sopportare i consumi richiesti dal motore (vedi dati
sulla targhetta).
Inoltre è indispensabile che l’impianto sia munito di
protezione (salvavita) di max. 30 mA.
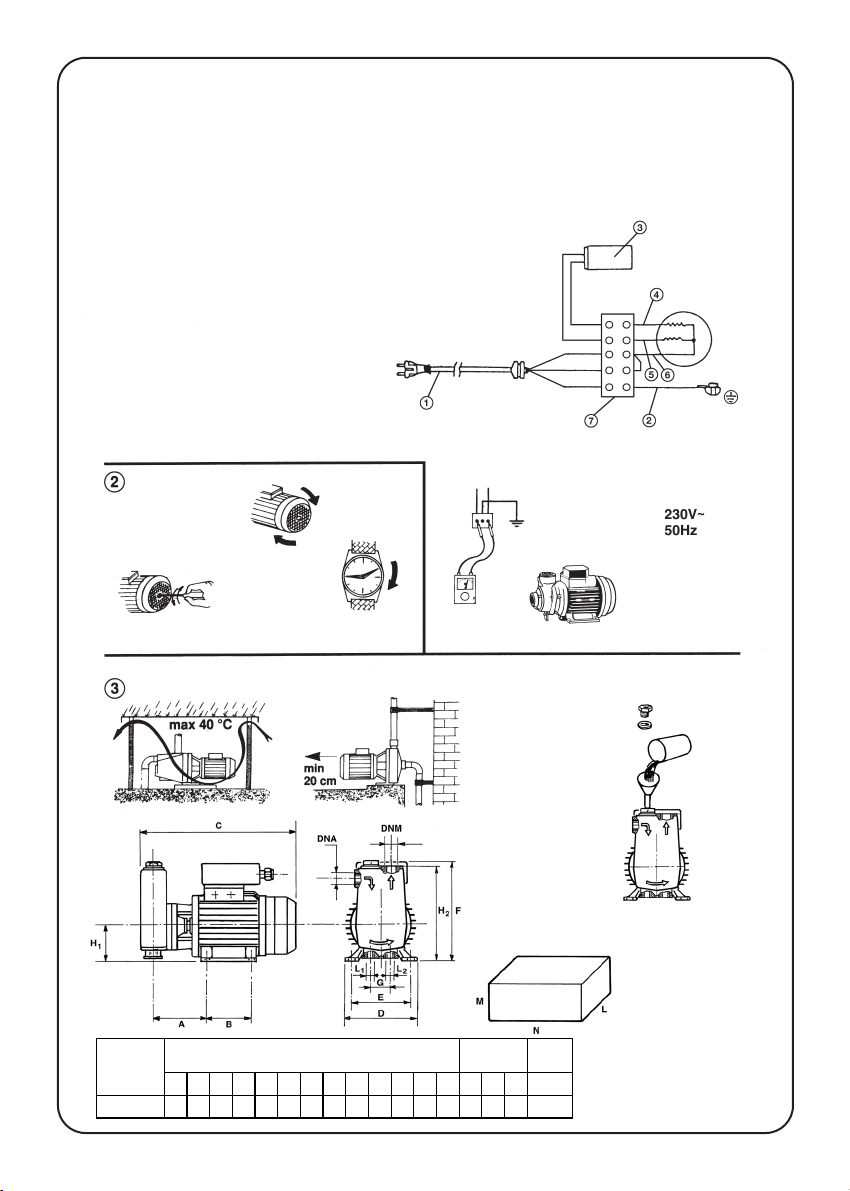
Le elettropompe già fornite di cavo e spina, devono
essere collegate ad una presa di corrente adatta per
presa SCHUKO, con doppio contatto di terra. Per
nessun motivo tagliare e/o sostituire la spina fornita di
serie. Fornirsi eventualmente di adattatore.
Se il cavo di alimentazione è danneggiato, esso deve
essere sostituito dal costruttore o dal suo servizio
assistenza tecnica o comunque da persona con
qualifica similare, in modo da prevenire
ogni rischio.
6.1 A L’apparecchio deve essere posto in modo che la
spina sia accessibile.
6.2 Verifica di funzionamento
Prima di installare l’elettropompa è consigliabile fare
una prova del motore a vuoto. Facendo molta
attenzione che tutti i contatti elettrici siano ben sigillati,
far partire l’elettropompa osservando la ventola di
raffreddamento posizionata sul retro del motore (Fig.
2). Verificare che il senso di rotazione sia quello
indicato dalla freccia impressa sul corpo pompa.
CAP. 7 INSTALLAZIONE
L’elettropompa è un apparecchio elettrico e come tale
va posizionato in un luogo protetto da intemperie (sole,
pioggia, neve, etc). Inoltre non deve essere esposta a
getti d’acqua e il luogo in cui si trova deve essere
adeguatamente ventilato.
7.1 Posizionamento fisso
Il posizionamento deve essere effettuato su di una
superficie perfettamente piana e solida. Nello scegliere
la posizione, fate attenzione e rispettate le distanze
minime previste da muri o pareti (Fig. 3) per agevolare
eventuali operazioni di uso e manutenzione. E’
importante che l’elettropompa sia posizionata il più
vicino possibile alla fonte di gasolio (max. 6 m di
distanza).
7.2 Installazione
A) Utilizzare tubazioni metalliche o di materiale plastico
ad alto grado di resistenza.
B) Se si utilizzano tubi flessibili in aspirazione o in
mandata, evitare di piegarli per non causare
strozzature.
C) Le tubazioni devono essere di diametro adeguato
alle bocche dell’elettropompa, dotate di manicotti
filettati che dovranno essere sigillati con sigillanti
adeguati.
D) Se il tubo di aspirazione è più lungo di 4 m., è
necessario che questo abbia un diametro superiore
a quello della bocca di aspirazione. Inoltre si
consiglia di installare una valvola di fondo munita di
filtro.
E) All’uscita del tubo di mandata è consigliabile
montare una valvola a sfera.
F) Fissare i tubi di aspirazione in modo che il peso e le
vibrazioni non gravino sull’elettropompa.
CAP. 8 UTILIZZO E MESSA IN FUNZIONE
8.1 Messa in funzione
A) Prima di tutto assicurarsi nuovamente che i contatti
elettrici siano ben chiusi e sigillati, che il cavo di
alimentazione non abbia subito danni durante
l’installazione e poi chiudere la saracinesca in
mandata.
B) Procedere al riempimento dell’elettropompa tramite
l’apposito foro di riempimento e rimuovere il tappo
(Fig. 4). Una volta riempito completamente il corpo
pompa e il tubo di aspirazione, chiudere il foro di
riempimento (Fig. 4).
C) Inserire la spina nella presa di corrente o azionare
l’interruttore di alimentazione. Prima di effettuare
questa operazione, fare attenzione a quanto
descritto al cap. 3 par. 3.1.
D) L’elettropompa comincerà quindi a lavorare.
8.2 Avvertenze importanti
A) Evitare di far lavorare l’elettropompa a secco (senza
gasolio all’interno del corpo pompa).
B) Il funzionamento prolungato con la saracinesca in
mandata chiusa può creare seri danni.
C) In caso di mancanza di corrente elettrica in rete, è
consigliabile staccare la spina dalla presa o
disinserire l’interruttore.
8.3 Arresto
A) Si consiglia di chiudere la saracinesca in mandata
prima di spegnere l’elettropompa. Questo eviterà
eventuali colpi d’ariete. Quindi spegnere
l’interruttore.
B) Se l’elettropompa non sarà usata per un periodo più
o meno lungo, si consiglia di scaricarla dal gasolio
presente nel corpo pompa.
CAP. 9 MONTAGGIO E SMONTAGGIO
L’elettropompa non ha parti accessorie staccate,
pertanto non necessita di alcun montaggio.
L’eventuale smontaggio dell’elettropompa deve essere
eseguito solo ed esclusivamente presso centri di
assistenza o da tecnici qualificati.
CAP. 10 MANUTENZIONE E RIPARAZIONE
10.1 Manutenzione
Qualsiasi operazione di manutenzione deve essere
eseguita solo dopo aver disinserito la spina elettrica.
L’elettropompa non necessita di particolari
manutenzioni all’interno, pertanto astenersi dallo
smontaggio della stessa. E’ comunque molto
importante che la parte aspirante e di mandata sia
sempre mantenuta perfettamente pulita e libera da
eventuali corpi ostruenti.
CAP. 11 RISCHI MECCANICI
11.1 Parti meccaniche soggette ad usura
A) La tenuta meccanica (Dis.5 pos.17) si può usurare
anche dopo un periodo relativamente breve,
soprattutto se sono stati pompati liquidi anche
leggermente abrasivi. Tale parte dovrà essere
I
5
WEC KG130 4-02-2008 11:09 Pagina 5