV) [PAR3 → L-SV] ........................................... 12
5.4 Output Settings............................................................................................................................................................. 12
5.4.1 Selecting a Control Output [PAR3 → OUT2]...................................................................................................... 12
5.4.2 SSR Function [PAR3 → O2.SR]......................................................................................................................... 12
5.4.3 Current Loop Output Range Settings [PAR3 → O2MA]..................................................................................... 12
5.5 Control Output.............................................................................................................................................................. 13
5.5.1 Heating Control [PAR3 → O-FT → HEAT] or Cooling Control [PAR3→ O-FT → COOL]................................ 13
5.5.2 Heating & Cooling Control [PAR3 → O-FT → H-C]........................................................................................... 13
5.5.3 Deadband/Overlap Band [PAR2 → DB]............................................................................................................. 14
5.5.4 MV Upper Limit Value [PAR2 → H-MV] and MV Lower Limit Value [PAR2 → L-MV]........................................ 17
5.5.5 MV Settings for Sensor Break Error [OPEN] [PAR5 → ErMV] .......................................................................... 18
5.5.6 Ramp Settings [PAR2 → RAMU/ RAMD/ rUNT] ................................................................................................ 18
5.5.7 Auto/Manual control settings............................................................................................................................... 19
5.5.7.1 Switching Between Manual/Auto Control................................................................................................. 19
5.5.7.2 Initial MV for Manual Control [PAR5 → ItMV].......................................................................................... 20
5.5.7.3 Initial MV Manual Control [PAR5 → PrMV] ............................................................................................. 21
5.6 Temperature Control..................................................................................................................................................... 21
5.6.1 Temperature Control Mode [PAR3 → C-MD]...................................................................................................... 21
5.6.2 ON/OFF Control with Hysteresis Function [PAR3 → C-MD → ONOF] ............................................................. 21
5.6.3 PID Control [PAR3 → C-MD → PID] ................................................................................................................. 22
5.6.3.1 Setting the Proportional Band for Heating [PAR2 → H-P] and Cooling [PAR2 → C-P].......................... 23
5.6.3.2 Setting Integral Time for Heating [PAR2 → H-I] and Cooling [PAR2 → C-I] .......................................... 23
5.6.3.3 Setting Differential Time for Heating [PAR2 → H-D] and Cooling [PAR2 → C-D] .................................. 23
5.6.3.4 Setting Control Period for Heating [PAR3 → H-T] and Cooling [PAR3 → C-T]...................................... 23
5.6.3.5 Offset Correction / Manual Reset Settings [PAR2 → REST] .................................................................. 23
5.6.4 Auto-Tuning......................................................................................................................................................... 24
5.6.4.1 Auto-Tuning ON/OFF [PAR2 → AT] ........................................................................................................ 24
5.6.5 Auto-Tuning Mode Settings [PAR3 → AT.t]......................................................................................................... 24