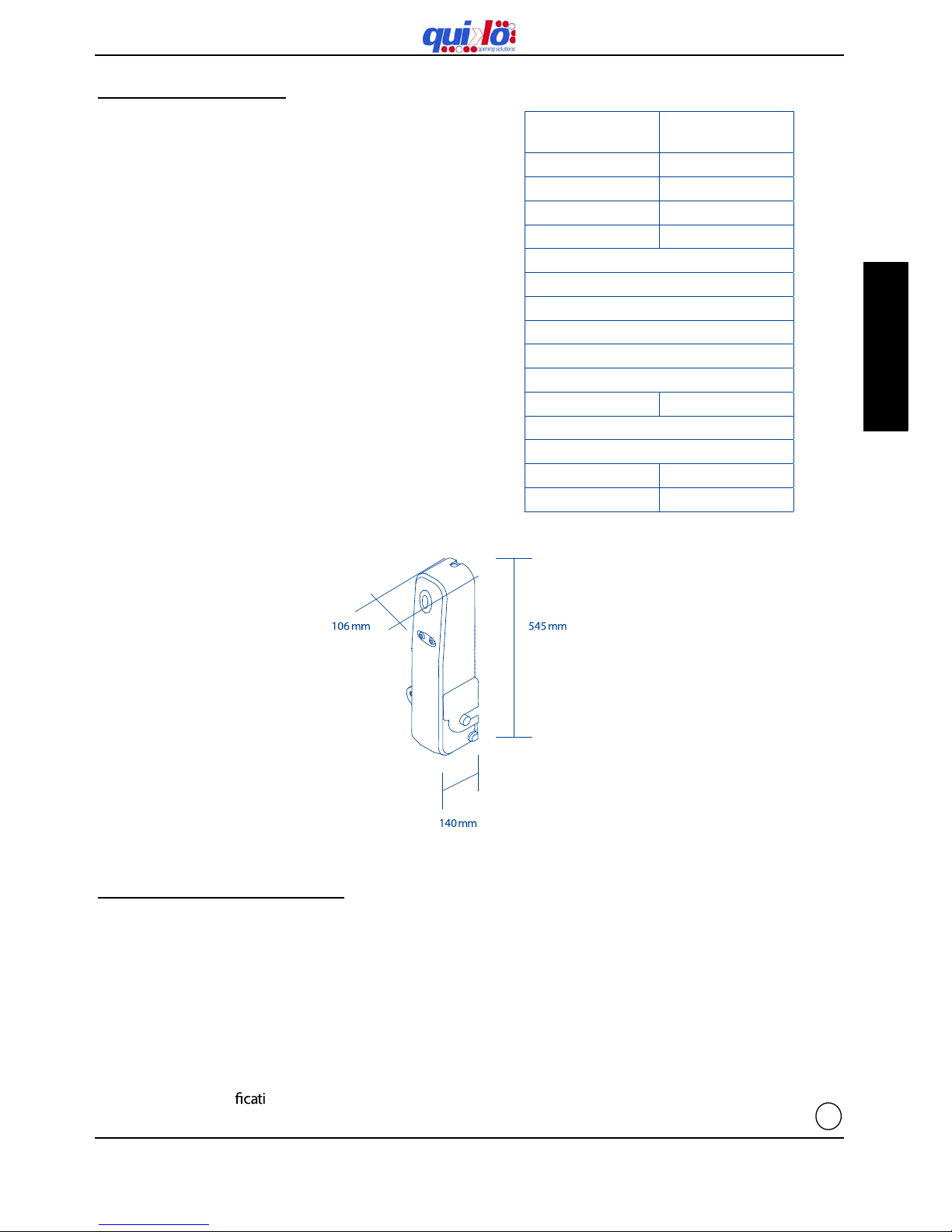
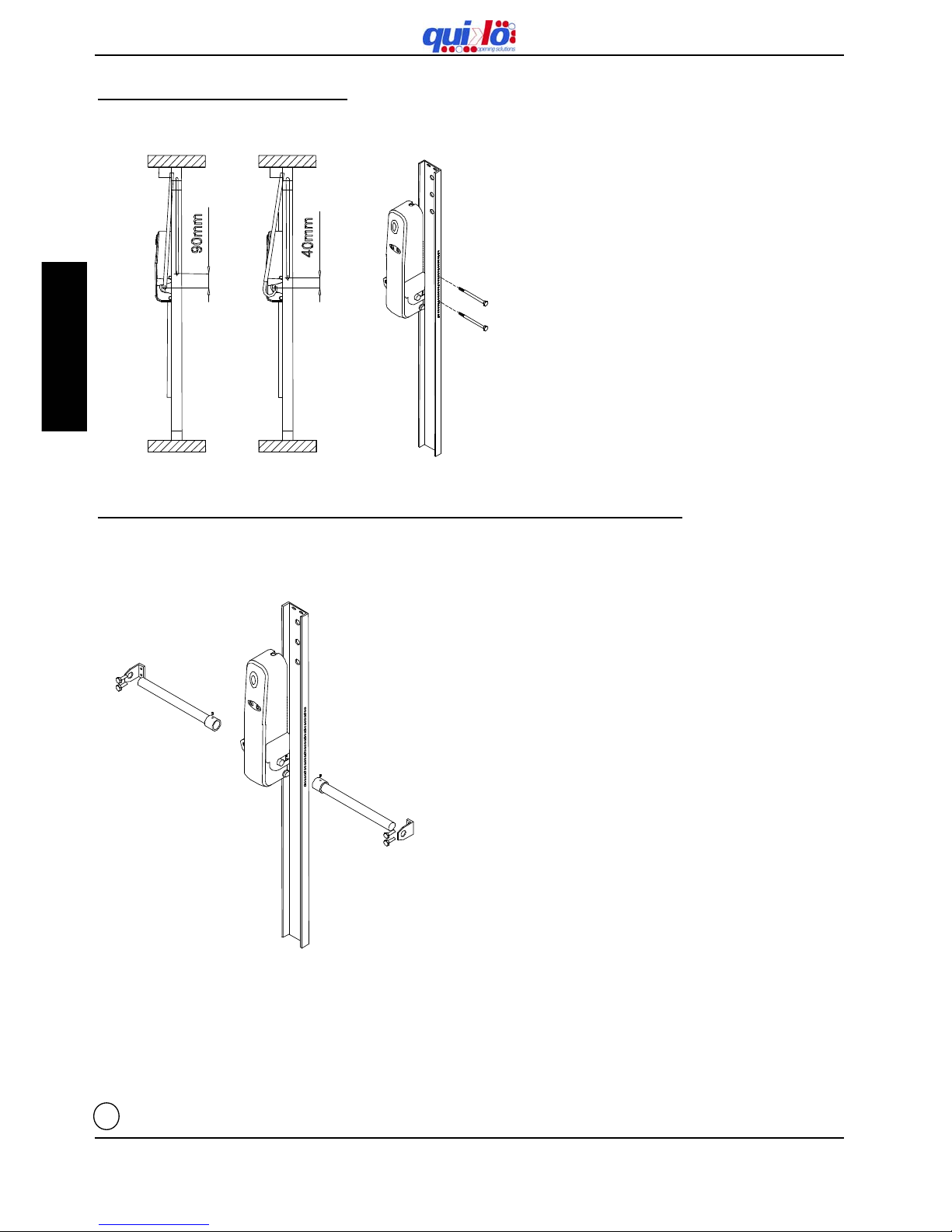
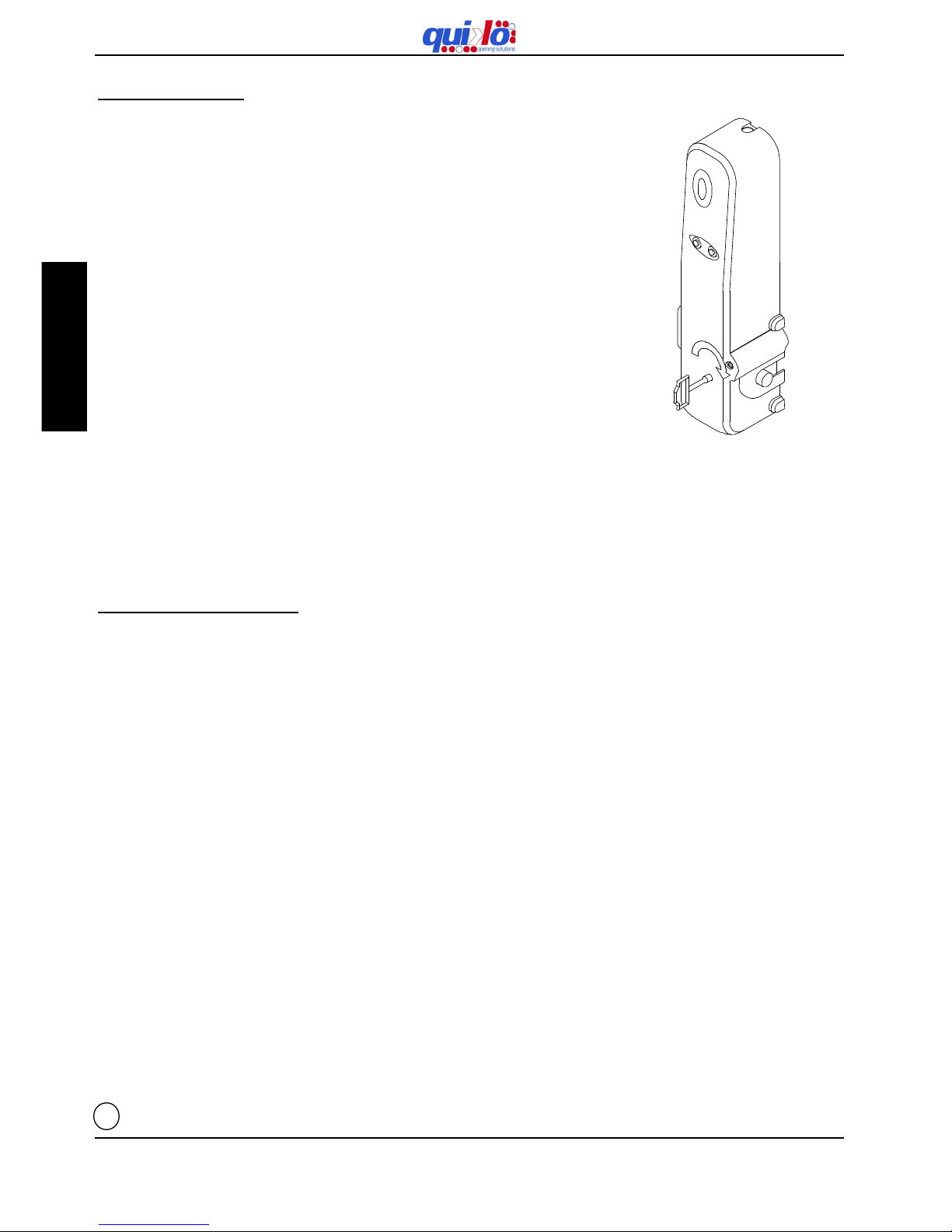
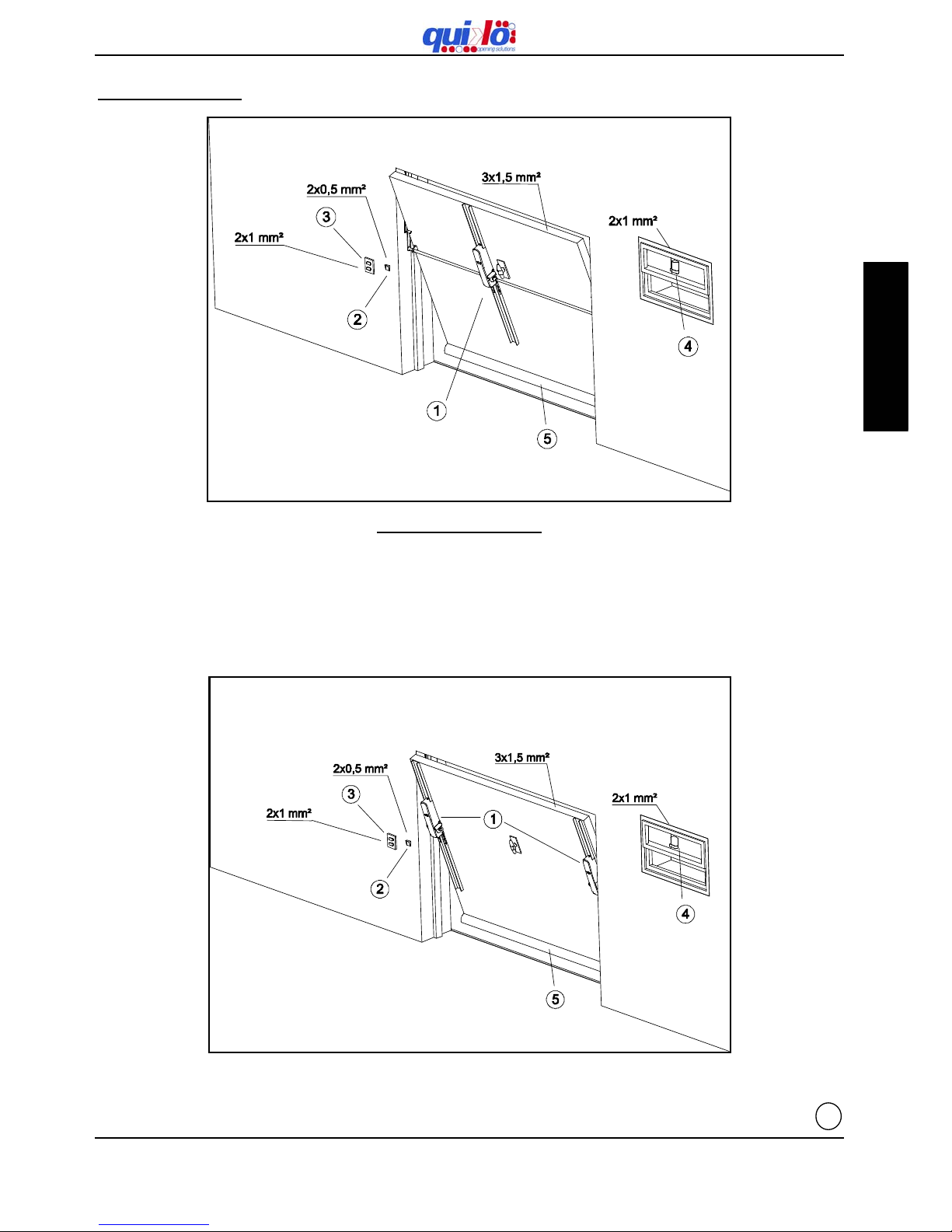
9
USE
T he gear motors located in the automation have a long life; nonetheless,their regular functioning can
be jeopardized by the state of the tilting gate.
Therefore we describe a few operations to maintain the tilting gate ecient.
Warning:Non-specialized sta cannot operate the gate during maintenance. You are advised to cut
the network power in order to avoid accidents or shocks. If the power must be on for various
inspections, you are advised to check and/or deactivate any possible control devices (remote
controls, keyboards, etc…) except for the devise used by the maintenance operator.
Routine maintenance
Each of the following operations must be done when needed and in all cases at least every
6 months
-clean and lubricate the moving parts;
-check the stability of the automatism and the tightness of all screws;
-check the gate stability and that the movement is normal with no frictions;
-check the correct functioning of all command and safety functions.
Extraordinary Maintenance
If special maintenance is required for mechanical parts, you are advised to send the gear motor out
for repairs to be performed by the technicians at the manufacturer.
It is absolutely forbidden to use the device for any other purposes. The installed control board (which
must have built-in electric friction), allows to select the following functions:
automatic: one control impulse will open or close the tilting gate;
semi-automatic: one control impulse will open or close the tilting gate.
In case of blackout, act on the manual unlocking device and move manually tilting gate. Remember
that this is an automatic device powered by electricity, consequently use with care. In particular,
remember:
-not to touch the device with wet hands and/or wet or bare feet;
-to turn off electricity before opening the control box and/or actuator;
-not to pull the lead to pull the plug out;
-to put the gate in movement only when it is completely visible;
-to keep out of the gate’s range of action if it is moving. Wait until it has stopped;
-not to let children or animals play near the gate;
-not to let children use the remote control or other operating devices;
-to carry out routine maintenance;
-in case of failure, to turn off electricity and operate tilting gate manually only if it is possible and
safe. Do not perform any intervention and call an authorized technician.
MAINTENANCE
E
N
G
L
I
S
H