9
ENGLISH
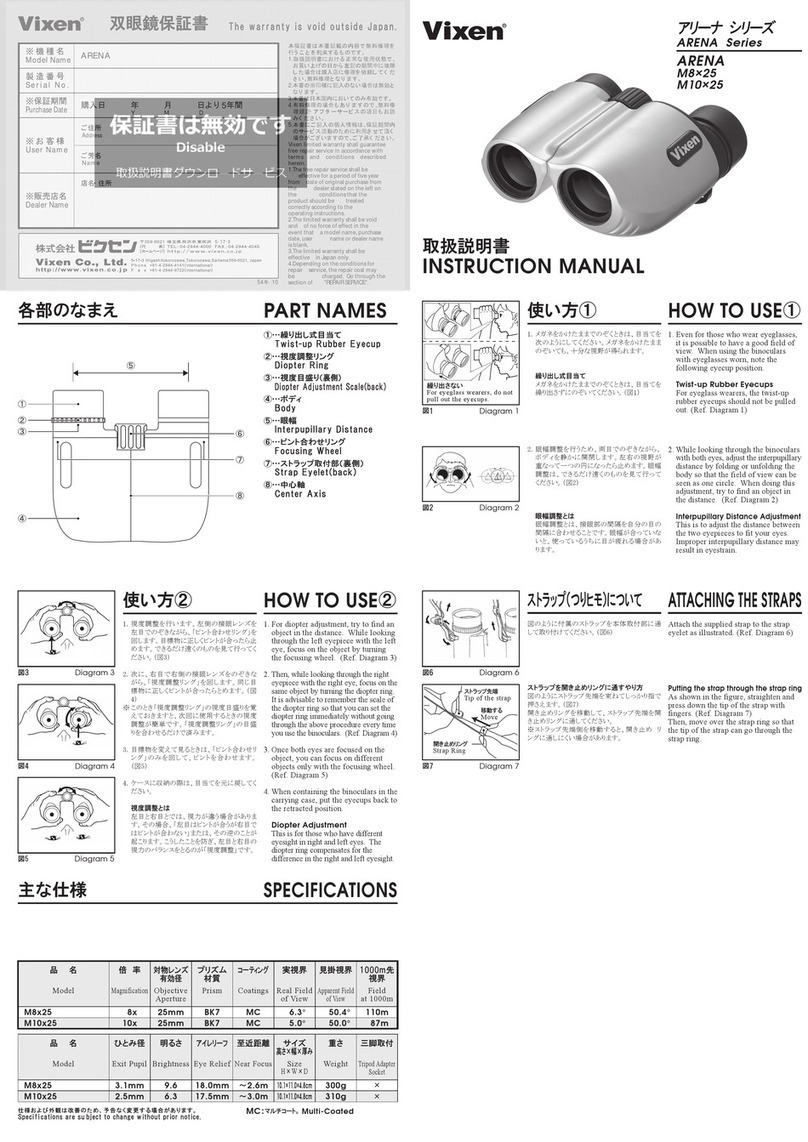
DESCRIPTION OF SUB-ASSEMBLIES AND OPERATING ELEMENTS
The optical system shown is a very modern system of a direct-vision prism
binocular telescope. lts design ensures the minimum size of instrument and
an extreme weight reduction without limiting the optical main parameters
embodied up to now in traditionally-designed high-quality equipment. As a
result, the 7x40 / 10x42 B/GA is aimed at high climatic and dynamic loads.
In addition to the extreme robustness of the instrument, its high dust- and
water-tightness is particularly important.
The lens is designed as an air-gap lens with principal planes pulled forwards.
In this way, the distance between back lens and image is shortened and so
low overall length is obtained.
The eyepiece is a zemented lens system with an exit pupil intercept length
of SAP > 20 mm (the proper model for spectacle wearers).
The inversion lens system consists of a pentaprism and a half pentaprism.
This combination enables the flat method of construction to be achieved.
The eyecups are rubber shaped parts which can be turned inside out and
which permit observation with the naked eye in spite of the long pupit inter-
cept length. Observation with spectacles is possible when the eyecups are
turned inside out.
The eyepiece cap is a plastic shaped part and is used to protect the eyepiece
lens from condensation and mechanical damage in the carrying position. lt
is attached to the shoulder strap and is removable (4 fig. 1).
The lens caps are plastic shaped parts and used to protect the front lenses
from contamination and mechanical damage when carried. They are
attached to the lens impact guard (5 fig. 1).
The casing and lens impact guard are rubber shaped parts, removable for
ease of maintenance, and are used to protect the instrument from shock
and impact. The casing is ribbed longitudinally for better handling (2 fig. 1).
The hinged joint is designed as an articulated hinge and is used to vary the
interocular distance from diameter 60 mm to 75 mm (1 fig. 1).
The shoulder strap is a „Dederon“ strap which enables the instrument to
hang while being carried without a case. lt is attached to loops on the strap
and held in the correct position by strap slides (3 fig. 1).
UTILISATION OF INSTRUMENT
Correct hold
The full performance of the telescope is only achieved when held in the
steadiest possible position. When observation is carried out, hold the
eyepiece cap aganist the telescope with the thumbs. The lens caps hang
freely downwards. Put the eyecups firmly against the eyebrows. This
prevents interfering incident light coming from the side.