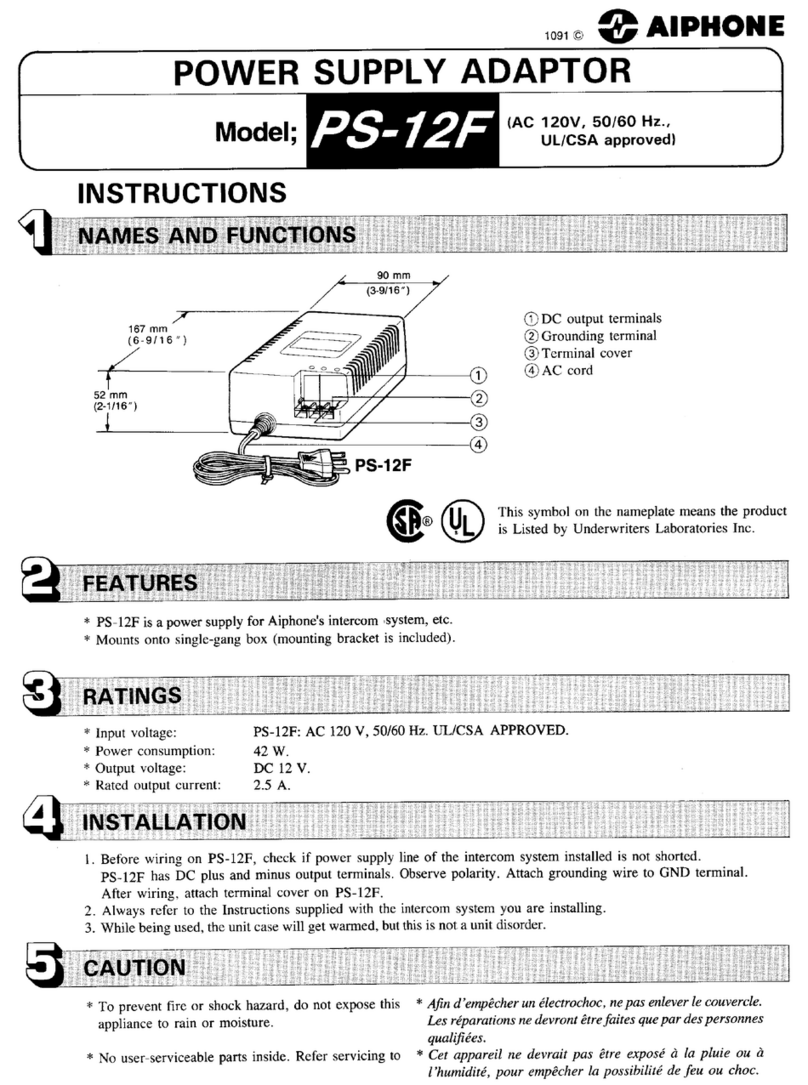
TunerStage
O I.D.MOSFET
The FM front-end RF amplifier in model SX-?
(and SX-6) featuresan I.D. MOS FET (ion-implan-
tation dual gate MOS FET) - P001 manufactured
by PioneerSemiconductor Laboratory. The major
featuresof this FET - P001 include high gain,Iow
noise, Iow distortion and low IM (P.G. 25dB/
100MHz,N.F. 2dBl100MH2,
I.M. -54d8/107dBp)
as a result of an extremely accurate short channel
obtained by a "self aligning" operation involving
a "local silicon oxidation" process.Furthermore,
a O.4p narrow channel (1/3rd to 1/5th the width
in normal components) has beenachievedby the
ion-implantation double diffusion construction.
Use of this FET in the FM front-end greatly
assistsin improving sensitivity and reducing inter-
ference.
o Pulse-SwallowPLL
Synthesizer
When the VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator)
frequency is very high and the CMOS progmmm-
able divider operating frequency is exceeded, the
PLL will cease to function. Two methods are
presently available
to resolvethis problem. In one
of these methods (the fixed divider system), an
ECL (Emitter to Emitter Coupled Logic) prescaler
is positioned in front of the programmable
divider.
And when, for example, a 1/10 prescaleris em-
ployed to obtain 25kHz step frequencies, the
referencefrequency will be 2.5kHz. This frequency
is very low and cannot be adequatelyremoved by
the low-pass filter. As a result, signal components
are leaked into the mixer leading to deterioration
in the S/N ratio. This is one of the main dis-
advantages
of the fixed divider system.
The other method available
is the pulse-swallow
system which employs a specialfrequency divider
called a "two-modulus prescaler" instead of the
prescaler used in the fixed divider system. In this
method, a 25kHz step synthesizer will generatea
25kHz reference frequency and a 50kHz step
synthesizer will generate a 50kHz reference
frequency, resulting in a much higher S/N ratio
than in the fixed prescalersystem.
The pulse-swallow
systememployed in the SX-7
is incorporated in an IC (M54922P) controlled by
microcomputer.
Amplifier Stage
o Non-SwitchingAmplifier
(SX-7,
SX-6,SX-s)
In non-switching amplifiers, the output stage
transistor biasis controlled on the basisof class
B
operating point in order to maintain the operation
within the operating region (between cutoff and
saturation) and thereby suppressthe generation of
switchingdistortion.
The basic non-switching amplifier circuitry is
outlined in Fig. 1-2. To simplify the diagram,
transistor Vgn and diode Vg, E1 and E2 are
assumedto be 0.6V and the transistorbasecurrent
is disregarded.While no input signalisapplied,the
voltage drop across R5 and R6 may also be dis-
regarded.And if the voltageacrossR1 and R2 due
to idle current is ignored, the voltages at different
positionswill beasshownin the diagram.
When an input signalis applied, a voltage will be
generated
acrossRt by NPN stage
(Q1/Q3) oper-
ation during the positiveportion of the signal.This
voltage is applied to the Q5 emitter-follower
(voltage gain of about 1) resulting in almost the
same voltage being generated across Rb. This
voltage is then added to the output stage bias
voltage. Hence, the PNP stage(Q2/Q4) maintains
the same bias conditions as when no signal was
applied, which meansthere is no cutoff. Likewise,
the NPN stagemaintains the samebias conditions
during the negative portion of the signal as when
no signalwasapplied, againeliminating any cutoff.
Fis.
1-1 Pulse
swallowsystem
I
Fig.
1-2 Basiccircuitryof Non
SwitchingAmplifier