NXP Semiconductors i.MX RT Series User manual

1 Overview
This document focuses on the procedure of entering boundary scan mode for
board-level test. It provides the setup sequence and script examples to ensure
first-pass success.
Engineers should understand the standard for test access port and boundary
scan architecture from IEEE 1149.1.
1.1 Boundary Scan
Boundary scan is a method for testing interconnects on PCBs and internal IC
sub-blocks. It is defined in the IEEE 1149.1 standard.
In boundary scan test, each primary input and output signal on a device is supplemented with a multi-purpose memory element
called a boundary scan cell. These cells are connected to a shift register, which is referred to as the boundary scan register. This
register can be used to read and write port states.
In normal mode, these cells are transparent and the core is connected to the ports. In boundary scan mode, the core is isolated
from the ports and the port signals are controlled by the JTAG interface.
Figure 1 shows the principle of boundary scan chain.
Contents
1 Overview......................................... 1
1.1 Boundary Scan............................ 1
1.2 Test Access Port (TAP) JTAG..... 2
2 Installing software............................3
3 Hardware connection diagram........ 3
4 BSDL file validation using Lauterbach
JTAG debugger...............................8
5 Introduction to other EVK board of
i.MX RT series...............................13
6 Revision history.............................14
AN12919
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series
Rev. 1 — March 2, 2021 Application Note

Figure 1. Boundary scan principle
1.2 Test Access Port (TAP) JTAG
The TAP is a general-purpose port and it can provide access to many test support functions built into the component. It has four
or five signals, as described in Table 1.
NXP Semiconductors
Overview
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 2 / 15

Table 1. JTAG pin signal description
Signal name I/O type Description
TCK Input The test clock input provides the clock for the test logic.
TMS Input The value of the signal present at TMS at the time of a rising edge at TCK
determines the next state of the TAP controller.
TDI Input Serial test instructions and data are received by the test logic.
TDO Output Serial output for test instructions and data from the test logic.
TRST_N Input Optional active low signal to reset the TAP controller.
2 Installing software
The TRACE32 installation package can be found on the Lauterbach page.
Download the
TRACE32_201909.7z
to the computer and install it.
1. Because the installation package is relatively large, you can install software components according to the target
processor to save hard disk space.
2. You can find installed driver at
C:\T32\bin\windows64\drivers
.
3 Hardware connection diagram
The TRACE32 debugger hardware always consists of:
• Universal debugger hardware
• Debug cable specific to the processor architecture
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of hardware connection.
NXP Semiconductors
Installing software
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 3 / 15
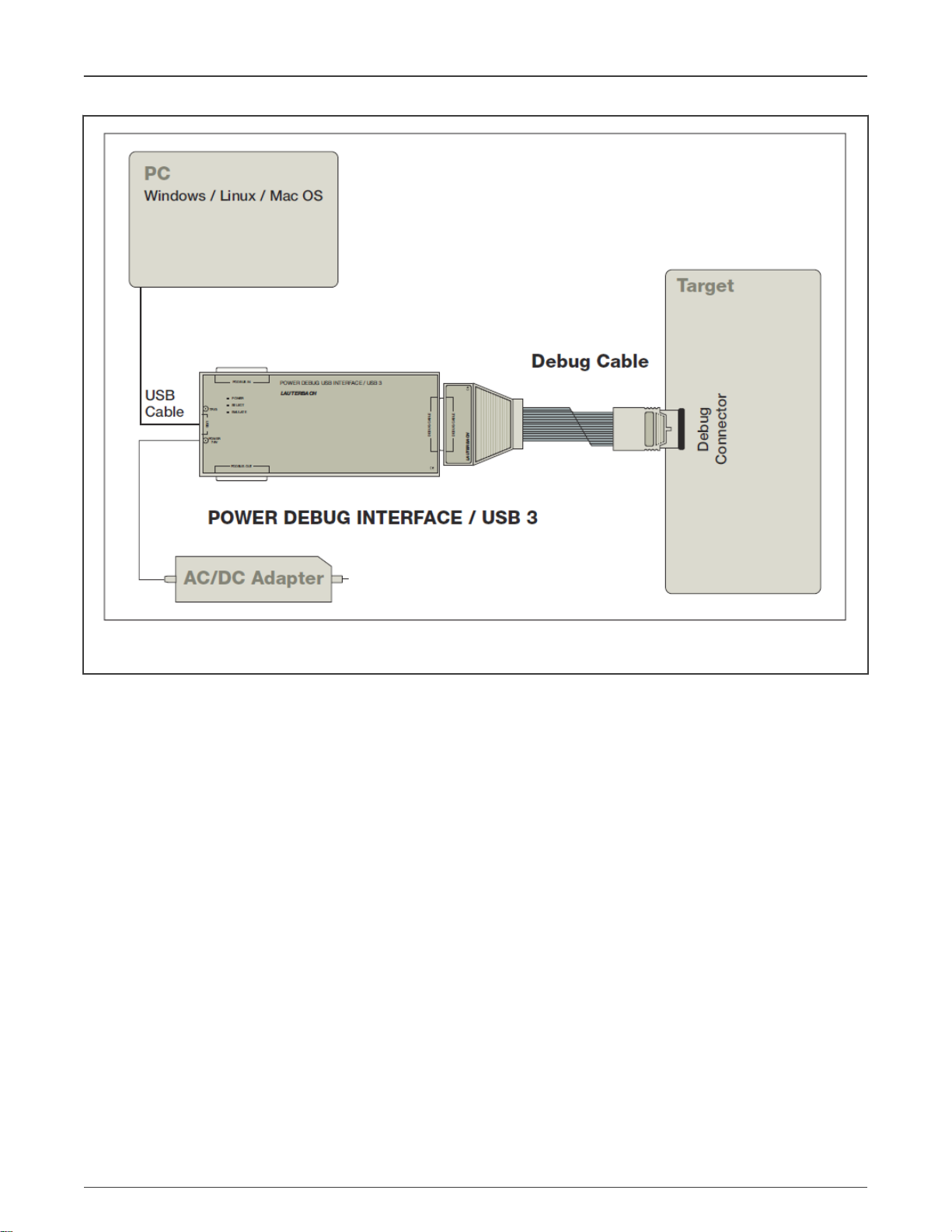
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of hardware connection
Suggestions for users include:
• To prevent the debuggers or target being damaged, it is forbidden to plug or unplug the debugger while target is powered on.
The recommended sequence for powering on or off is as follow:
— Power on: debugger >target
— Power off: target >debugger
• The debugger interface has pin1. Please double check the direction to prevent damages to the debugger or target.
• It is recommended to press F1 to enter the on-line help system to get familiar with debugger.
1. Taking RT1064 EVK board as an example, the hardware connection is as shown in Figure 3.
a. Connect Lauterbach JTAG debugger to the EVK board by the 20pin JTAG interface.
b. Connect to the PC through the USB cable, and then power on the debugger with a 5 V power adapter.
c. Connect the EVK USB port to the PC.
NXP Semiconductors
Hardware connection diagram
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 4 / 15

Figure 3. RT1064 EVK board hardware connection
2. Apply the NXP-MCUBootUtility-2.3.0 to burn one bit, 0x460 Boot Cfg1, in eFuse to enable JTAG. It can’t go back to SWD
after eFuse burn. Figure 4 shows the setup information.
NXP Semiconductors
Hardware connection diagram
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 5 / 15

Figure 4. NXP-MCUBootUtility-2.3.0 in eFuse to enable JTAG
3. Check the signals of three pins, TEST_MODE, GPIO_AD_B0_08, POR_B , according to the settings corresponding to
the COMPLIANCE_PATTERN part of the
BSDL
file. They should have the same status, 011, on the EVK board. Figure 5 is
compliance_patterns part of the
BSDL
file. Figure 6 shows test mode and the por_b connection.
Figure 5. COMPLIANCE_PATTERN PART OF BSDL FILE
NXP Semiconductors
Hardware connection diagram
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 6 / 15

Figure 6. Test mode and POR connection
4. The value of GPIO_AD_B0_08 is 1 in the
BSDL
file, but we pull down it to GND on the EVK board. So we should disconnect
the resistor R303 ground terminal, and pull up this pin with DCDC_3V3.
Figure 7. GPIO_AD_B0_08 connection
5. We used OPENSDA circuit on the RT1064 EVK board, which will affect the JTAG signal level during the Boundary
Scan test. So we should disconnect the SWD jump connectors, J47, J48, J49, and J50. Figure 8 shows SWD jump
connector disconnection.
NXP Semiconductors
Hardware connection diagram
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 7 / 15
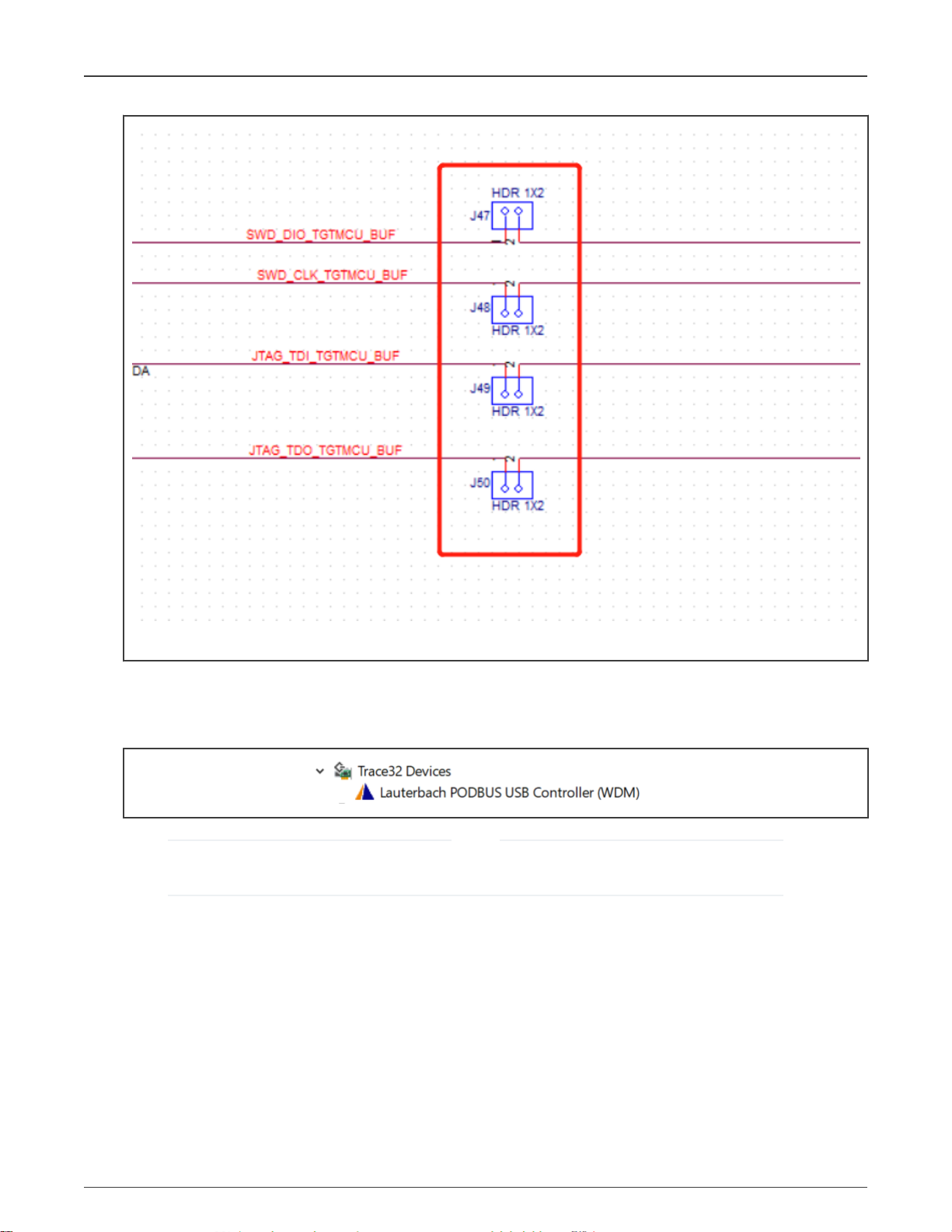
Figure 8. SWD jump connector disconnection
4 BSDL file validation using Lauterbach JTAG debugger
1. Trace32 Devices should appear in the Device Manager.
Lauterbach JTAG debugger recommended is LA-4533 Debug-USB3, with LA-7960/4513. Related information can
be found on the lauterbach page.
NOTE
2. Open the TRACE32 software and choose ARM32 USB.
NXP Semiconductors
BSDL file validation using Lauterbach JTAG debugger
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 8 / 15

3. Type in below commands, with each command followed by entering:
SYStem.Down
BSDL.RESet
BSDL.ParkState Select-DR-Scan
BSDL.state
4. BSDL.state window should now appear. Click the FILE button and load the BSDL file you want to validate. Figure 9 shows
the BSDL.state window.
Figure 9. BSDL.state window
5. After loading the file, type in command as below:
BSDL.SOFTRESET
6. Switch to the Check tab of the BSDL.state window. Click BYPASSall and IDCODEall button to see if both results can pass.
The BYPASS/CLAMP/HIGHZ check pass, as shown in Figure 10.
NXP Semiconductors
BSDL file validation using Lauterbach JTAG debugger
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 9 / 15

Figure 10. BYPASS and IDCODE check
7. Click the SAMPLEall button, and you will see No result becomes Test done. Double click the entity name, and the
BSDL.SET window appears, as shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11. SAMPLE check
8. In the BSDL.SET window, uncheck Intern to filter out the internal registers. The remaining contents are the sampled value
on each signal pins. Use a multimeter to measure voltage of at least three signal pins, and see if the logic state matches
the sampled value. SAMPLE check pass, Figure 12 shows BSDL.SET window.
NXP Semiconductors
BSDL file validation using Lauterbach JTAG debugger
Introduction to Boundary Scan of i.MX RT Series, Rev. 1, March 2, 2021
Application Note 10 / 15
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents

















