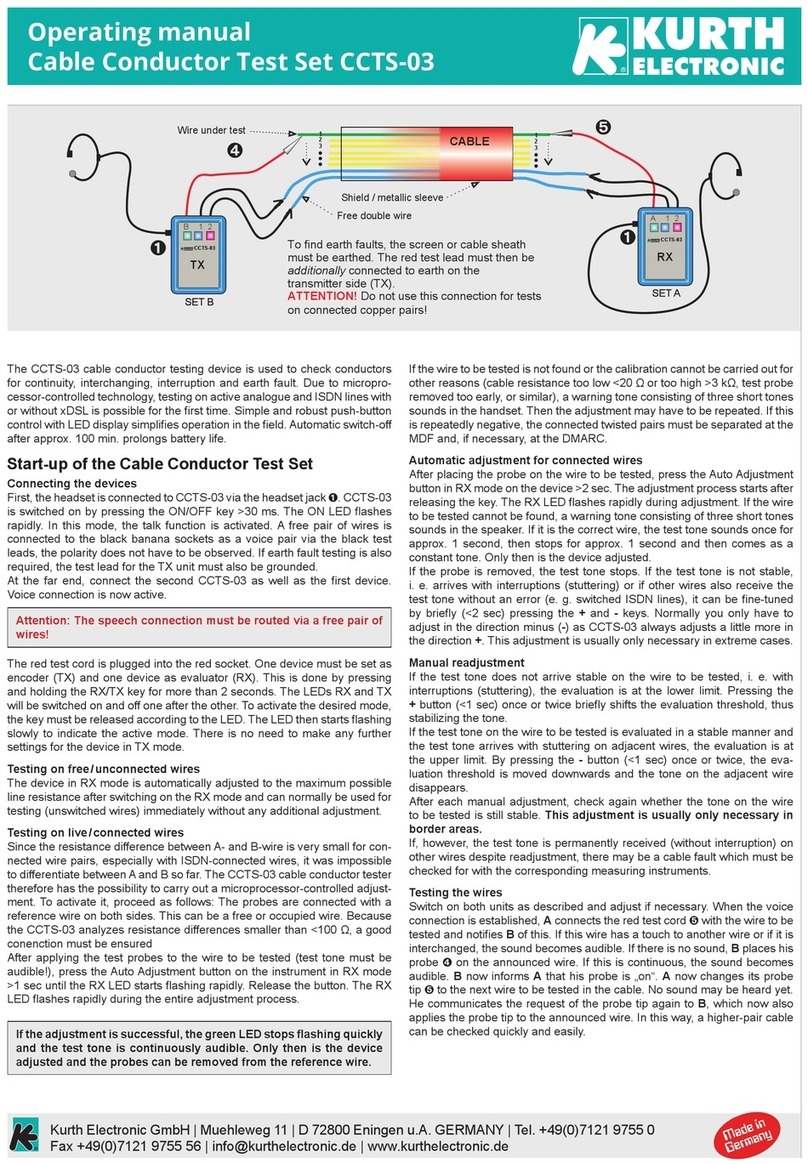
General Information
4
1.3 How to use this Guide
This guide was designed to describe the operational modes of the Composite Insulator Testers:
The reader is invited to use the digital (PDF) version of this document to allow searching by
keywords. Select Edit, then Find from the pull-down menu, or select Ctrl+F to access the Find
menu.
1.4 List of Associated References
[1] “Suspension Insulator Puncture Insulator Tester”; Report No. ELE 92-62; Bonneville Power Administration Division of
Laboratories; December 7, 1992.
[2] G.H. Vaillancourt, J.P. Bellerive, M. St-Jean, C. Jean, “New Live Line Insulator Tester for Porcelain Insulators on High-Voltage
Power Line,” IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, Vol. 9, January 1994, pp. 208-219.
[3] “J.C. Pohlman, C.R. Davis, “Cracked Insulators Create Hazardous Working Conditions During Restoration after Extreme Ice
Storms,” Proceedings of ESMO-95, Columbus, Ohio, USA, October 29 - November 3, 1995, IEEE Paper 95CH35755.
[4] A.S. Jagtiani, J.R. Booker, “Aging of Porcelain Insulators Under Mechanical and Electrical Stress on EHV AC Lines,” Proceedings of
ESMO-95, Columbus, Ohio, USA, October 29 - November 3, 1995, IEEE Paper ESMO 95-CP-08.
[5] G. H. Vaillancourt, M. Hamel, J. Frate, “Experience with Two Faulty Composite Insulators Detection Methods in Hydro-Quebec,”
Conference Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, Montreal, Canada, August 25-29, 1997.
[6] G. H. Vaillancourt, P. Bilodeau, “Diagnostic Testing of Composite Insulators Used on Series Compensation Platforms in Hydro-
Quebec,” Conference Proceedings of 11th International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, London, England, August 22-27,
1999.
[7] G. H. Vaillancourt, S. Carignan, C. Jean, “Experience with the detection of faulty composite insulators on High-Voltage power lines
by the E-field measurement method,” IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, Val. 13, No. 2, April 1998, pp 661-666.
[8] Y.C. Chen, C. R. Li, X. Liang, S. Wang, “The Influence of Water and Pollution on Diagnosing Defective Composite Insulators by E-
field Mapping,” Conference Proceedings of 11th International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, London, England, August 22-
27, 1999.
[9] D. H. Shaffner, D. L. Ruff, G. H. Vaillancourt, “Experience with a Composite Insulator Testing Instrument based on the Electric
Field method” ESMO 2000, Montreal, Canada, October 8-12, 2000.
[10] L. J. Fernandez, J. M. Munoz, A. Andrés, "Electric field measurement on composite insulators using live working techniques", 5th
International Conference on Live Maintenance, ICOLIM 2000, Madrid, Spain, May 17-19, 2000.
[11] I. Gutman (SE), A. Pigini (IT) et al. "Assessment of Composite Insulators by means of Online Diagnosis", CIGRE WG B2.21 2013.
[12] C. Jean, "High Voltage Insulator Testing based on Electric Field method" 2015 INMR World Congress Conference, Munich,
Germany, September 2015.