PR electronics 2286 User manual

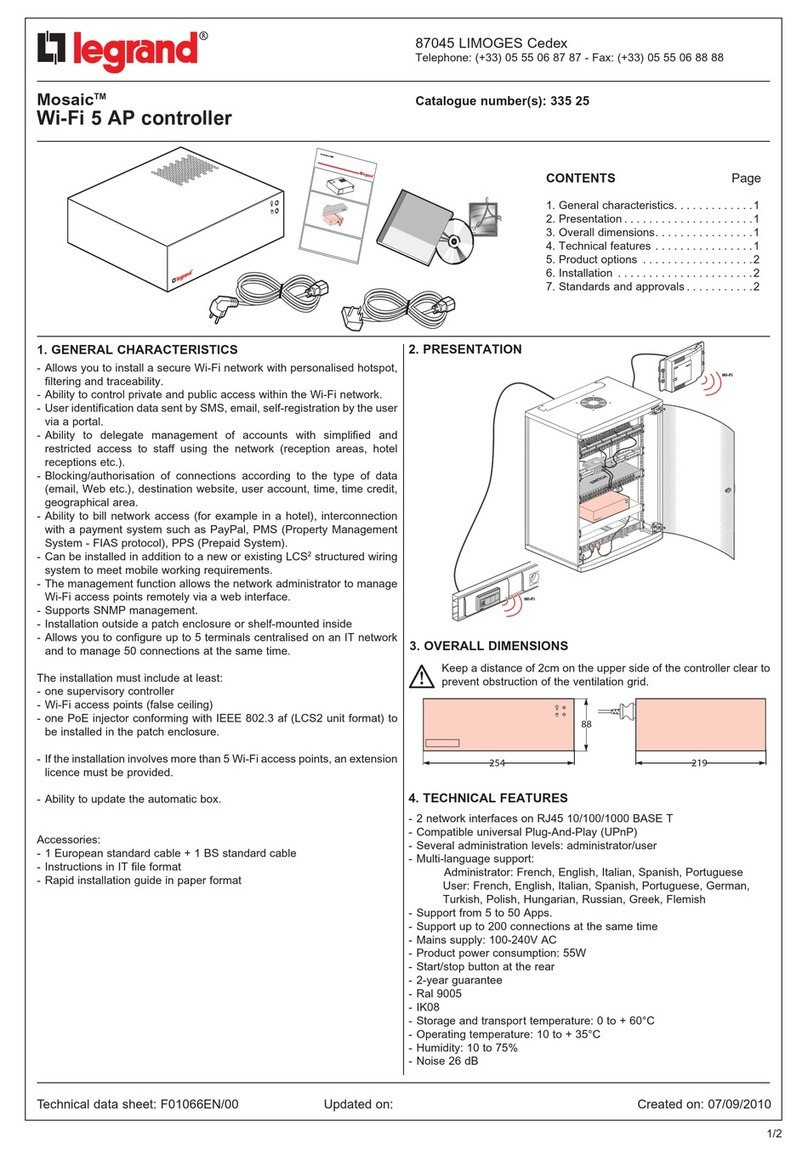
PERFORMANCE
MADE
SMARTER
Product manual
2286
Signal controller
TEMPERATURE | I.S. INTERFACES | COMMUNICATION INTERFACES | MULTIFUNCTIONAL | ISOLATION | DISPLAY
No. 2286V102-UK
From serial no.: 191695001

6 Product Pillars
to meet your every need
With our innovative, patented technologies, we make signal conditioning smarter and simpler. Our portfolio is composed of six
product areas, where we offer a wide range of analog and digital devices covering over a thousand applications in industrial
and factory automation. All our products comply with or surpass the highest industry standards, ensuring reliability in even
the harshest of environments and have a 5-year warranty for greater peace of mind.
Individually outstanding, unrivalled in combination
Our range of temperature transmitters and sensors provides the highest level of signal integrity from the
measurement point to your control system. You can convert industrial process temperature signals to analog, bus or
digital communications using a highly reliable point-to-point solution with a fast response time, automatic self-
calibration, sensor error detection, low drift, and top EMC performance in any environment.
Our unique range of single devices covering multiple applications is easily deployable as your site standard. Having
one variant that applies to a broad range of applications can reduce your installation time and training, and greatly
simplify spare parts management at your facilities. Our devices are designed for long-term signal accuracy, low
power consumption, immunity to electrical noise and simple programming.
We provide inexpensive, easy-to-use, future-ready communication interfaces that can access your PR installed base
of products. All the interfaces are detachable, have a built-in display for readout of process values and diagnostics,
and can be configured via push-buttons. Product specific functionality includes communication via Modbus and
Bluetooth and remote access using our PR Process Supervisor (PPS) application, available for iOS and Android.
Our display range is characterized by its flexibility and stability. The devices meet nearly every demand for display
readout of process signals and have universal input and power supply capabilities. They provide a real-time
measurement of your process value no matter the industry and are engineered to provide a user-friendly and reliable
relay of information, even in demanding environments.
We deliver the safest signals by validating our products against the toughest safety standards. Through our
commitment to innovation, we have made pioneering achievements in developing I.S. interfaces with SIL 2 Full
Assessment that are both efficient and cost-effective. Our comprehensive range of analog and digital intrinsically
safe isolation barriers offers multifunctional inputs and outputs, making PR an easy-to-implement site standard.
Our backplanes further simplify large installations and provide seamless integration to standard DCS systems.
Our compact, fast, high-quality 6 mm isolators are based on microprocessor technology to provide exceptional
performance and EMC-immunity for dedicated applications at a very low total cost of ownership. They can be
stacked both vertically and horizontally with no air gap separation between units required.

2286V102-UK 3
Signal controller
2286
Table of contents
Warning ................................................................................................ 4
Symbol identification .................................................................................... 4
Safety instructions ...................................................................................... 5
How to dismantle system 2200 .......................................................................... 6
Application ............................................................................................. 7
Technical characteristics ................................................................................. 7
Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Functions............................................................................................... 7
Output ................................................................................................. 8
Electrical specifications .................................................................................. 9
Order ................................................................................................... 11
Block diagram - 2286A .................................................................................. 11
Block diagram - 2286B .................................................................................. 11
Hardware programming .................................................................................. 12
Routing diagram ........................................................................................ 13
Programming / operating the function keys ............................................................... 14
Description of functions (selection of application) ......................................................... 17
Document history ....................................................................................... 20

HAZARD-
OUS
VOLTAGE
INSTAL-
LATION
GENERAL
Warning
This device is designed for connection to hazardous electric voltages.
Ignoring this warning can result in severe personal injury or mechanical damage.
To avoid the risk of electric shock and fire, the safety instructions of this manual must be observed and
the guidelines followed.
The specifications must not be exceeded, and the device must only be applied as described in the
following.
Prior to the commissioning of the device, this manual must be examined carefully.
Only qualified personnel (technicians) should install this device.
If the equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the
equipment may be impaired.
Warning
Until the device is fixed, do not connect hazardous voltages to the device.
The following operations should only be carried out on a disconnected device and under ESD-safe
conditions:
Dismantlement of the device for setting of DIP switches and jumpers.
General mounting, wire connection and disconnection.
Troubleshooting the device.
Repair of the device and replacement of circuit breakers must be done by PR electronics A/S only.
Warning
To keep the safety distances, devices with two built-in relays must not be connected to both hazardous
and non-hazardous voltages on the same device’s relay contacts.
SYSTEM 2200 must be mounted in socket type S3B Releco (order no 7023).
Symbol identification
Triangle with an exclamation mark: Read the manual before installation and commissioning of the
device in order to avoid incidents that could lead to personal injury or mechanical damage. Warning /
demand. Potentially lethal situations.
The CE mark proves the compliance of the device with the essential requirements of the EU directives.
The UKCA mark proves the compliance of the device with the essential requirements of the UK
regulations.
The double insulation symbol shows that the device is protected by double or reinforced insulation.

Safety instructions
Definitions
Hazardous voltages have been defined as the ranges: 75 to 1500 Volt DC, and 50 to 1000 Volt AC.
Technicians are qualified persons educated or trained to mount, operate, and also trouble-shoot technically correct and in
accordance with safety regulations.
Operators, being familiar with the contents of this manual, adjust and operate the knobs or potentiometers during normal
operation.
Receipt and unpacking
Unpack the device without damaging it and check whether the device type corresponds to the one ordered. The packing
should always follow the device until this has been permanently mounted.
Environment
Avoid direct sun light, dust, high temperatures, mechanical vibrations and shock, and rain and heavy moisture. If necessary,
heating in excess of the stated limits for ambient temperatures should be avoided by way of ventilation.
The device must be installed in pollution degree 2 or better.
The device is designed to be safe up to an altitude of 2 000 m.
The device is designed for indoor use.
Mounting
Only technicians, who are familiar with the technical terms, warnings, and instructions in the manual and who are able to
follow these, should connect the device. Should there be any doubt as to the correct handling of the device, please contact
your local distributor or, alternatively,
PR electronics A/S
www.prelectronics.com
Mounting and connection of the device should comply with national legislation for mounting of electric materials, i.e. wire
cross section, protective fuse, and location.
Descriptions of input / output and supply connections are shown in the block diagram and side label.
The following apply to fixed hazardous voltages-connected devices:
The max. size of the protective fuse is 10 A and, together with a power switch, it should be easily accessible and close to
the device. The power switch should be marked with a label telling it will switch off the voltage to the device.
Year of manufacture can be taken from the first two digits in the serial number.
Calibration and adjustment
During calibration and adjustment, the measuring and connection of external voltages must be carried out according to the
specifications of this manual. The technician must use tools and instruments that are safe to use.
Normal operation
Operators are only allowed to adjust and operate devices that are safely fixed in panels, etc., thus avoiding the danger of
personal injury and damage. This means there is no electrical shock hazard, and the device is easily accessible.
Cleaning
When disconnected, the device may be cleaned with a cloth moistened with distilled water.
Liability
To the extent the instructions in this manual are not strictly observed, the customer cannot advance a demand against PR
electronics A/S that would otherwise exist according to the concluded sales agreement.

6 2286V102-UK
How to dismantle system 2200
Picture 1:
The back panel of the module is detached from the housing by way of a
screwdriver.
Picture 2:
After this, the back panel can be pulled out together with the PCB, but
please notice the position of the PCB as there is a number of different
positions in the house. Do not pull the wires unnecessarily, instead pull the
PCB.
Switches and jumpers can now be moved.
When assembling the back plate and housing, please make sure no wires are
stuck.

2286V102-UK 7
Signal controller 2286
• Multiple functions
• Programmable from front
• 3-digit LED display
• Analog or Pt100 input
• Relay outputs
• Max. 50% offset
Application
PID on/off controller, PI step controller or 3-band controller with analog or Pt100 input. As trip amplifier with setpoint
adjustment through external current / voltage signal with neutral zone surrounding the setpoint. Especially suitable in
applications where easy 11-pole relay socket mounting is required for instance in a panel. Possibility for readout of process
data through the built-in display.
Technical characteristics
The 2286 is microprocessor-controlled and basic-calibrated. This means that the input and output can be programmed acc. to
the requested signal range without any re-adjustment. Thereby a high degree of accuracy and flexibility are ensured. The
output consists of two relays with a make contact connected to a common point. The user interface consists of a 3-digit
display and 3 function keys in the front. The interface is used to change a function or an input signal range.
Inputs
Analog inputs - 2286A
The A and B channels can be freely programmed via the front keys and JP1 and JP2 to current in the range 0...20 mA or voltage
in the range 0...10 VDC with a max. offset of 50% of the actual max. value.
Pt100 input - 2286B
Linearized Pt100 temperature input in the range -99...+850 °C with 3-wire connection. The temperature range can be scaled
via the front keys. Max. offset is 50% of max. temperature, min. span is 50°C.
Functions
PID on/off controller
Accurate setting of the regulation parameters XP (proportional band), TI (integrating time) and TD (differentiating time), with
the units selected as XP %, TI s and TD s. Minimum XP is 0.01% equivalent to a gain of 10,000. By setting TI and TD to 0, the
function will be a pure proportional controller. The controller adjusts the time interval between the pulses on the output, the
pulse width is set by the parameter TP. When the process value is outside the proportional band, the output gives a constant
up / down signal until the process value is brought within the proportional band. Hereafter the output pulses with a variable
interval depending on the distance from the setpoint. The neutral zone is an accepted deviation in relation to an ideal output
value, where no function is required on the output. The neutral zone is set in %. The setpoint can be selected as internal
(external setpoint input disabled) or as external (current / voltage).
PI step controller
The PI step controller is especially suitable for control of motor-driven
valves, throttle valves and dosage units. When the process value is outside the proportional band, the output will give a
constant up / down signal until the process value is brought within the proportional band. Hereafter the output pulses with a
variable OFF time depending on the distance from the setpoint. A selected minimum ON time protects the motor against too
short activations.
The regulation parameters are XP (proportional band), tAU (exponential average time of the active relay state) - functions as
integrating time, tP (the shortest active time of the relays) and nEU (neutral zone) - the band that the process is to be kept
within. The setpoint can be selected as internal (external setpoint input disabled) or as external (current / voltage).

8 2286V102-UK
3-band controller
The neutral zone is an accepted deviation in relation to the setpoint where no function is required on the output. The neutral
zone is set in % of the input span and centered around the setpoint. If the process input drops below the neutral zone, the UP
relay is activated until the process input rises to the setpoint value. Similarly the DOWN relay is activated if the process input
rises above the neutral zone, and releases when the input signal drops to the setpoint value. The setpoint can be selected as
internal (external setpoint input disabled) or as external (current / voltage).
dl/dt function
The function monitors the size of the decrease or increase (dl) of the input within a set period of time (dt). If the set ratio, i.e.
change per time unit, is exceeded, the relays will be activated. A time constant can be selected for the averaging of the input
value.
Comparator with an external setpoint
The process value is compared to the external setpoint, and if the two signals differ, a relay will be activated, i.e. the UP relay
for process values larger than the setpoint plus a ½ neutral zone, and the DOWN relay for values below the setpoint minus a ½
neutral zone.
Trip amplifier with an external setpoint
The relay function can be selected for increasing / decreasing or window. As a trip amplifier the relays can be activated
individually when the input value differs from the setpoint plus or minus the neutral zone. The window function activates a
relay when the process value differs by more than the neutral zone from the setpoint. The two relays can be activated
independently by a common setpoint.
Output
2 relay outputs with a make contact connected to a common point.
Relay outputs can be installed in PELV/SELV circuits.

2286V102-UK 9
Electrical specifications
Environmental conditions
Operating temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -20 to +60°C
Calibration temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20...28°C
Relative air humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < 95% RH (non-cond.)
Protection degree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . IP50
Mechanical specifications
Dimensions (HxWxD) (D is excl. pins) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.5 x 35.5 x 84.5 mm
Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140 g
Common specifications
Supply voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19.2...28.8 VDC
Internal consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 W
Max. consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 W
Isolation test / operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.75 kVAC / 250 VAC
PELV/SELV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . IEC 61140
Signal / noise ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Min. 60 dB
Signal dynamics, input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 bit
Proportional band (XP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.01...999 %
Gain, 1/XP =. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1...10000 gg
Integrating time (TI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0...999 s
Dierentiating time (TD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0...999 s
Neutral zone (nEU). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0...99.9 %
Pulse time (TP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.01...400 s
Minimum pulse time (TP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.01...10 s
Response time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < 60 ms
Temperature coecient. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ± 0.01% of span/°C
Linearity error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ± 0.1% of span
Eect of supply voltage change. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ± 0.002% of span/%V
Auxiliary voltages:
Reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 VDC ± 0.5% / 15 mA
EMC immunity influence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ± 0.5%
Electrical specifications - INPUT
Current input
Measurement range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0...20 mA
Min. measurement range (span) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 mA
Max. oset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50% of selected max. value
Input resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 Ω
Voltage input
Measurement range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0...10 VDC
Min. measurement range (span) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200 mV
Max. oset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50% of selected max. value
Input resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nom. 10 MΩ
Pt100 input 2286B
Measurement range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -99...+850°C
Min. measurement range (span) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50°C
Max. oset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50% of selected max. value
Cable resistance per wire (max.). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 Ω
Sensor current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nom. 1.25 mA
Response time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < 100 ms
Basic accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < ± 0.2°C
Temperature coecient:
span < 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 0.01°C/°Camb.
span > 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 0.01% of span/°Camb.
Immunity influence:
span ≤ 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1% of span
span ≥ 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5% of span
Eect of sensor cable resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . < 0.002 Ω/Ω

0,10 A
1,00 A
0 V 50 V 100 V 150 V 200 V 250 V
CURRENT
U
RELAY
10 2286V102-UK
Electrical specifications - OUTPUT
Relay outputs
Max. voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250 VAC / VDC
Max. AC current. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 A
Max. AC power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500 VA
Max. DC current, resistive load:
@ Urelay ≤ 30 VDC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 ADC
@ Urelay >30 VDC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . [1380 x U -2
relay x 1.0085Urelay] ADC
Graphic depiction of [1380 x U -2
relay x 1.0085Urelay]:
Observed authority requirements
EMC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2014/30/EU & UK SI 2016/1091
LVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2014/35/EU & UK SI 2016/1101
RoHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2011/65/EU & UK SI 2012/3032
EAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . TR-CU 020/2011
Of span = Of the presently selected range
Urelay
50 V 150 V0 V 100 V 200 V 250 V
Current
0.10 A
0.40 A
0.80 A
0.20 A
1.00 A
0.60 A
2.00 A
3.00 A

2286V102-UK 11
Order
Type Input
2286 Voltage / current
Temperature
: A
: B
Block diagram - 2286A
Block diagram - 2286B
9
10
CP U
E E P R OM
Vreg.
3
+
-
V
+
-
V
+
-
+
-
V +
V -
DC
DC
e
JP
1
JP
2
A /D
PGA
PGA
50
50
11
2
A /D
1
12286A
V +
V +
V +
5
7
6
R el. 1
R el. 2
Up
Down
Supply+24VDC
Supplygnd.
Input + (setp.,B-ch)
Input + (proc.,A-ch)
Input gnd.
Input gnd.
V ref.
Input :B
2.5VDC
Rel.1N.O.
Rel.2N.O.
Relay common
Neutral
Input: A
9
10
Pt100
CP U
E E P R OM
Vreg.
3
+
-
V
+
-
V +
V -
DC
DC
e
JP
1
A /D
PGA
50
11
A /D
PGA
2
1
10
32286B
V +
V +
V +
5
7
6
R el. 1
R el. 2
V +
Supply+24VDC
Supplygnd.
Input + (setp.,B-ch)
Input +
Comp. +
Input gnd.
Input -
Input :B
2.5VDC
Rel.1N.O.
Rel.2N.O.
Relay common
Up
Down
Neutral
V ref.
1.25 mA
V ref.
Input: A

12 2286V102-UK
Hardware programming
Input:
Channel B
0...20 mA
0...10 VDC
JP2
JP1
ON
OFF
MENU 2.3 = I
MENU 2.3 = U
Channel B
0...20 mA
0...10 VDC
JP2
JP1
ON
OFF
MENU 3.3 = I
MENU 3.3 = U

2286V102-UK 13
Routing diagram
5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3
3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3
2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3
4.0 4.1 4.2
5. 4
0.0
1.0
5.15.0
If nobuttonsarepressedfora periodof20 minutes,
displayreturns tostage0.0.
Fast Setting
Downcountsetpoint
Storeand exit fast setting
001=PIDon/o controller
002=PIstepcontroller
003=3-pointcontroller
004=dI/dtfunction
005=Comparator
006=Trip amplier
040 = enablechangeinallstages
- - -= disablechange
Controller
functionApplication
Program
access
Input 0%
Pt100: -99 ... 850°CPt 100: -99 ...850°CPt 100: No function
Input 0%
Input 100%
Input 100%
Passwordcode
Parameters
0.0...20.0mA
0.0...10.0VDC
0.0...20.0mA
0.0...10.0VDC
0.0...20.0mA
0.0...10.0VDC
0.0...20.0mA
0.0...10.0VDC
Input A
Input B
Upcountsetpoint
Relay
output
Uprelay
function
On= N.O.
OFF=N.C.
On= N.O.
OFF=N.C.
Downrelay
function
Input type
U=voltage
I= current
U=voltage
I= current
Input type
Frequency
50 Hz
60 Hz
Ainput
Binput
Output
Pt100:°C
Defaultdisplay
1.0Parameterline
Menu5.1 = 1
Function: PID ON / OFF contr.
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
Setpoint
Proportionalband
Integratingtime
Dierentialtime
Pulsewidth
Neutralzone
Setpointint./external
Direct/inverting
Menu5.1 = 3
Function: 3-point controller
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
Menu5.1 = 5
Function: Comparator
1.1
1.2
Setpoint
Neutralzone
Setpointint./external
Direct/inverting
Neutralzone
Hysteresis
Menu5.1 = 2
Function: PI step controller
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
Menu5.1 = 6
Function: Tripamplier
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
Menu5.1 = 4
Function: dI/dt function
1.1
1.2
1.3
Setpoint
Proportionalband
Relaytimeconstant
Minimum pulse time
Neutralzone
Pulsewidth hysteresis
Setpointint./external
Direct/inverting Tau value
dIrelay1
dIrelay2
Tripfunction relay1
Tripfunction relay2
Neutralzonerelay 1
Neutralzonerelay 2
Hysteresisrelay1
Hysteresisrelay2
Press or 2s forautomaticcounting.
Memory
Programming
Pressand hold ,thenpress
tostorechanges
Changeof parameter
Next digit orpoint
Goto entry menu /Leave
menuwithout changes
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
HysteresisdI1/dt
HysteresisdI2/dt
Sampling(s*1000)
Sampling(s)

14 2286V102-UK
Programming / operating the function keys
Documentation for routing diagram
The programming is menu-controlled. The main menus are numbered in level 0 (x.0), and the submenus are numbered in level
1 (x.1 to x.5). Each submenu has an accompanying entry menu. The menus are structured in such a way that the menus most
frequently used are closer to the default menu 0.0. Please note that programming is only possible when submenu 5.4 PAS has
the value 040.
Main, sub-, and entry menus are selected by the 3 function keys 3, 1and 2as
outlined in the routing diagram.
Activating 2in the submenus will display the current value of the entry and
parameter selection menus.
In entry menus, the digit that can be changed will flash.
Active digit position is shifted by the 3key, and the value is changed by the 1key.
When the decimal point flashes, its position can be changed by the 1key.
In entry menus with fixed parameters, you switch between the parameters by the 1
key.
Save by first activating 3and then 1simultaneously.
To return to the previous menu without changing the parameters, activate 2.
If a non-valid value is entered, the display will show Err for 2 s and then return to the
entry menu with the initial parameters.
0.0 Default - The selection is displayed in menu 5.3.
The diplay returns to default at power ON, or if no keys have been activated for a period of 20 minutes.
3Fast Setting - Short cut key for change of setpoint
When internal setpoint setting has been selected, a fast change of setpoint is possible by way of the Fast Setting
function. In this menu, the function keys have a special function, as 1upcounts the setpoint and 3downcounts the
setpoint from the value it had when activated.
The setpoint value is displayed in % of the input span.
Activate 2to store the displayed setpoint value.
5.15.0
Memory
Programming
Press and hold , then press
to store changes
Change of parameter
Next digit or point
Go to entry menu / Leave
menu without changes
0.0
Fast Setting
Downcount setpoint
Store and exit fast setting
Upcount setpoint
Press or for 2 s for automatic counting.

2286V102-UK 15
1.0 PAr - Parameter menu - entry of parameters.
The parameter menu bar varies according to the selected function in menu 5.1 -FUn. See the description of function
under FUn.
Menu 5.1 = { 1: PID on off controller }
1.1 SEt - Setpoint.
Possible selections are 0...99.9% of the input span.
1.2 hP - Proportional band.
Possible selections are 0.01...999%.
1.3 tI - Integrating time.
Possible selections are 0...999 s.
1.4 tD - Differentiating time.
Possible selections are 0...999 s.
1.5 tP - Pulse time, the active time of the relays.
Valid selections are 0.01...400 s.
1.6 nEU - Neutral zone, accepted deviation in relation to the ideal output value.
Possible selections are 0.1...99.9%.
1.7 IE - Internal or external setpoint.
Possible selections are I - internal, or E - external.
Selection of internal or external setpoint. When internal setpoint has been selected, input B is disabled and the
setpoint value is set in menu 1.1. When external setpoint has been selected, the signal type and range of the
setpoint are set in menu 3.0.
1.8 dI - Direct / Inverted controlling method.
Possible selections are dIr - direct, or InU - inverted.
Selection of direct or inverted setting range. When the selection is direct, a process value > the setpoint will result
in an active UP relay. When the selection is inverted, a process value > the setpoint will result in an active DOWN
relay.
Menu 5.1 = { 2: PI step controller }
1.1 SEt - Setpoint.
Possible selections are 0...99.9% of the input span.
1.2 hP - Proportional band.
Possible selections are 0.01...999%.
1.3 tAU - Exponential average time of the active relay state.
Possible selections are 0.1...999 s.
The period in which the relay is active is exponentially averaged and forms part of the control loop.
1.4 tP - Minimum pulse time, shortest active time for the relays.
Valid selections are 0.01...10 s.
1.5 nEU - Neutral zone, accepted deviation in relation to the setpoint.
Possible selections are 0.1...99.9% of the input span.
1.6 HSt - Pulse width hysteresis.
Setting should be: 0 < HSt < nEU
Possible selections are 0...99.9%.
1.7 IE - Internal or external setpoint.
Possible selections are I - internal, or E - external.
Selection of internal or external setpoint. When internal has been selected, input B is disabled and the setpoint
value is set in menu 1.1. When external has been selected, the signal type and range of the setpoint are set in menu
3.0.
1.8 dI - Direct / Inverted controlling method.
Possible selections are dIr - direct, or InU - inverted.
When a direct controlling method has been selected, a process value > the setpoint will result in an active UP relay.
When an inverted controlling method has been selected, a process value > the setpoint will result in an active DOWN
relay.

16 2286V102-UK
Menu 5.1 = { 3: 3-point controller }
1.1 SEt - Setpoint.
Possible selections are 0...99.9% of the input span.
1.2 nEU - Neutral zone, accepted deviation in relation to the setpoint.
Possible selections are 0.1...99.9% of the input span.
1.3 IE - Internal or external setpoint.
Possible selections are I - internal, or E - external.
Selection of internal or external setpoint. When internal has been selected, input B is disabled and the setpoint
value is set in menu 1.1. When an external setpoint has been selected, the signal type and range of the setpoint are
set in menu 3.0.
1.4 dI - Direct / Inverted controlling method.
Possible selections are dIr - direct, or InU - inverted.
Selection of direct or inverted controlling method. When direct has been selected, a process value > the setpoint will
result in an active UP relay.
When inverted has been selected, a process value > the setpoint will result in an active DOWN relay.
Menu 5.1 = { 4: dI/dt function }
1.1 tAU - Exponential averaging of the input.
Possible selections are 0.00...999 s.
1.2 dI1 - Change of input in % of the input span for UP relay.
Possible selections are -99...100%.
1.3 dI2 - Change of input in % of input span for DOWN relay.
Possible selections are -99...100%.
1.4 HS1 - Hysteresis in % of input span for UP relay.
Possible selections are 0...200%.
1.5 HS2 - Hysteresis in % of input span for DOWN relay.
Possible selections are 0...200%.
1.6 dt3 - Requested time interval between the samplings in s * 1000.
Possible selections are 0...003 s * 1000.
1.7 dt0 - Requested time interval between the samplings in s.
Possible selections are 0...999 s.
1.6 + 1.7(dt3 + dt0) The sum of the 2 parameters.
Possible selections are 0.02...3600 s.
Menu 5.1 = { 5: comparator }
1.1 nEU - Neutral zone in % of the input span.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.
1.2 HSt - Hysteresis in % of the input span.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.
Menu 5.1 = { 6: trip amplifier }
1.1 tF1 - Trip function for UP relay.
Possible selections are increasing / decreasing or window.
1.2 tF2 - Trip function for DOWN relay.
Possible selections are increasing / decreasing or window.
1.3 nE1 - Neutral zone in % of the input span for UP relay.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.
1.4 nE2 - Neutral zone in % of the input span for DOWN relay.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.
1.5 HS1 - Hysteresis in % of the input span for UP relay.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.

2286V102-UK 17
Description of functions (selection of application)
1.6 HS2 - Hysteresis in % of the input span for DOWN relay.
Possible selections are 0.00...100%.
2.0 InA - Setting of signal input A.
2.1 IAL - Setting of 0% input signal.
Possible selections are current 0.0...20.0 mA, or voltage 0.0...10.0 VDC.
For devices with a Pt100 input, the valid 0% temperature is
-99...850°C.
2.2 IAH - Setting of 100% input signal.
Possible selections are current 0.0...20.0 mA, or voltage 0.0...10.0 VDC.
For devices with a Pt100 input, the valid 100% temperature is
-99...850°C.
2.3 UI - Selection of current / voltage input.
Possible selections are I - current input, or U - voltage input.
Selection of I for current, or U for voltage input. For devices with a Pt100 input, this menu has no function.
See the hardware programming for correct jumper setting.
3.0 Inb - Setting of signal input B.
3.1 IbL - Setting of 0% input signal.
Possible selections are current 0.0...20.0 mA, or voltage 0.0...10.0 VDC.
3.2 IbH - Setting of 100% input signal.
Possible selections are current 0.0...20.0 mA, or voltage 0.0...10.0 VDC.
3.3 UI - Selection of current / voltage input.
Possible selections are I - current input, or U - voltage input.
Selection of I for current, or U for voltage input.
See the hardware programming for correct jumper setting.
4.0 OUt - Setting of relay function.
4.1 On1 - Setting of UP relay function.
Possible selections are On = N.O., or OFF = N.C. relay function.
4.2 On2 - Setting of DOWN relay function.
Possible selections are On = N.O., or OFF = N.C. relay function.
Selection of function / description of functions
5.0 APP - Selection of function.
5.1 FUn - Selection of function.
Possible selections are:
001 = PID on/off controller:
The controller controls the time interval between the active relay outputs whereas the ON time of the relays is set
by the parameter Tp. When the process value is outside the proportional band, the UP / DOWN relay is permanently
activated. When the process value is within the proportional band, the UP / DOWN relay will be de-activated within a
variable interval depending on the distance from the setpoint. The neutral zone is the percentage On time (Tp%),
where no function is required on the output.
In a correctly tuned PID controller the constant error will be eliminated. This means that at a correctly tuned Xp, Ti,
Td, and Tp a regulation accuracy can be obtained close to what the process value can be measured to. It is therefore
important that the proportional band Xp, the integrating time Ti, the differentiating time Td, and the pulse time Tp
are tuned according to the individual process. Before setting the parameters, the method of regulation directly /
inverted must be determined. Direct controlling results in an active UP relay when the process value > the setpoint.
Inverted controlling results in an active DOWN relay when the process value > the setpoint.
Inexperienced users may use the following “rule-of-thumb” for determining the process parameters:
1. The pulse time Tp is set to a value so short that the process value is barely affected by the supplied energy.
2. Set Xp at max., Ti and Td to 0 (only proportional controlling).
3. Reduce Xp until the process starts oscillating.
4. Increase Xp twofold.
5. Set Ti at max.
6. Reduce Ti until the process starts oscillating again.

18 2286V102-UK
7. Increase Ti twofold.
8. If the controller is too slow reaching its setpoint, the differential controller can be activated. The differentiating
function augments the control signal proportionally to the rise time of the process signal. Therefore the setting
varies according to the process.
002 = PI step controller:
The controller controls motor-driven valves, throttle valves and dosage units via the UP / DOWN relays by a variable
OFF time according to the difference between the process value and setpoint and to the selected regulation
parameters. The variable parameters are: Xp - the proportional band, tAU - the exponential average time of the
active relay state - functions as integrating time, tP - the shortest active time of the relays, nEU - the neutral zone,
i.e. the band that the process is to be kept within, and HSt - the pulse width hysteresis within the neutral zone.
The PI step controller can be set as follows:
1. The setting method direct / inveted is determined. Direct controlling results in an active UP relay when the
process value > the setpoint. Inverted controlling results in an active DOWN relay when the process value > the
setpoint.
2. The minimum pulse width tP is set in s. A reasonable start value is 0.5% of the actuating time - the period from
closed to open state of the actuator.
3. The neutral zone nEU is set as the band which the controlling process is to be kept within. The neutral zone is set
in % of the input span.
4. The hysteresis HSt is set in % of the input span. A value of nEU/4 is a reasonable start value. In processes with
large dead times, HSt can with advantage be diminished.
5. Set the proportional band Xp (hP) to max. = 999% and tAU to max. = 999 s.
6. Reduce Xp (hP) until the process starts oscillating.
7. Increase Xp (hP) twofold.
8. Reduce tAU until the process starts oscillating.
9. Increase tAU twofold.
003 = 3-point controller:
The neutral zone, which is set in % of the input span, is placed symmetrically around the setpoint setting. When the
process input is lower than the neutral zone, the UP relay is activated until the process input increases to the
setpoint value. When the process input is higher than the neutral zone, the DOWN relay is activated until the process
input decreases to the setpoint value. The setting parameters are SEt setpoint, nEU neutral zone, dIr direct, and InU
inverted. Direct / inverted reverses the state of the UP / DOWN relays.
004 = dI/dt control:
The function monitors the size of the decrease or increase (dl) of the input within a set period of time (dt). A time
constant for the input value can be selected. The limit of the magnitude of the decrease / increase (dI) is entered in
the menus 1.2 and 1.3. The period of time (dt) over which the change is to be monitored is entered in the menus 1.6
and 1.7. At a positive (dI/dt), the relays will be activated when the change of the input signal exceeds the value (dI)
in menu 1.2 or 1.3 within the set period of time (dt) in menus 1.6 and 1.7. The relays will be de-activated when the
change is lower than the (dI) minus HS (the hysteresis) per (dt).
At a negative (dI/dt), the relays will be activated when the change of the input signal drops below the value (dI) in
menu 1.2 or 1.3 within the set period of time (dt) in menus 1.6 and 1.7. The relays will be de-activated when the
change is larger than the (dI) plus HS (the hysteresis) per (dt).
005 = Comparator with an external setpoint:
The process input A is compared with the external setpoint on input B. When the two signals are within the neutral
zone, no relays are active. When A is smaller than B minus ½ neutral zone, the DOWN relay changes its state. When A
is larger than B plus ½ neutral zone, the UP relay changes its state. The hysteresis is placed inside the neutral zone.
006 = Trip amplifier / window with an external setpoint:
Input A is connected to the process signal and input B is connected to an external setpoint.
The relay trip function can be selected as TF = Increment, decrement, or Window. If the trip function has been
selected as 1.1 = InC, the UP relay will be activated, when the input value (input A) is larger than the external
setpoint (input B).The relay will be de-activated again when the input value is smaller than the setpoint minus the
hysteresis. If the function 1.1 = dEC has been selected, the UP relay will be activated when the input value is
smaller than the setpoint. The relay will be de-activated again when the input value is larger than the setpoint plus
the hysteresis.
The neutral zone will offset the setpoint by the value entered in 1.3 nE1 and 1.4 nE2 - positive for increasing (TF =
InC), and negative for decreasing (TF = DEC) input value (input A). If you request the relays to be activated at
different input values, two different neutral zones must be entered.
The same description applies to DOWN relay.
The two trip relays use the same external setpoint (input B).

2286V102-UK 19
Window:
When the input signal is within the setpoint ± the neutral zone, the relay is inactive. The relay will be activated
when the input signal exceeds the setpoint ± the neutral zone.
When the input signal approaches the setpoint from a higher value, the relay will be de-activated at the setpoint
plus the neutral zone minus the hysterersis.
When the input signal approaches the setpoint from a lower value, the relay will be de-activated at the setpoint
minus the neutral zone plus the hysteresis.
This description applies to both UP and DOWN relay.
5.2 FrQ - Frequency.
Possible selections are 50 or 60 Hz.
Selection of common mode frequency suppression.
5.3 dSP - Default display.
Possible selections are the A / B input or output.
The display is the percentage of Full Span. For modules with a Pt100 input, also °C can be displayed.
5.4 PAS - Password.
Possible selections are 0... 999.
When the password is 040, changes can be made in all menu points. When the password is <> 040, programming is
blocked in all menu points but open to reading of settings.

20 2286V102-UK
Document history
The following list provides notes concerning revisions of this document.
Rev. ID Date Notes
102 2232 Relay data updated, graph with resistive loads
inserted.
UKCA added.
Other manuals for 2286
2
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents
Other PR electronics Controllers manuals

PR electronics
PR electronics 5105B User manual

PR electronics
PR electronics 9203 Series User guide

PR electronics
PR electronics 2224 User manual

PR electronics
PR electronics 2286 User manual

PR electronics
PR electronics 2286 User manual

PR electronics
PR electronics 9203 Series User manual

PR electronics
PR electronics 9202 Series Instruction sheet

PR electronics
PR electronics 2224 User manual