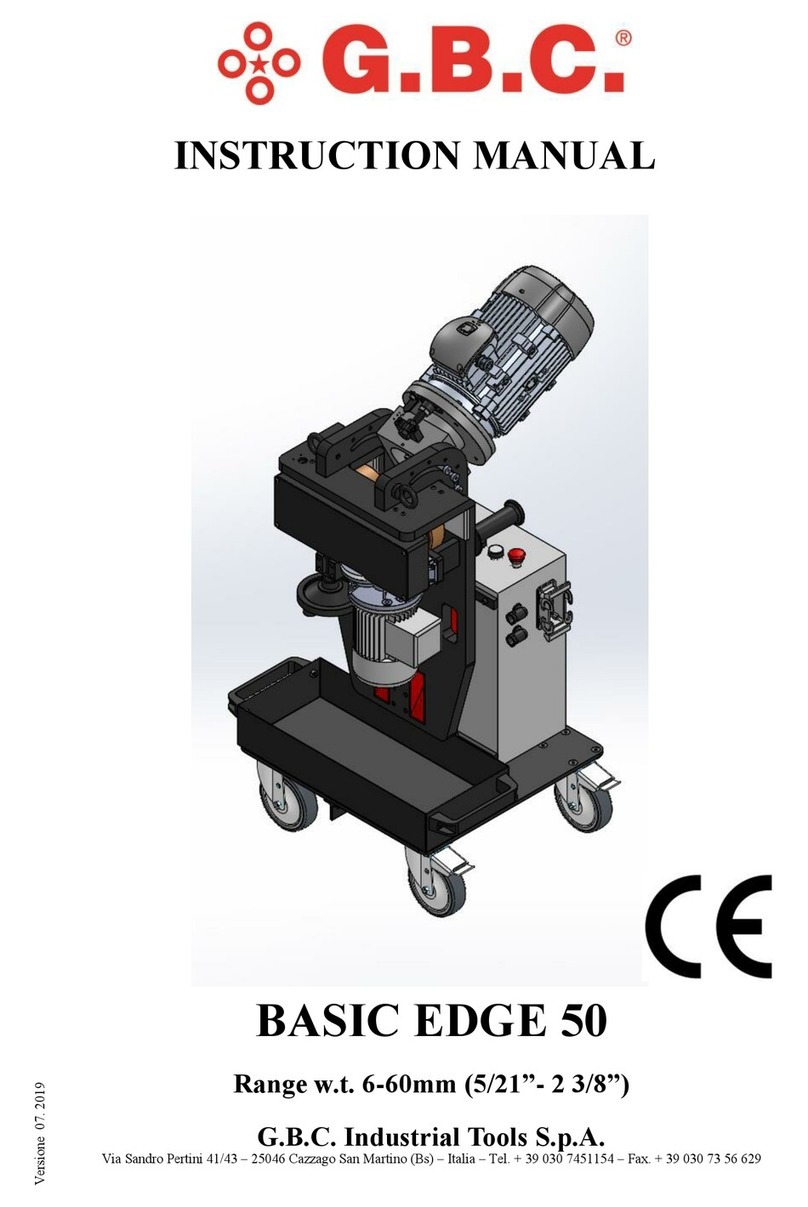
PROTA ProtaSteel 2021 User manual

Table of Contents
ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 2
1. Introduction 4
2. Exporting model to ProtaSteel 4
3. User Interface 5
4. Zoom & Pan Methods 6
5. Selection Methods 6
6. Views & View Settings 6
7. Creating new Views 7
8. Visibility & Selectability 8
9. Macros 9
10. Insert Sag rods 10
11. Adjustment of members by creating points 12
12. Adjustment of members orientation & coordinates 13
13. Steel Connections 15
14. Base Plate Connection 17
15. Fin Plate Connection 18
16. Stiffened End Plate Connection 20
17. Haunch Connection 20
18. Stiffened End Plate Connection 21
19. Corner Bolted Gusset Plate Connection 21
20. Bolted Gusset Plate Connection 22
21. Splice Connection 23
22. Truss End Plate With Gusset Plate 24
23. Welded Pipe Connection (info only) 25
24. Beam to (RC) Wall/Column Connection (info only) 25
25. Intelliconnect For Fully Automated Steel Connection Design 26
26. Connection Design Reports 34
27. Connection Design Summary Table 35
28. Collision / Clash Checks 36
29. Audit Model 37
30. Detail Item Manager 37
31. Preparing Engineering Drawings 40
32. Drawing Module 40
33. Creating Drawings via Drawing Manager 40
34. Profile Annotation 43
35. Dimension 44
36. Creating Connection Detail 45
37. Numbering Objects 48

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 4
1. Introduction
Thank you for choosing ProtaSteel –Steel detailing & connection creation module of the ProtaStructure
suite. The main steel model must be created in ProtaStructure. The model can be exported & opened in
ProtaSteel seamlessly. In ProtaSteel, you can :
•Model ancillary/secondary steel members such as roof purlins, girts, sag rods, staircase, etc.
•Adjust members to final positions for accurate detailing
•Create and design steel connections
•Create any steel connections manually, save them macro library and re-use them at similar
nodes.
•Produce engineering drawings of the steel structure and connections
•Sharing the 3D model created with other BIM platform such as Tekla Structures.
Before you proceed, it is highly recommended you go through ProtaStructure Quick Start Guide as
knowledge of the fundamentals of ProtaStructure is required.
This Quick Start Guide aims to get you up and running quickly. You should be able to learn the
fundamentals of ProtaSteel in approximately 2 hours by following this simple guide.
2. Exporting model to ProtaSteel
A sample steel model is already created & installed in default installation folder of ProtaStructure. We
will now open the model, run analysis & export to ProtaSteel :
➢Start ProtaStructure and the Open Project dialog will appear.
➢Select & open project “Quick_Start Steel_Complete”
➢Go to Analysis
→
Building Analysis
➢Go to Analysis tab
→
Tick Building Analysis
→
Start
➢Close the Building Analysis menu
➢Go to Steel Design (top menu)
→
Load ProtaSteel
ProtaSteel will start and load the project model. ProtaSteel model is created in subfolder “ProtaSteel” in
the project folder.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 5
3. User Interface
The various components of ProtaSteel user interface are as shown below:
Default views are created under the Views folder in the Explorer pane in the left pane. By the default the
views created are 3D view & plan view of each stories. Double-click on the desired view to access it.
The graphical editor supports multiple windows; you can open as many windows as you desire.
Modelling can be done both on the plan view as well as the 3D View.
Frame Creation Tool
In ProtaSteel, you can only create joist, purlin, girt, stair member, eaves beam & sag rods. Main
members such as beam, column & brace must be created in ProtaStructure.
Manual Detailing Tool
These are secondary detailing tools such as weld creation, section plate creation, element cutting &
trimming & profile adjustments.
Connections Macros
These are all the steel connections creation tools, eg. gusset plate, fin plate, haunch, splice etc.
Tip : If you hover the mouse cursor over any icons, a tooltip will appear with detail explanation on how
to use it. By right-clicking on the macro icon, you can set the default parameters that will be used each
time it is run.
File tools
Project
Explore
r
Model View
Frame tools
Manual Detailing
Connection Macros
Secondary Macros
Visibility Filters
Selectability Filters
Utilities
View Mode
View Creation
Point tools
Copy, Mirror
& Rotate
Reference Object
Views Tool
Bar
Bottom Status Bar
Working Units

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 6
4. Zoom & Pan Methods
The view manipulation is similar to ProtaStructure. You will find it easiest to use the mouse wheel to:
Zoom in –scroll your mouse wheel up
Zoom out –scroll mouse wheel down
Pan (move) –hold down the middle mouse wheel and drag
Rotate –Right click & drag
The following keyboard shortcut keys are useful :
Zoom All –Home key →Zoom so that all content is visible in the viewport
Origin of Interest –F9 key →Select an origin of interest by clicking on any node or any
object (such as bolt or plate). The model will then rotate around the selected
point.
5. Selection Methods
➢Left-click on the entity to select the entity.
➢To select multiple entities, hold down CTRL key while you pick them
You can drag with the mouse to access further selection options:
➢Drag from left to right to create a rectangular box. When you release the mouse button, all
entities completely contained within the box will be selected
➢Drag from right to left similarly and all the entities that are contained within the box and which
cross it boundaries will be selected
➢To deselect all entities, left-click on any empty space anywhere in the viewport.
6. Views & View Settings
By default, the 3D view general is created & shown when you open the project. The plan of each storey
is also created.
The views are shown under the View folder in the left Explorer pane.
➢Double-click on the desired view in the left-hand Explorer pane to open it.
You can open as many views that you like.
➢Double-click on Views will open the View Manager where you can
quickly :
•Open a view
•Close a view
•Delete a View
•Display the View Properties

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 7
If you have multiple views opened, you can manage them, e.g, fit them into the screen by going to
Windows (top menu) →Tile Horizontal / Tile Vertical / Cascade.
You can change the Object Draw Mode by going to Views (top menu) →Object Draw Modes
The shortcut icon can also be found on the right-
hand most vertical toolbars
➢Press Alt + D continuously will cycle through
the draw modes.
7. Creating new Views
New views can be created by going to Views →Create View
Let us create a new sectional view along grid 3 :
➢Go to Views
→
Create Views
→
By Two Points
➢Click two points to define a plane
→
the view will be created as shown below
2
1
Note : The sectional view is actually created from the same 3D model but viewed from a different camera
angle or orientation. Changes made to the active view are automatically reflected in all other views. The
extent, boundary and objects to display can be set via View Properties.
Tip: A white line arrow will appear once
the mouse cursor hovers on 2nd point.
This white line indicates the direction of
viewing. In this case, the above view is
looking into the building.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 8
To access the View Properties:
➢Double-click anywhere on the new view
→
The View Properties will appear
➢Give the view a new name “Axis 3”
➢Change the Up(+) & Down (-ve) to 1000mm & -1000mm respectively
This means that the view will only show elements 1m into & out of the plane. This will make the
view less cluttered as elements along other grids will be hidden. If zero values are entered, then
it will be unlimited.
•Up-Down Method :
-Partial : Any element that exists partially within the set extents will be shown
-Full : Only elements that exist fully within the set extents will be shown
➢Click OK to close the dialog & view will be updated.
Any sectional view is inherently a 3D view, hence you can still rotate the view.
➢Right-click & drag to rotate the Axis 3 view
Notice that only members within the 1 m extent is shown.
➢Go to View Properties again
➢Change the Up-Down method in View properties to FULL
→
Apply
Notice all the beams out of the plane of Axis 3 will hidden.
➢Press F4 to restore lookup (i.e. restore to original viewing direction)
8. Visibility & Selectability
You can control what objects are visible and selectable by assessing the Drawing Settings dialog :
➢Pick Drawing Settings in View Properties dialog
Important : You must give the view a new name and check / tick “Save” to ensure the view is saved.
Only saved views can be used to generate drawings in the drawing module.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 9
9. Macros
Most of the icons in ProtaSteel such as purlins, sag rods, girts & connections are called “macros”. A
macro is generally defined as a shortcut tool that specifies how a certain input sequence will result in a
desired output according to a defined procedure. The instruction on how to use each macro is shown in
the tooltip if you hover the mouse cursor over the icon.
•Before creating the element using the macro, you can set the macro settings, e.g. member profile,
plate offsets, bolts, etc. by right-clicking on the macro icon which will bring up the Macro dialog.
•Once a macro is clicked, the mouse cursor will change to the hand icon meaning that it is waiting
for object(s) selection or crosshair +meaning it is waiting for point selection. Perform the required
action(s) to get the desired result, as stated in the tooltip.
•The macro will remain activated; you can continue use the macro without having to click on the
macro icon again.
•Once you have finished, you must press ESC to cancel & stop the macro. The mouse cursor will
change back to default arrow (selection mode).
•After creating the elements in a group such as the purlins, each element will have its individual
properties; which can be changed by double-clicking on it →this will bring up the Element dialog.
•However, all the elements are still associated with the macro & can be changed in a group.
This can be done by selecting the macro sign & then press ENTER will bring up the macro dialog.
After making the changes, clicking Apply will apply to all the elements associated with the macro.
Clicking Get will set it default for this macro for this and future projects.
•If you have problems selecting the macro sign, you can select any element or component of the
macro (e.g. a plate of a connection) then press “M” →this will select the macro →followed by
ENTER which will expose the Macro dialog.
•You can select all the elements associated with the macro by selecting the macro sign or an element
of the macro →press “CTRL + M”.
•You can also delete all the elements & components of a macro by selecting the macro sign & then
press DELETE.
•It is highly recommended you review settings of the macro before executing it.
➢Alternatively, click on the
Visibility/Selectability icon “…”
in the middle toolbar
➢Turn off the Grids & Points
➢Apply & see effect
➢Go back & turn them back on
You can Save these different settings as
different name to quickly re-use them.
The shortcuts to visibility / selectability
objects are in the middle toolbar.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 10
10. Insert Sag rods
In ProtaStructure, the main steel members are modelled & designed; usually omitting the minor or non-
structural members to keep the model size manageable & efficient. After the model is transferred to
ProtaSteel, you might then want to add ancillary steel members such as sag rods.
We will insert some sag rods between the girts along axis 3 :
➢Double-click on 3D View in the Explorer pane to go to the default 3D view
➢Right-click on Sag Rod icon
→
This will expose the Sag Rod Macro Dialog.
➢Key in the offsets 50mm & Number of Intervals = 3 (as shown below)

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 11
➢Untick the diagonal so that it will not be included
➢Choose the section profile by clicking on “…” (as shown above)
→
Pick Round Bar D10
→
Select
➢Pick Get to make these input
the default from now on
→
OK
Each sag rod has its individual properties & can be selected, deleted or changed.
➢Double-clicking it will reveal its properties.
All the sag rods are represented by the macro sign They can be changed in a group by selecting this
macro sign →press “Enter” as stated previously.
➢Left-click on the Sag Rod icon
Notice the cursor turn to a hand icon meaning that it
is waiting for required element selection action(s).
➢1–Left-click on bottommost girt
➢2–Left-click on topmost girt
➢Right-click
→
Sag Rods will be inserted
➢Insert sag rods for another panel between grid B, C & D
using the same steps above, i.e. start by picking the
bottommost girt (no need to pick the sag rod icon
again)
➢Once complete, press ESC to cancel the Sag Rod macro
action.
Notice the cursor changes back to default arrow .
1
2
Macro Sign

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 12
You can use Sag Rod Connection or Sag Rod Holes macros to create connections to sag rods and
girts/purlins.
11. Adjustment of members by creating points
In ProtaSteel, you might also want to adjust the position of members that are not exactly at the correct
position, i.e. fine-tuning of final member positions for detailing purposes.
In ProtaStructure, all the braces inserted will join at the top of beams instead at the middle (centroid) of
the beam. This is because the analytical position of any beam in elevation is at the top of the beam.
➢Double-click on previously created Axis 3 view in the Explorer pane
➢Zoom in to the location of the diagonal braces between grid C & D
1
2
New Point
➢Press Alt + D until you see the outline of
members only (wireframe mode)
➢Click “Create Dividing Points” icon at
the right-hand tool bar
➢1–Click top point of the beam
➢2- Click bottom point of the beam
A new point “+” is created as shown in the
left figure.
➢Press ESC to stop the function
As you can see, the diagonal bracings are connected to the
top of the beam. It ismore accurate for the bracings to join
at the middle of the beam.
To do that, we must create a point (or node) in the middle
of the beam.
With the point created, we can then move the ends of the
bracing to this point.
TIP : Press Alt + D continuously will cycle through the
draw modes.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 13
12. Adjustment of members orientation & coordinates
All member position & orientation can also be changed without creating new points. We will make such
minor adjustments to some of the floor braces:
➢Double-click on Storey 1 view to open that view
➢Right-click & drag to rotate it a 3D view
➢Zoom to the joint GL 2/B-C where the secondary, main beam & 2 horizontal “L” brace meet
➢Press F9 & click on the joint to set it as point of interest so that rotation is about this point
2
3
1
Before
After
➢Click Adjust Profile Manually icon in
the top menu toolbars
➢1–Select the diagonal top bracing
➢2- Click on existing end point
➢3- Click on the new point
The brace end will be shifted to the new
point.
➢Repeat the above Step 1 to 3 for the other
bottom diagonal brace.
The final positions of the diagonal braces are
as shown in the left figure.
➢Double-click on PS View 1 in the Explorer
pane to go to the 3D view.
➢Zoom in the same location & check the
diagonal braces final positions to ensure
they are correct.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 14
Notice L braces orientation is not symmetrical with the other. We will rotate the brace so that flange of
the brace is aligned with the flange of the beam.
There is still a problem in the vertical position of the brace as it is too close to the top of the beams. Usually
braces are connected to the middle of the beam so transfer of force is to the centroid of the members
and there will less clashes in the connection. Minor shift in the vertical alignment can be done by pressing
➢Select the brace
➢Press Ctrl + Q to rotate it until the correct
orientation is achieved as shown in the left figure
➢Repeat for the other brace
The braces are coming in too close to the secondary
beam. We can shift it slightly away.
➢Press Ctrl + W to offset the brace horizontally until it
is farthest away from the secondary beam
➢Repeat for the other brace
➢Double-click on the right L brace
Profile Properties dialog allows you to change :
•Profile /Section type by picking “…”
•Alignment (Out of Plane, In-plane, Rotation)
•Offsets Start & End
•Draw Frame Coordinate System
➢Change Frame Coordinate System to For Analysis & design
→
Apply
Notice 3 arrows showing local axis appear at the frame end. Red
arrow = x-axis; Green arrow is y-axis; Blue arrow is z-axis.
If the axes is not visible, please ALT+D to change to Wireframe
➢Enter z Start & End Offset to 100 mm
→
Apply
➢Check the 3D view to ensure brace is moved down
➢Repeat for the other brace (-100mm)
→
OK to exit
Shift away
Ctrl + E
away
Ctrl + W
away
Ctrl + R
away
F9 & click here
Shift away

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 15
Ctrl + W. However, if you try this you will find that the offsets are too small. Further detail adjustment can
be done by exposing the Profile properties.
Preserve constructive changes during model re-import
In the General Definitions tab, the option “Preserve constructive changes during model re-import” is
by default checked.
13. Steel Connections
Once we have finalized position of the steel members, we can start “connecting” the steel members, i.e.
create connections. Connections can be created in two ways:
1. Automatically using the connection macros
2. Manually by using the Plates, Bolts, Welds & Cuts commands
The automatic connection macros will automatically create the appropriate connection. If there are
internal forces transferred from ProtaStructure, they will be automatically taken in the connection design.
Detail design check is performed for the following connections in accordance to EuroCode 3, AISC (LRFD),
AISC (ASD), BS5950 :
•Beam to Beam Connections: End Plate, Stiffened End Plate, Fin Plate
•Beam to Column Connections: End Plate, Stiffened End Plate, Fin Plate
•Beam to Beam End Plate Connection
•Haunch Connection
•Direct Welding Connection
•Simple Base Plate Connection
•Flange Plate Moment Connection
•Extended End Plate Connection
•Bolted Gusset Plate Connection
•Corner Bolted Gusset Plate Connection
This will preserve the member offset adjustents (e.g.
member position & orietation) made in ProtaSteel during
subsequent re-import from ProtaStructure. During the
next import, the import log file will show a warning :
Imported Frame's ID in *.cdf file[xxx]: Frame is locked. Therefore,
in plane, out of plane and start/end offsets were not applied.
Ignore the above warning if you want the member offsets
to be retained in ProtaSteel.
If this option is unticked (disabled), offsets done in
ProtaSteel will be discarded during the next re-import
from ProtaStructure.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 16
•Welded Gusset Plate Connection
•Corner Welded Gusset Plate Connection
•Truss Seating Connection
For the above connections, detail design report can be produced which includes both geometric checks
and capacity checks. In addition, intermediate calculations, references to the appropriate clauses of the
design code, and corresponding equation are shown for easy checking.
Basic material capacity checks are performed for the following for the standard connections :
•All Bolted & welded gusset plate
•Purlin & Girt
•Splice connections
•Flange Plate Moment connections
For the above connections, the following basic material strength checks are performed:
•Plate bearing check
•Bolt shear & Bolt tension check
•Weld stress check
•Plate tension & plate bending check
The above are basic checks and not clause by clause code specific checks. No design report can be
produced. You are advised to perform your own additional calculation checks if required.
The force used in the automatic connections are obtained from the higher of the two values :
1. The critical design forces of the connected members imported from ProtaStructure
2. User-defined Capacity Ratio in the Profile Properties > Detailing Definitions.
Capacity Ratio = Design Force / Maximum Member Capacity (equal less than 1)
This is to prevent unrealistic design when the design forces are very small or negligible.
For example, in determination of the number of bolts for a simple beam to beam fin plate :
•The critical design shear imported from ProtaStructure is 30 kN. This requires 1 number of bolts.
•The Shear Capacity Ratio of the beam is set to 0.3. This works out to be 100 kN which requires 2
number of bolts.
•The final design shear force used is 100kN and hence 2 number of bolts is chosen.
There is no check or design at all for the following connections: Haunch Connection, Apex Haunch
Connection, Direct Welding Connection, Base Plate Without Design, Eaves Beam Connection, Profile Fit
Connection, Sag Rod Connection & Sag Rod Holes, Welded Pipe Connection, Beam to Wall Connection,
Apex Truss Gusset Connection & Truss End Plate With Gusset Plate Connection.
Before performing connection design, we should customize the default design parameter :
➢Go to File →Settings →Project Preferences
➢Ensure that Design Standards for Connections is set to EC3
➢General Overdesign Factor for Connections = 1
This means that the connections will generally design for 100% of the member capacity. This setting
works in combination with capacity ratios of the connecting members (changed via Profile dialog →

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 17
Detailing Definitions). The Capacity Ratio is automatically calculated = Design force divided by the
actual capacity of the member. Hence, Capacity Ratio x Overdesign Factor = Final Factor.
➢For example, under Steel Detailing ensure the following
•Plates : Preferred Plate Material = S355
•Bolts : Preferred Bolt Material = Class 8.8
•General Weld : Preferred Weld Material = Class 42
➢Apply
→
OK
14. Base Plate Connection
In order to create a base plate connection to columns, we can use the base plate macros. There are two
base plate macros in ProtaSteel for creating the base plate connection.
•Base Plate Connection (without design)
•Simple Base Plate Connection (with design)
In ProtaSteel, restraints are indicated with the ball and cubic objects in green. If the connection is
defined as moment connection in ProtaStructure, it is shown with ball+cubic object. If the connection is
designed as a pinned connection, it is shown with only a ball object.
Using with “Base Plate (without design) Macro”, all types are created.
➢Select the “Base Plate Connection Macro”
➢Select the column.
➢The connection is created under of column.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 18
Pinned connections can be created by the “Simple Base Plate Macro”. This macro can design and create
calculation report. All parameters can be changed in macro properties.
15. Fin Plate Connection
We will create a fin plate connection between the adjacent main & primary beam joint.
➢Right-click of the Fin Connection macro
The Fin Plate Macro dialog will appear which allows you to customize the connections.
➢Go to the Design Tab & ensure the following :
•Design Standard = EC3
Note : Slip Coefficient is blank & hence will follow the Project Preferences
→
Bolts settings
➢Pick Get to make it default settings for this connection type for all projects from now on.
➢Zoom GL 2/B-C to the previous joint where the secondary, main beam & 2 “L” brace meet.
Important Note :The capacity ratio works in combination with General Overdesign factor for
Connections (in Project Preference). Hence, Capacity Ratio x Overdesign Factor = Final Factor.
➢Double-click on the secondary beam
➢In Profile Properties, go to Detailing
Definitions tab
The Capacity Ratio defaults to 0.3 for this beam.
This will be used to calculate the minimum
design shear used for the connection.
The Analysis tab shows the geometric properties
of the member.
➢Apply
→
OK
1
➢Select the “Simple Base Plate Connection Macro”
➢Select the column.
➢The connection is created under of column.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 19
We will now insert a fin plate connection at the primary &
secondary beam joint.
➢Pick Fin Plate Connection
➢1–Pick the main beam
➢2–Pick the secondary beam
➢Right-click 3 times
A fin plate connection will be created.
1
2
We will now insert corner bolted gusset plate for the L
brace that uses the beam fin plate as boundary.
➢Pick Corner Bolted Gusset Plate Connection
➢1–Pick the main beam
➢2–Pick the brace
➢3–Pick the blue fin plate
The connection is created. Repeat the same for the other
brace.
1
2
3
Macro Sign
Tip :
❖The connection consists of plates, bolts & welds. Each element has its individual properties &
can be selected, deleted or changed. Double-clicking it will reveal the element properties.
❖The entire connection is represented by the macro sign . Double-clicking on it will bring out
the Macro dialog box where the entire connection can be changed.
❖It is highly recommended you review settings of the connection macro before executing it.

ProtaSteel 2021 - Quick Start Guide 20
16. Stiffened End Plate Connection
We will create Beam to Beam End Plate Connection between the main & secondary beam.
➢Zoom to the adjacent joint GL 2/B-C where the secondary & main beam meet
17. Haunch Connection
We will create a haunch connection between the column and beam at GL B/2.
We will now insert the haunch connection.
➢Pick Haunch Connection
➢1–Pick the column
➢2–Pick the beam
The connection is created. The blue transparent box is the
cut object. This can be turn on/off in Visibility dialog.
➢Repeat the same for the other end of beam to column
joint
1
2
➢Pick Stiffened End Plate Connection
➢1–Pick the main beam
➢2–Pick the secondary beam
The connection is created. This maybe a more
preferable in terms of load transfer & ease of
assembly & construction.
➢Right click on the Haunch Connection
icon
➢In Haunch Macro, go to Figure 2 tab
➢Ensure that all the end plates A,B,C & D is
checked
➢Apply
→
OK to exit
Table of contents